Abstract
Objective
This study aims to investigate the efficacy of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy with TEC regimen (taxotere–epirubicin–cyclophosphamide) in the treatment of breast cancer (BC) patients.
Method
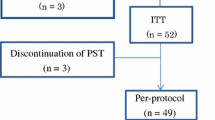
Total of 118 BC patients were recruited from the Department of Breast Surgery in Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2012, in this study. The clinical data and serum samples were collected from each patient prior to the study. All patients were given four cycles of TEC chemotherapy before surgery.
Results
The overall response rate of TEC regimen in the treatment of BC was 67.8 % (80/118), clinical complete response rate was 3.4 % (4/118), and clinical partial response rate was 64.4 % (76/118). Furthermore, we found that age, tumor size, lymph node metastasis and clinical stages of patients had no statistically significant difference (all P > 0.05). Both negative ER status and negative PR status were statistically related to better response (P = 0.033 and P = 0.024, respectively) when compared with the positive ER status and positive PR status, while such association was not observed between the negative HER-2 status and positive HER-2 status (P > 0.05). In addition, the efficacy of triple-negative breast cancer was significantly better than that of luminal A, luminal B and HER-2+ cancers (all P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference among the HER-2+, luminal A, luminal B groups (all P > 0.05).
Conclusion
Our study support the view that BC cases under the TEC chemotherapy were related to higher overall response rates; and the chemotherapy with the TEC regimen could be served as an effective therapy in the treatment of BC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes K (1990) A simplified anatomical approach to thin section, high resolution CT of the ear and facial nerve. Radiogr Today 56:18–23
Anders CK, Carey LA (2009) Biology, metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 9(Suppl 2):S73–S81. doi:10.3816/CBC.2009.s.008
Assi HA, Khoury KE, Dbouk H, Khalil LE, Mouhieddine TH, El Saghir NS (2013) Epidemiology and prognosis of breast cancer in young women. J Thorac Dis 5:S2–S8. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.05.24
Ho ML, Hsiao YH, Su SY, Chou MC, Liaw YP (2014) Mortality of breast cancer in Taiwan, 1971–2010: temporal changes and an age-period-cohort analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol. doi:10.3109/01443615.2014.935717
Khokhar A (2013) View point: how to make women familiar with their breasts? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:5539–5542
Pediconi F, Napoli A, Di Mare L, Vasselli F, Catalano C (2012) MRgFUS: from diagnosis to therapy. Eur J Radiol 81(Suppl 1):S118–S120. doi:10.1016/S0720-048X(12)70049-9
Yang XR, Chang-Claude J, Goode EL, Couch FJ, Nevanlinna H, Milne RL, Gaudet M, Schmidt MK, Broeks A, Cox A, Fasching PA, Hein R, Spurdle AB, Blows F, Driver K, Flesch-Janys D, Heinz J, Sinn P, Vrieling A, Heikkinen T, Aittomaki K, Heikkila P, Blomqvist C, Lissowska J, Peplonska B, Chanock S, Figueroa J, Brinton L, Hall P, Czene K, Humphreys K, Darabi H, Liu J, Van’t Veer LJ, van Leeuwen FE, Andrulis IL, Glendon G, Knight JA, Mulligan AM, O’Malley FP, Weerasooriya N, John EM, Beckmann MW, Hartmann A, Weihbrecht SB, Wachter DL, Jud SM, Loehberg CR, Baglietto L, English DR, Giles GG, McLean CA, Severi G, Lambrechts D, Vandorpe T, Weltens C, Paridaens R, Smeets A, Neven P, Wildiers H, Wang X, Olson JE, Cafourek V, Fredericksen Z, Kosel M, Vachon C, Cramp HE, Connley D, Cross SS, Balasubramanian SP, Reed MW, Dork T, Bremer M, Meyer A, Karstens JH, Ay A, Park-Simon TW, Hillemanns P, Arias Perez JI, Menendez Rodriguez P, Zamora P, Benitez J, Ko YD, Fischer HP, Hamann U, Pesch B, Bruning T, Justenhoven C, Brauch H, Eccles DM, Tapper WJ, Gerty SM, Sawyer EJ, Tomlinson IP, Jones A, Kerin M, Miller N, McInerney N, Anton-Culver H, Ziogas A, Shen CY, Hsiung CN, Wu PE, Yang SL, Yu JC, Chen ST, Hsu GC, Haiman CA, Henderson BE, Le Marchand L, Kolonel LN, Lindblom A, Margolin S, Jakubowska A, Lubinski J, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Gorski B, Gronwald J, Hooning MJ, Hollestelle A, van den Ouweland AM, Jager A, Kriege M, Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Collee M, Wang-Gohrke S, Pylkas K, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Mononen K, Grip M, Hirvikoski P, Winqvist R, Mannermaa A, Kosma VM, Kauppinen J, Kataja V, Auvinen P, Soini Y, Sironen R, Bojesen SE, Orsted DD, Kaur-Knudsen D, Flyger H, Nordestgaard BG, Holland H, Chenevix-Trench G, Manoukian S, Barile M, Radice P, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ, Tamimi R, Sangrajrang S, Brennan P, McKay J, Odefrey F, Gaborieau V, Devilee P, Huijts PE, Tollenaar RA, Seynaeve C, Dite GS, Apicella C, Hopper JL, Hammet F, Tsimiklis H, Smith LD, Southey MC, Humphreys MK, Easton D, Pharoah P, Sherman ME, Garcia-Closas M (2011) Associations of breast cancer risk factors with tumor subtypes: a pooled analysis from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 103:250–263. doi:10.1093/jnci/djq526
Hulka BS, Moorman PG (2008) Breast cancer: hormones and other risk factors. Maturitas 61:203–213 discussion 213
Kaufmann M, von Minckwitz G, Mamounas EP, Cameron D, Carey LA, Cristofanilli M, Denkert C, Eiermann W, Gnant M, Harris JR, Karn T, Liedtke C, Mauri D, Rouzier R, Ruckhaeberle E, Semiglazov V, Symmans WF, Tutt A, Pusztai L (2012) Recommendations from an international consensus conference on the current status and future of neoadjuvant systemic therapy in primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 19:1508–1516. doi:10.1245/s10434-011-2108-2
Symmans WF, Hatzis C, Sotiriou C, Andre F, Peintinger F, Regitnig P, Daxenbichler G, Desmedt C, Domont J, Marth C, Delaloge S, Bauernhofer T, Valero V, Booser DJ, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2010) Genomic index of sensitivity to endocrine therapy for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:4111–4119. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.4273
Alvarez RH, Valero V, Hortobagyi GN (2010) Emerging targeted therapies for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:3366–3379. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.4011
Sanchez-Munoz A, Plata-Fernandez Y, Jaen A, Lomas M, Fernandez M, Llacer C, Fernandez M, Ribelles N, Alba E, Sanchez-Rovira P (2013) Proliferation determined by ki67 marker and pCR in locally advanced breast cancer patients treated with neo-adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast J 19:685–686. doi:10.1111/tbj.12194
Penault-Llorca F, Vincent-Salomon A (2003) Roles of the pathologist in neoadjuvant chemotherapy: evaluation of response, prognostic and predictive factors. Ann Pathol 23:555–563
Smith IC, Heys SD, Hutcheon AW, Miller ID, Payne S, Gilbert FJ, Ah-See AK, Eremin O, Walker LG, Sarkar TK, Eggleton SP, Ogston KN (2002) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: significantly enhanced response with docetaxel. J Clin Oncol 20:1456–1466
Singh RB, Chander S, Mohanti BK, Pathy S, Kumar S, Bhatla N, Thulkar S, Vishnubhatla S, Kumar L (2013) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with weekly paclitaxel and carboplatin followed by chemoradiation in locally advanced cervical carcinoma: a pilot study. Gynecol Oncol 129:124–128. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.01.011
Gianni L, Dafni U, Gelber RD, Azambuja E, Muehlbauer S, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, Baselga J, Jackisch C, Cameron D, Mano M, Pedrini JL, Veronesi A, Mendiola C, Pluzanska A, Semiglazov V, Vrdoljak E, Eckart MJ, Shen Z, Skiadopoulos G, Procter M, Pritchard KI, Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Bell R, Herceptin Adjuvant Trial Study T (2011) Treatment with trastuzumab for 1 year after adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer: a 4-year follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 12:236–244. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70033-X
Chen X, Ye G, Zhang C, Li X, Chen Y, Xie X, Zheng H, Cao Y, Wu K, Ni D, Tang J, Wei Z, Shen K (2013) Superior outcome after neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, anthracycline, and cyclophosphamide versus docetaxel plus cyclophosphamide: results from the NATT trial in triple negative or HER2 positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 142:549–558. doi:10.1007/s10549-013-2790-9
Egawa-Takata T, Ueda Y, Kuragaki C, Miyake T, Miyatake T, Fujita M, Yoshino K, Nakashima R, Okazawa M, Tsutsui T, Morishige K, Kimura T, Yamasaki M, Nishizaki T, Nagamatsu M, Ito K, Asada M, Ogita K, Wakimoto A, Yamamoto T, Nishio Y, Enomoto T (2011) Chemotherapy for endometrial carcinoma (GOGO-EM1 study): TEC (paclitaxel, epirubicin, and carboplatin) is an effective remission-induction and adjuvant therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68:1603–1610. doi:10.1007/s00280-011-1638-4
Martin M, Pienkowski T, Mackey J, Pawlicki M, Guastalla JP, Weaver C, Tomiak E, Al-Tweigeri T, Chap L, Juhos E, Guevin R, Howell A, Fornander T, Hainsworth J, Coleman R, Vinholes J, Modiano M, Pinter T, Tang SC, Colwell B, Prady C, Provencher L, Walde D, Rodriguez-Lescure A, Hugh J, Loret C, Rupin M, Blitz S, Jacobs P, Murawsky M, Riva A, Vogel C, Breast Cancer International Research Group I (2005) Adjuvant docetaxel for node-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med 352:2302–2313. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043681
Yao X, Hosenpud J, Chitambar CR, Charlson J, Cheng YC (2012) A phase II study of concurrent docetaxel, epirubicin and cyclophosphamide as a neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. J Cancer 3:145–151. doi:10.7150/jca.3980
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, Bassett LW, Berry D, Bland KI, Borgen PI, Clark G, Edge SB, Hayes DF, Hughes LL, Hutter RV, Morrow M, Page DL, Recht A, Theriault RL, Thor A, Weaver DL, Wieand HS, Greene FL (2002) Revision of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 20:3628–3636
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Iwata H, Sato N, Masuda N, Nakamura S, Yamamoto N, Kuroi K, Kurosumi M, Tsuda H, Akiyama F, Ohashi Y, Toi M (2011) Docetaxel followed by fluorouracil/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide as neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with primary breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 41:867–875. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyr081
Watanabe H, Okada M, Kaji Y, Satouchi M, Sato Y, Yamabe Y, Onaya H, Endo M, Sone M, Arai Y (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours-revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 36:2495–2501
von Minckwitz G, Kummel S, Vogel P, Hanusch C, Eidtmann H, Hilfrich J, Gerber B, Huober J, Costa SD, Jackisch C, Loibl S, Mehta K, Kaufmann M, German Breast Group (2008) Neoadjuvant vinorelbine–capecitabine versus docetaxel–doxorubicin–cyclophosphamide in early nonresponsive breast cancer: phase III randomized GeparTrio trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:542–551. doi:10.1093/jnci/djn085
Rastogi P, Anderson SJ, Bear HD, Geyer CE, Kahlenberg MS, Robidoux A, Margolese RG, Hoehn JL, Vogel VG, Dakhil SR, Tamkus D, King KM, Pajon ER, Wright MJ, Robert J, Paik S, Mamounas EP, Wolmark N (2008) Preoperative chemotherapy: updates of national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project protocols B-18 and B-27. J Clin Oncol 26:778–785. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.0235
Untch M, Konecny GE, Paepke S, von Minckwitz G (2014) Current and future role of neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Breast. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2014.06.004
Burdette-Radoux S, Wood ME, Olin JJ, Laughlin RS, Crocker AM, Ashikaga T, Muss HB (2007) Phase I/II trial of adjuvant dose-dense docetaxel/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide (TEC) in stage II and III breast cancer. Breast J 13:274–280. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4741.2007.00421.x
Chen XS, Ma CD, Wu JY, Yang WT, Lu HF, Wu J, Lu JS, Shao ZM, Shen ZZ, Shen KW (2010) Molecular subtype approximated by quantitative estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and Her2 can predict the prognosis of breast cancer. Tumori 96:103–110
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Wolff AC, Mangu PB, Temin S (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Oncol Pract 6:195–197. doi:10.1200/JOP.777003
Cuzick J, Dowsett M, Pineda S, Wale C, Salter J, Quinn E, Zabaglo L, Mallon E, Green AR, Ellis IO, Howell A, Buzdar AU, Forbes JF (2011) Prognostic value of a combined estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, Ki-67, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 immunohistochemical score and comparison with the Genomic Health recurrence score in early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29:4273–4278. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.31.2835
Lindstrom LS, Karlsson E, Wilking UM, Johansson U, Hartman J, Lidbrink EK, Hatschek T, Skoog L, Bergh J (2012) Clinically used breast cancer markers such as estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 are unstable throughout tumor progression. J Clin Oncol 30:2601–2608. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.2482
Chen S, Liu Y, Ouyang QW, Huang L, Luo RC, Shao ZM (2014) Clinical and pathological response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on primary tumor reduction is correlated to survival in hormone receptor-positive but not hormone receptor-negative locally advanced breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. doi:10.1245/s10434-014-3894-0
Zhang N, Moran MS, Huo Q, Haffty BG, Yang Q (2011) The hormonal receptor status in breast cancer can be altered by neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a meta-analysis. Cancer Invest 29:594–598. doi:10.3109/07357907.2011.621913
van de Ven S, Smit VT, Dekker TJ, Nortier JW, Kroep JR (2011) Discordances in ER, PR and HER2 receptors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 37:422–430. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.11.006
Kinsella MD, Nassar A, Siddiqui MT, Cohen C (2012) Estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and HER2 expression pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy in primary breast carcinoma: a single institutional experience. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 5:530–536
Zheng S, Zhang BL, Xiao T, Zou SM, Xue LY, Luo W, Guo L, Liu XY, Lu N (2011) Comparison of histopathologic changes and expression of biomarkers in breast carcinoma before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 40:465–470
Estevez LG, Cuevas JM, Anton A, Florian J, Lopez-Vega JM, Velasco A, Lobo F, Herrero A, Fortes J (2003) Weekly docetaxel as neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III breast cancer: efficacy and correlation with biological markers in a phase II, multicenter study. Clin Cancer Res 9:686–692
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Krishnamurthy S, Yamamura Y, Broglio KR, Pusztai L, Buzdar AU, Hortobagyi GN, Esteva FJ (2004) Lack of association between amplification of her-2 and response to preoperative taxanes in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 101:258–263. doi:10.1002/cncr.20348
Learn PA, Yeh IT, McNutt M, Chisholm GB, Pollock BH, Rousseau DL Jr, Sharkey FE, Cruz AB, Kahlenberg MS (2005) HER-2/neu expression as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant docetaxel in patients with operable breast carcinoma. Cancer 103:2252–2260. doi:10.1002/cncr.21037
Rody A, Karn T, Gatje R, Ahr A, Solbach C, Kourtis K, Munnes M, Loibl S, Kissler S, Ruckhaberle E, Holtrich U, von Minckwitz G, Kaufmann M (2007) Gene expression profiling of breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide within the GEPARTRIO trial: HER-2, but not topoisomerase II alpha and microtubule-associated protein tau, is highly predictive of tumor response. Breast 16:86–93. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2006.06.008
Dede DS, Gumuskaya B, Guler G, Onat D, Altundag K, Ozisik Y (2013) Evaluation of changes of biologic markers ER, PR, HER 2 and Ki-67 in breast cancer with administration of neoadjuvant dose-dense doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel. J BUON 18:57–63
O’Neill F, Madden SF, Clynes M, Crown J, Doolan P, Aherne ST, O’Connor R (2013) A gene expression profile indicative of early stage HER2 targeted therapy response. Mol Cancer 12:69. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-69
Amos KD, Adamo B, Anders CK (2012) Triple-negative breast cancer: an update on neoadjuvant clinical trials. Int J Breast Cancer 2012:385978. doi:10.1155/2012/385978
Toi M, Nakamura S, Kuroi K, Iwata H, Ohno S, Masuda N, Kusama M, Yamazaki K, Hisamatsu K, Sato Y, Kashiwaba M, Kaise H, Kurosumi M, Tsuda H, Akiyama F, Ohashi Y, Takatsuka Y, Japan Breast Cancer Research Groyp (2008) Phase II study of preoperative sequential FEC and docetaxel predicts of pathological response and disease free survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat 110:531–539. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9744-z
von Minckwitz G, Martin M (2012) Neoadjuvant treatments for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Ann Oncol 23(Suppl 6):vi35–vi39. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds193
Keam B, Im SA, Kim HJ, Oh DY, Kim JH, Lee SH, Chie EK, Han W, Kim DW, Moon WK, Kim TY, Park IA, Noh DY, Heo DS, Ha SW, Bang YJ (2007) Prognostic impact of clinicopathologic parameters in stage II/III breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant docetaxel and doxorubicin chemotherapy: paradoxical features of the triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 7:203. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-7-203
Wang S, Yang H, Tong F, Zhang J, Yang D, Liu H, Cao Y, Liu P, Zhou P, Cheng L, Liu M, Guo J (2009) Response to neoadjuvant therapy and disease free survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 36:255–258
Masuda H, Masuda N, Kodama Y, Ogawa M, Karita M, Yamamura J, Tsukuda K, Doihara H, Miyoshi S, Mano M, Nakamori S, Tsujinaka T (2011) Predictive factors for the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:911–917. doi:10.1007/s00280-010-1371-4
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Research Project of Liaoning Province (No. 2012225016). We would like to acknowledge the helpful comments on this paper received from our reviewers.
Conflict of interest
No competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, L. et al. Efficacy of neo-adjuvant chemotherapy with TEC regimen on breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75, 301–308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2646-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2646-y