Abstract
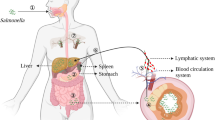
OsmY is a periplasmic protein with two BON domains which may attach to phospholipid membranes. Previous reports showed that the expression of OsmY in Escherichia coli was hyperosmotically inducible and RpoS dependent. But little work was done to investigate the expression and function of OsmY in Salmonella. Here, we detected the endogenous OsmY in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. Typhi) with polyclonal antibody. The results showed that the expression of OsmY was also RpoS dependent and was activated under stationary phase. Further, using in vitro culture, we established the Salmonella pathogenesis island (SPI)-1 and SPI-2-inducing conditions with hyperosmolarity and low-phosphate, low-magnesium medium (pH 5.8), respectively, and found that only SPI-2-inducing conditions can activate the expression of OsmY. osmY deletion mutant showed delayed growth compared with wild-type S. Typhi in SPI-2-inducing conditions. The results indicated that OsmY may function to resist the stress and be favorable for Salmonella’s replication in the Salmonella-containing vesicles of macrophage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron AD, Dorman CJ (2012) A fundamental regulatory mechanism operating through OmpR and DNA topology controls expression of Salmonella pathogenicity islands SPI-1 and SPI-2. PLoS Genet 8:e1002615
Coombes BK, Brown NF, Valdez Y, Brumell JH, Finlay BB (2004) Expression and secretion of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 virulence genes in response to acidification exhibit differential requirements of a functional type III secretion apparatus and SsaL. J Biol Chem 279:49804–49815
Crump JA, Mintz ED (2010) Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Clin Infect Dis 50:241–246
de Jong HK, Parry CM, van der Poll T, Wiersinga WJ (2012) Host-pathogen interaction in invasive Salmonellosis. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002933
Dong T, Schellhorn HE (2010) Role of RpoS in virulence of pathogens. Infect Immun 78:887–897
Du H, Sheng X, Zhang H, Zou X, Ni B, Xu S, Zhu X, Xu H, Huang X (2011) RpoE may promote flagellar gene expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi under hyperosmotic stress. Curr Microbiol 62:492–500
Du H, Wang M, Luo Z, Ni B, Wang F, Meng Y, Xu S, Huang X (2011) Coregulation of gene expression by sigma factors RpoE and RpoS in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi during hyperosmotic stress. Curr Microbiol 62:1483–1489
Ellermeier JR, Slauch JM (2007) Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:24–29
Feklistov A, Sharon BD, Darst SA, Gross CA (2014) Bacterial sigma factors: a historical, structural, and genomic perspective. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:357–376
Figueira R, Holden DW (2012) Functions of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI-2) type III secretion system effectors. Microbiology 158:1147–1161
Gong H, Su J, Bai Y, Miao L, Kim K, Yang Y, Liu F, Lu S (2009) Characterization of the expression of Salmonella type III secretion system factor PrgI, SipA, SipB, SopE2, SpaO, and SptP in cultures and in mice. BMC Microbiol 9:73
Jishage M, Ishihama A (1995) Regulation of RNA polymerase sigma subunit synthesis in Escherichia coli: intracellular levels of sigma 70 and sigma 38. J Bacteriol 177:6832–6835
Jishage M, Iwata A, Ueda S, Ishihama A (1996) Regulation of RNA polymerase sigma subunit synthesis in Escherichia coli: intracellular levels of four species of sigma subunit under various growth conditions. J Bacteriol 178:5447–5451
Lange R, Hengge-Aronis R (1994) The cellular concentration of the sigma S subunit of RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli is controlled at the levels of transcription, translation, and protein stability. Genes Dev 8:1600–1612
Lawhon SD, Khare S, Rossetti CA, Everts RE, Galindo CL, Luciano SA, Figueiredo JF, Nunes JE, Gull T, Davidson GS, Drake KL, Garner HR, Lewin HA, Baumler AJ, Adams LG (2011) Role of SPI-1 secreted effectors in acute bovine response to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium: a systems biology analysis approach. PLoS One 6:e26869
Liechty A, Chen J, Jain MK (2000) Origin of antibacterial stasis by polymyxin B in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1463:55–64
McGhie EJ, Brawn LC, Hume PJ, Humphreys D, Koronakis V (2009) Salmonella takes control: effector-driven manipulation of the host. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:117–124
Nikolaus T, Deiwick J, Rappl C, Freeman JA, Schroder W, Miller SI, Hensel M (2001) SseBCD proteins are secreted by the type III secretion system of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 and function as a translocon. J Bacteriol 183:6036–6045
Oh JT, Cajal Y, Skowronska EM, Belkin S, Chen J, Van Dyk TK, Sasser M, Jain MK (2000) Cationic peptide antimicrobials induce selective transcription of micF and osmY in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1463:43–54
Rhodius VA, Suh WC, Nonaka G, West J, Gross CA (2006) Conserved and variable functions of the sigmaE stress response in related genomes. PLoS Biol 4:e2
Srikanth CV, Mercado-Lubo R, Hallstrom K, McCormick BA (2011) Salmonella effector proteins and host-cell responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:3687–3697
Xu S, Zhang H, Sheng X, Xu H, Huang X (2008) Transcriptional expression of fljB: z66, a flagellin gene located on a novel linear plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi under environmental stresses. New Microbiol 31:241–247
Yeats C, Bateman A (2003) The BON domain: a putative membrane-binding domain. Trends Biochem Sci 28:352–355
Yim HH, Villarejo M (1992) osmY, a new hyperosmotically inducible gene, encodes a periplasmic protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 174:3637–3644
Yim HH, Brems RL, Villarejo M (1994) Molecular characterization of the promoter of osmY, an rpoS-dependent gene. J Bacteriol 176:100–107
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from Jiangsu University (14JDG043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xueming Zheng and Ying Ji have contributed equally to this work.
Ying Ji—Co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Ji, Y., Weng, X. et al. RpoS-Dependent Expression of OsmY in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi: Activation Under Stationary Phase and SPI-2-Inducing Conditions. Curr Microbiol 70, 877–882 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0802-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0802-1