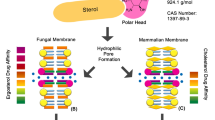
Abstract
Over the years, lipids of non-pathogenic yeast such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae have been characterized to some details; however, a comparable situation does not exist for the human pathogenic fungi. This review is an attempt to bring in recent advances made in lipid research by employing high throughput lipidomic methods in terms of lipid analysis of pathogenic yeasts. Several pathogenic fungi exhibit multidrug resistance (MDR) which they acquire during the course of a treatment. Among the several causal factors, lipids by far have emerged as one of the critical contributors in the MDR acquisition in human pathogenic Candida. In this article, we have particularly focused on the role of lipids involved in cross talks between different cellular circuits that impact the acquisition of MDR in Candida.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon RD, Lamping E, Holmes AR, Niimi K, Bare PV, Keniya MV, Tanabe K, Niimi M, Goffeau A, Monk BC (2009) Efflux-mediated antifungal drug resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:291–321
Chandra J, McCormick TS, Imamura Y, Mukherjee PK, Ghannoum MA (2007) Interaction of Candida albicans with adherent human peripheral blood mononuclear cells increases C. albicans biofilm formation and results in differential expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Infect Immun 75:2612–2620
Chen YL, Montedonico AE, Kauffman S, Dunlap JR, Menn FM, Reynolds TB (2010) Phosphatidylserine synthase and phosphatidylserine decarboxylase are essential for cell wall integrity and virulence in Candida albicans. Mol Microbiol 75(5):1112–1132. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.07018.x
Daleke DL (2007) Phospholipid flippases. J Biol Chem 282(2):821–825. doi:10.1074/jbc.R600035200
Dhamgaye S, Bernard M, Lelandais G, Sismeiro O, Lemoine S, Coppée JY, Le Crom S, Prasad R, Devaux F (2012) RNA sequencing revealed novel actors of the acquisition of drug resistance in Candida albicans. BMC Genomics 13:396–408
Ejsing CS, Sampaio JL, Surendranath V, Duchoslav E, Ekroos K, Klemm RW, Simons K, Shevchenko A (2009) Global analysis of the yeast lipidome by quantitative shotgun mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(7):2136–2141. doi:10.1073/pnas.0811700106
Gaur M, Choudhury D, Prasad R (2005) Complete inventory of ABC proteins in human pathogenic yeast, Candida albicans. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 9(1):3–15. doi:10.1159/000088141
Gaur M, Puri N, Manoharlal R, Rai V, Mukhopadhayay G, Choudhury D, Prasad R (2008) MFS transportome of the human pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. BMC Genomics 9:579–591. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-579
Gulshan K, Moye-Rowley WS (2011) Vacuolar import of phosphatidylcholine requires the ATP-binding cassette transporter Ybt1. Traffic 12(9):1257–1268. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01228.x
Gulshan K, Schmidt JA, Shahi P, Moye-Rowley WS (2008) Evidence for the bifunctional nature of mitochondrial phosphatidylserine decarboxylase: role in Pdr3-dependent retrograde regulation of PDR5 expression. Mol Cell Biol 28:5851–5864
Gulshan K, Shahi P, Moye-Rowley WS (2010) Compartment-specific synthesis of phosphatidylethanolamine is required for normal heavy metal resistance. Mol Biol Cell 21(3):443–455. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-06-0519
Heitman J (2011) Microbial pathogens in the fungal kingdom. Fungal Biol Rev 25(1):48–60
Hitchcock CA, Barrett-Bee KJ, Russell NJ (1986) The lipid composition of azole-sensitive and azole-resistant strains of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol 132:2421–2431
Holthuis JC, Levine TP (2005) Lipid traffic: floppy drives and a superhighway. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(3):209–220
Ikeda M, Kihara A, Igarashi Y (2006) Lipid asymmetry of the eukaryotic PM: functions and related enzymes. Biol Pharm Bull 29(8):1542–1546
Johnson SS, Hanson PK, Manoharlal R, Brice SE, Cowart LA, Moye-Rowley WS (2010) Regulation of yeast nutrient permease endocytosis by ATP-binding cassette transporters and a seven-transmembrane protein, RSB1. J Biol Chem 285(46):35792–35802. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.162883
Lattif AA, Chandra J, Chang J, Liu S, Zhou G, Chance MR, Ghannoum MA, Mukherjee PK (2008) Proteomic and pathway analyses reveal phase-dependent over-expression of proteins associated with carbohydrate metabolic pathways in Candida albicans biofilms. Open Proteomics J 1:5–26
Lattif AA, Mukherjee PK, Chandra J, Roth MR, Welti R, Rouabhia M, Ghannoum MA (2011) Lipidomics of Candida albicans biofilms reveals phase-dependent production of phospholipid molecular classes and role for lipid rafts in biofilm formation. Microbiology 157(11):3232–3242. doi:10.1099/mic.0.051086-0
Löffler J, Einsele H, Hebart H, Schumacher U, Hrastnik C, Daum G (2000) Phospholipid and sterol analysis of plasma membranes of azole-resistant Candida albicans strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett 185:59–63
Mansfield BE, Oltean HN, Oliver BG, Hoot SJ, Leyde SE, Hedstrom L, White TC (2010) Azole drugs are imported by facilitated diffusion in Candida albicans and other pathogenic fungi. PLoS Pathog 30(6 (9)):e1001126. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001126
Maurya IK, Thota CK, Verma SD, Sharma J, Rawal MK, Ravikumar B, Sen S, Chauhan NC, Lynn AM, Chauhan VS, Prasad R (2013) Rationally designed transmembrane peptide mimics of the multidrug transporter protein Cdr1 act as antagonists to selectively block drug efflux and chemosensitize azole-resistant clinical isolates of Candida albicans. J Biol Chem 7(288 (23)):16775–16787. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.467159
Morschhäuser J (2010) Regulation of multidrug resistance in pathogenic fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 47(2):94–106. doi:10.1016/j.fgb.2009.08.002
Mukherjee PK, Chandra J, Kuhn DM, Ghannoum MA (2003) Mechanism of fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans biofilms: phase-specific role of efflux pumps and membrane sterols. Infect Immun 71:4333–4340
Mukhopadhyay K, Prasad T, Saini P, Pucadyil TJ, Chattopadhyay A, Prasad R (2004) Membrane sphingolipid–ergosterol interactions are important determinants of multidrug resistance in Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48(5):1778–1787
Niimi M, Firth NA, Cannon RD (2010) Antifungal drug resistance of oral fungi. Odontology 98(1):15–25. doi:10.1007/s10266-009-0118-3
Noble SM, French S, Kohn LA, Chen V, Johnson AD (2010) Systematic screens of a Candida albicans homozygous deletion library decouple morphogenetic switching and pathogenicity. Nat Genet 42(7):590–598. doi:10.1038/ng.605
Noël T (2012) The cellular and molecular defense mechanisms of the Candida yeasts against azole antifungal drugs. J Mycol Med 22(2):173–178. doi:10.1016/j.mycmed.2012.04.004
Pasrija R, Krishnamurthy S, Prasad T, Ernst JF, Prasad R (2005a) Squalene epoxidase encoded by ERG1 affects morphogenesis and drug susceptibilities of Candida albicans. J Antimicrob Chemother 55:905–913
Pasrija R, Prasad T, Prasad R (2005b) Membrane raft lipid constituents affect drug susceptibilities of Candida albicans. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1219–1223
Pasrija R, Panwar SL, Prasad R (2008) Multidrug transporters CaCdr1p and CaMdr1p of Candida albicans display different lipid specificities: both ergosterol and sphingolipids are essential for targeting of CaCdr1p to membrane rafts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:694–704
Pfaller MA (2012) Antifungal drug resistance: mechanisms, epidemiology, and consequences for treatment. Am J Med 125(1 Suppl):S3–S13. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.11.001
Pfaller MA, Diekema DJ (2007) Epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: a persistent public health problem. Clin Microbiol Rev 20:133–163. doi:10.1128/CMR.00029-06
Pomorski T, Menon AK (2006) Lipid flippases and their biological functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(24):2908–2921
Prasad R, Goffeau A (2012) Yeast ATP-binding cassette transporters conferring multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol 66:39–63 Epub 2012 Jun 11
Prasad R, Kapoor K (2005) Multidrug resistance in yeast Candida. Int Rev Cytol 242:215–248
Prasad R, De Wergifosse P, Goffeau A, Balzi E (1995) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel gene of Candida albicans, CDR1, conferring multiple resistance to drugs and antifungals. Curr Genet 27(4):320–329
Prasad T, Saini P, Gaur NA, Vishwakarma RA, Khan LA, Haq QM, Prasad R (2005) Functional analysis of CaIPT1, a sphingolipid biosynthetic gene involved in multidrug resistance and morphogenesis of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(8):3442–3452
Richardson DM (2005) Changing patterns and trends in systemic function infections. J Antimicrob Chemother 56(Suppl 1):i5–i11
Schlame M, Rua D, Greenberg ML (2000) The biosynthesis and functional role of cardiolipin. Prog Lipid Res 39:257–288
Sebastian TT, Baldridge RD, Xu P, Graham TR (2012) Phospholipid flippases: building asymmetric membranes and transport vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821(8):1068–1077. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.12.007
Shahi P, Moye-Rowley WS (2009) Coordinate control of lipid composition and drug transport activities is required for normal multidrug resistance in fungi. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794:852–859
Shevchenko A, Simons K (2010) Lipidomics: coming to grips with lipid diversity. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(8):593–598. doi:10.1038/nrm2934
Shingu-Vazquez M, Traven A (2011) Mitochondria and fungal pathogenesis: drug tolerance, virulence, and potential for antifungal therapy. Eukaryot Cell 10:1376–1383
Shukla S, Rai V, Banerjee D, Prasad R (2006) Characterization of Cdr1p, a major multidrug efflux protein of Candida albicans: purified protein is amenable to intrinsic fluorescence analysis. Biochemistry 45(7):2425–2435
Simons K, Sampaio JL (2011) Membrane organization and lipid rafts. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(10):a004697. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a004697
Singh A, Prasad R (2011) Comparative lipidomics of azole sensitive and resistant clinical isolates of Candida albicans reveals unexpected diversity in molecular lipid imprints. PLoS One 6(4):e19266. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019266
Singh A, Prasad T, Kapoor K, Mandal A, Roth M, Welti R, Prasad R (2010) Phospholipidome of Candida: each species of Candida has distinctive phospholipid molecular species. OMICS 14(6):665–677. doi:10.1089/omi.2010.0041
Singh A, Yadav V, Prasad R (2012) Comparative lipidomics in clinical isolates of Candida albicans reveal crosstalk between mitochondria, cell wall integrity and azole resistance. PLoS One 7(6):e39812. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039812
Singh A, Mahto KK, Prasad R (2013) Lipidomics and in vitro azole resistance in Candida albicans. OMICS 17(2):84–93. doi:10.1089/omi.2012.0075
Smriti, Krishnamurthy S, Dixit BL, Gupta CM, Milewski S, Prasad R (2002) ABC transporters Cdr1p, Cdr2p and Cdr3p of a human pathogen Candida albicans are general phospholipid translocators. Yeast 19(4):303–318
Tuite NL, Lacey K (2013) Overview of invasive fungal infections. Methods Mol Biol 968:1–23. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-257-5_1
van Helvoort A, Smith AJ, Sprong H, Fritzsche I, Schinkel AH, Borst P, van Meer G (1996) MDR1 P-glycoprotein is a lipid translocase of broad specificity, while MDR3 P-glycoprotein specifically translocates phosphatidylcholine. Cell 87(3):507–517
van Meer G, Voelker DR, Feigenson GW (2008) Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:112–124. doi:10.1038/nrm2330
Wenk MR (2005) The emerging field of lipidomics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:594–610
Yeater KM, Chandra J, Cheng G, Mukherjee PK, Zhao X, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Kwast KE, Ghannoum MA, Hoyer LL (2007) Temporal analysis of Candida albicans gene expression during biofilm development. Microbiology 153:2373–2385
Zhang YQ, Gamarra S, Garcia-Effron G, Park S, Perlin DS, Rao R (2010) Requirement for ergosterol in V-ATPase function underlies antifungal activity of azole drugs. PLoS Pathog 6(6):e1000939. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000939
Zhong Q, Gvozdenovic-Jeremic J, Webster P, Zhou J, Greenberg ML (2005) Loss of function KRE5 suppresses temperature sensitivity of mutants lacking mitochondrial anionic lipids. Mol Biol Cell 16:665–675
Zhong Q, Li G, Gvozdenovic-Jeremic J, Greenberg ML (2007) Up-regulation of the cell wall integrity pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae suppresses temperature sensitivity of the pgs1Δ mutant. J Biol Chem 282:15946–15953
Acknowledgments
The work from authors (RP) laboratory discussed has been supported in part by grants from the Department of Biotechnology (BT/PR11158/BRB/10/640/2008, BT/PR13641/Med/29/175/2010, BT/PR14879/BRB10/885/2010, BT/01/CEIB/10/III/12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Griac.
Special Issue: Yeast membranes and cell wall: From basics to applications
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, R., Singh, A. Lipids of Candida albicans and their role in multidrug resistance. Curr Genet 59, 243–250 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-013-0402-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-013-0402-1