Abstract
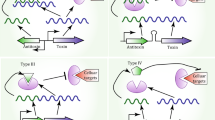
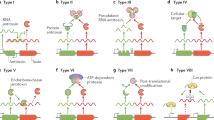
Toxin–antitoxin (TA) systems are widely conserved in prokaryotic plasmids and chromosomes and are linked to many roles in cell physiology, including plasmid maintenance, stress response, persistence and protection from phage infection. A TA system is composed of a stable toxin and a labile antitoxin that inhibits a harmful effect of the cognate toxin. When gene expression from the TA loci is repressed under certain conditions such as nutrient starvation, the toxin is freed from the rapidly degrading antitoxin and obstructs an essential cellular process, such as DNA replication, translation and peptidoglycan synthesis, which subsequently causes growth arrest. TA systems are classified into five types according to the nature and the function of antitoxins, and the activity of toxins is tightly regulated in a variety of ways. This short-review highlights several novel regulatory mechanisms for Escherichia coli toxins that we recently discovered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizenman E, Engelberg-Kulka H, Glaser G (1996) An Escherichia coli chromosomal “addiction module” regulated by guanosine 3′,5′-bispyrophosphate: a model for programmed bacterial cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6059–6063
Alawneh AM, Qi D, Yonesaki T, Otsuka Y (2016) An ADP-ribosyltransferase Alt of bacteriophage T4 negatively regulates the Escherichia coli MazF toxin of a toxin–antitoxin module. Mol Microbiol 99:188–198
Blower TR, Evans TJ, Przybilski R, Fineran PC, Salmond GPC (2012) Viral evasion of a bacterial suicide system by RNA–based molecular mimicry enables infectious altruism. PLoS Genet 8:e1003023
Buts L, Lah J, Dao-Thi MH, Wyns L, Loris R (2005) Toxin–antitoxin modules as bacterial metabolic stress managers. Trends Biochem Sci 30:672–679
Cerritelli SM, Crouch RJ (2009) Ribonuclease H: the enzymes in eukaryotes. FEBS J 276:1494–1505
Fineran PC, Blower TR, Foulds IJ, Humphreys DP, Lilley KS, Salmond GPC (2009) The phage abortive infection system, ToxIN, functions as a protein–RNA toxin–antitoxin pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:894–899
Fozo EM, Hemm MR, Storz G (2008) Small toxic proteins and the antisense RNAs that repress them. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72:579–589
Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Løbner-Olesen A (2005) Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:371–382
Germain E, Castro-Roa D, Zenkin N, Gerdes K (2013) Molecular mechanism of bacterial persistence by HipA. Mol Cell 52:248–254
Hu Y, Benedik MJ, Wood TK (2012) Antitoxin DinJ influences the general stress response through transcript stabilizer CspE. Environ Microbiol 14:669–679
Itoh T, Tomizawa J (1980) Formation of an RNA primer for initiation of replication of ColE1 DNA by ribonuclease H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:2450–2454
Jiang Y, Pogliano J, Helinski DR, Konieczny I (2002) ParE toxin encoded by the broad-host-range plasmid RK2 is an inhibitor of Escherichia coli gyrase. Mol Microbiol 44:971–979
Kai T, Selick HE, Yonesaki T (1996) Destabilization of bacteriophage T4 mRNAs by a mutation of gene 61.5. Genetics 144:7–14
Kamada K, Hanaoka F, Burley SK (2003) Crystal structure of the MazE/MazF complex: molecular bases of antidote-toxin recognition. Mol Cell 11:875–884
Kim Y, Wang X, Ma Q, Zhang XS, Wood TK (2009) Toxin–antitoxin systems in Escherichia coli influence biofilm formation through YjgK (TabA) and fimbriae. J Bacteriol 191:1258–1267
Koga M, Otsuka Y, Lemire S, Yonesaki T (2011) Escherichia coli rnlA and rnlB compose a novel toxin-antitoxin systems. Genetics 187:123–130
Leplae R, Geeraerts D, Hallez R, Guglielmini J, Drèze P, Van Melderen L (2011) Diversity of bacterial type II toxin–antitoxin systems: a comprehensive search and functional analysis of novel families. Nucleic Acids Res 39:5513–5525
Maisonneuve E, Castro-Camargo M, Gerdes K (2013) (p)ppGpp controls bacterial persistence by stochastic induction of toxin–antitoxin activity. Cell 154:1140–1150
Masuda H, Tan Q, Awako N, Wu KP, Inouye M (2012) YeeU enhances the bundling of cytoskeletal polymers of MreB and FtsZ, antagonizing the CbtA (YeeV) toxicity in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 84:979–989
Miller HI, Riggs AD, Gill GN (1973) Ribonuclease H (Hybrid) in Escherichia coli. Identification and characterization. J Biol Chem 248:2621–2624
Mutschler H, Gebhardt M, Shoeman RL, Meinhart A (2011) A novel mechanism of programmed cell death in bacteria by toxin–antitoxin systems corrupts peptidoglycan synthesis. PLoS Biol 9:e1001033
Naka K, Koga M, Yonesaki T, Otsuka Y (2014) RNase HI stimulates the activity of RnlA toxin in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 91:596–605
Ogura T, Hiraga S (1983) Mini-F plasmid genes that couple host cell division to plasmid prolifiretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4784–4788
Otsuka Y, Yonesaki T (2012) Dmd of bacteriophage T4 functions as an antitoxin against Escherichia coli LsoA and RnlA toxins. Mol Microbiol 83:669–681
Otsuka Y, Miki K, Koga M, Katayama N, Morimoto W, Takahashi Y, Yonesaki T (2010) IscR regulates RNase LS activity by repressing rnlA transcription. Genetics 185:823–830
Pecota DC, Wood TK (1996) Exclusion of T4 phage by the hok/sok killer locus from plasmid R1. J Bacteriol 178:2044–2050
Ren D, Bedzyk LA, Thomas SM, Ye RW, Wood TK (2004) Gene expression in Escherichia coli biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:515–524
Rocker A, Meinhart A (2015) Type II toxin: antitoxin systems. More than small selfish entities? Curr Genet. doi 10.1007/s00294-015-0541-7
Sberro H, Leavitt A, Kiro R, Koh E, Peleg Y, Qimron U, Sorek R (2013) Discovery of functional toxin/antitoxin systems in bacteria by shotgun cloning. Mol Cell 50:1–13
Schuster CF, Bertram R (2013) Toxin-antitoxin systems are ubiquitous and versatile modulators of prokaryotic cell fate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 340:73–85
Tadokoro T, Kanaya S (2009) Ribonuclease H: molecular diversities, substrate binding domains, and catalytic mechanism of the prokaryotic enzymes. FEBS J 276:1482–1493
Tan Q, Awano N, Inouye M (2011) Yee V is an Escherichia coli toxin that inhibits cell division by targeting the cytoskeleton proteins, FtsZ and MreB. Mol Microbiol 79:109–118
Wang X, Kim Y, Hong SH, Ma Q, Brown BL, Pu M et al (2011) Antitoxin MqsA helps mediate the bacterial general stress response. Nat Chem Biol 7:356–366
Wang X, Lord DM, Cheng HY, Osbourne DO, Hong SH, Sanchez-Torres V et al (2012) A new type V toxin-antitoxin system where mRNA for toxin GhoT is cleaved by antitoxin GhoS. Nat Chem Biol 8:855–861
Wei Y, Gao Z-Q, Otsuka Y, Naka K, Yonesaki T, Zhang H, Dong Y-H (2013) Structure-function studies of Escherichia coli RnlA reveal a novel toxin structure involved in bacteriophage resistance. Mol Microbiol 90:956–965
Yamaguchi Y, Inouye M (2009) mRNA interferases, sequence-specific endoribonucleases from the toxin–antitoxin systems. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 85:467–500
Yarmolinsky MB (1995) Programmed cell death in bacterial populations. Science 267:836–837
Zhang Y, Inouye M (2011) RatA (YfjG), an Escherichia coli toxin, inhibits 70S ribosome association to block translation initiation. Mol Microbiol 79:1418–1429
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Hara H, Kato I, Inouye M (2005) Insights into the mRNA cleavage mechanism by MazF, an mRNA interferase. J Biol Chem 280:3143–3150
Acknowledgments
The author cordially thanks Dr. Toshi Kawate at Cornell University for invaluable help with the manuscript. This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists B (25870386).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otsuka, Y. Prokaryotic toxin–antitoxin systems: novel regulations of the toxins. Curr Genet 62, 379–382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-015-0557-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-015-0557-z