Abstract.
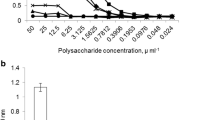
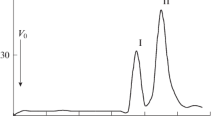
The exopolysaccharides produced by Rhizobium meliloti M11S inhibited nonspecifically the adsorption of phage NM8 by coating the cells. But lipopolysaccharides (LPS) had a specific inhibitory effect. Only the polysaccharide moiety of LPS, composed of glucose, glucosamine, galactose, 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), and large amounts of sialic acid, inhibited phage adsorption; neither the lipid A moiety nor a cellular glucan was involved. Rhizobium strains lacking sialic acids did not bind phage NM8. Inhibition of phage binding by lectin specific for N-acetylneuraminic acid demonstrated that phage NM8 bound to sialic acids. Preincubation of the phage with monosaccharides showed that inactivation of phage was very stereospecific for N-acetylneuraminic acid. Phage adsorption was also strongly inhibited by N-acetylglucosamine, which is not present in the LPS. Therefore, the receptor for phage NM8 appears to be a saccharide site, probably involving the acetyl groups of sialic acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 March 1996 / Accepted: 29 June 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Defives, C., Werquin, M., Mary, P. et al. Roles of Exopolysaccharides and Lipopolysaccharides in the Adsorption of the Siphovirus Phage NM8 to Rhizobium meliloti M11S Cells. Curr Microbiol 33, 371–376 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900130
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002849900130