Abstract
Purpose
Artemisinins are now established drugs for treatment of malaria. These agents have been shown to possess impressive anti-cancer properties. We have investigated the role of artemisone (ATM), a novel derivative of artemisinin (ART) in a cancer setting both alone and in combination with established chemotherapeutic agents.
Methods
The anti-proliferative effects of ART and ATM were tested on a panel of human cancer cells in vitro using the methylthiazoletetrazolium assay, and the effect on cell cycling established by flow cytometry. Immunoblot analyses were performed to determine effects at the molecular level. Finally, ART and ATM were combined with the common anti-cancer agents oxaliplatin, gemcitabine and thalidomide.
Results
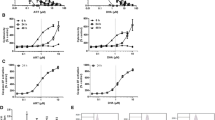
ART and ATM caused dose dependent decreases in cell number. ATM was consistently superior to ART, with IC50 s significantly lower in the former. Neither drug caused significant changes to the cell viability (%viable cells >95%), but arrested cell cycling. Blockade was either exclusively at the level of G1, or at all phases of the cell cycle, and associated with reductions in cyclin D1, CDK4 and pRb. Combination studies showed the anti-proliferative effect of ATM was often enhanced by addition of the other drugs, whilst ART exhibited antagonistic properties.
Conclusions
ART and ATM are active in cancer cell lines, with ATM displaying the greater anti-proliferative effect when used alone. ATM also enhances the effects of the above drugs, with ART being less likely to improve activities. Taken together, ATM should be thought of as the ART-derived compound next in line for further study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klayman DL (1985) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science 228:1049–1055
Golenser J, Waknine JH, Krugliak M, Hunt NH, Grau GE (2006) Current perspectives on the mechanism of action of artemisinins. Int J Parasitol 36:1427–1441
Krishna S, Bustamante L, Haynes RK, Staines HM (2008) Artemisinins: their growing importance in medicine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:520–527
Haynes RK, Fugmann B, Stetter J, Rieckmann K, Heilmann HD, Chan HW, Cheung MK, Lam WL, Wong HN, Croft SL, Vivas L, Rattray L, Stewart L, Peters W, Robinson BL, Edstein MD, Kotecka B, Kyle DE, Beckermann B, Gerisch M, Radtke M, Schmuck G, Steinke W, Wollborn U, Schmeer K, Romer A (2006) Artemisone—a highly active antimalarial drug of the artemisinin class. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 45:2082–2088
Li GQ, Arnold K, Guo XB, Jian HX, Fu LC (1984) Randomised comparative study of mefloquine, qinghaosu, and pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine in patients with falciparum malaria. Lancet 2:1360–1361
Li GQ, Guo XB, Fu LC, Jian HX, Wang XH (1994) Clinical trials of artemisinin and its derivatives in the treatment of malaria in China. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 88(Suppl 1):S5–S6
WHO Guidelines for the treatment of malaria (2006)
Vivas L, Rattray L, Stewart LB, Robinson BL, Fugmann B, Haynes RK, Peters W, Croft SL (2007) Antimalarial efficacy and drug interactions of the novel semi-synthetic endoperoxide artemisone in vitro and in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother 59:658–665
Ramharter M, Burkhardt D, Nemeth J, Adegnika AA, Kremsner PG (2006) In vitro activity of artemisone compared with artesunate against Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg 75:637–639
Nagelschmitz J, Voith B, Wensing G, Roemer A, Fugmann B, Haynes RK, Kotecka BM, Rieckmann KH, Edstein MD (2008) First assessment in humans of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and ex vivo pharmacodynamic antimalarial activity of the new artemisinin derivative artemisone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:3085–3091
Woerdenbag HJ, Moskal TA, Pras N, Malingre TM, el-Feraly FS, Kampinga HH, Konings AW (1993) Cytotoxicity of artemisinin-related endoperoxides to Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Nat Prod 56:849–856
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi H, Chitambar CR (2001) The anti-malarial artesunate is also active against cancer. Int J Oncol 18:767–773
Chen HH, Zhou HJ, Fang X (2003) Inhibition of human cancer cell line growth and human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis by artemisinin derivatives in vitro. Pharmacol Res 48:231–236
Nakase I, Lai H, Singh NP, Sasaki T (2008) Anticancer properties of artemisinin derivatives and their targeted delivery by transferrin conjugation. Int J Pharm 354:28–33
Li LN, Zhang HD, Yuan SJ, Tian ZY, Wang L, Sun ZX (2007) Artesunate attenuates the growth of human colorectal carcinoma and inhibits hyperactive Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Int J Cancer 121:1360–1365
Chen H, Sun B, Pan S, Jiang H, Sun X (2009) Dihydroartemisinin inhibits growth of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Drugs 20:131–140
Berger TG, Dieckmann D, Efferth T, Schultz ES, Funk JO, Baur A, Schuler G (2005) Artesunate in the treatment of metastatic uveal melanoma—first experiences. Oncol Rep 14:1599–1603
Singh NP, Panwar VK (2006) Case report of a pituitary macroadenoma treated with artemether. Integr Cancer Ther 5:391–394
Zhang ZY, Yu SQ, Miao LY, Huang XY, Zhang XP, Zhu YP, Xia XH, Li DQ (2008) Artesunate combined with vinorelbine plus cisplatin in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized controlled trial. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 6:134–138
Hou J, Wang D, Zhang R, Wang H (2008) Experimental therapy of hepatoma with artemisinin and its derivatives: in vitro and in vivo activity, chemosensitization, and mechanisms of action. Clin Cancer Res 14:5519–5530
Singh NP, Lai HC (2004) Artemisinin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Anticancer Res 24:2277–2280
Zhou HJ, Wang Z, Li A (2008) Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells HL60 via downregulation of transferrin receptor expression. Anticancer Drugs 19:247–255
Chen HH, Zhou HJ, Wang WQ, Wu GD (2004) Antimalarial dihydroartemisinin also inhibits angiogenesis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 53:423–432
Wartenberg M, Wolf S, Budde P, Grunheck F, Acker H, Hescheler J, Wartenberg G, Sauer H (2003) The antimalaria agent artemisinin exerts antiangiogenic effects in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived embryoid bodies. Lab Invest 83:1647–1655
Buommino E, Baroni A, Canozo N, Petrazzuolo M, Nicoletti R, Vozza A, Tufano MA (2009) Artemisinin reduces human melanoma cell migration by down-regulating alpha V beta 3 integrin and reducing metalloproteinase 2 production. Invest New Drugs 27:412–418
Ribeiro IR, Olliaro P (1998) Safety of artemisinin and its derivatives. A review of published and unpublished clinical trials. Med Trop (Mars.) 58:50–53
Gordi T, Lepist EI (2004) Artemisinin derivatives: toxic for laboratory animals, safe for humans? Toxicol Lett 147:99–107
Adjuik M, Babiker A, Garner P, Olliaro P, Taylor W, White N (2004) International Artemisinin Study Group. Artesunate combinations for treatment of malaria: meta-analysis. Lancet 363(9402):9–17
Liu WM (2008) Enhancing the cytotoxic activity of novel targeted therapies—is there a role for a combinatorial approach? Curr Clin Pharmacol 3(2):108–117 (Review)
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Liu WM, Scott KA, Shamash J, Joel S, Powles TB (2008) Enhancing the in vitro cytotoxic activity of Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in leukemic cells through a combinatorial approach. Leuk Lymphoma 49(9):1800–1809
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul 22:27–55
Batty KT, Davis TM, Thu LT, Binh TQ, Anh TK, Ilett KF (1996) Selective high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of artesunate and alpha- and beta-dihydroartemisinin in patients with falciparum malaria. J Chromatogr Biomed Appl 677:345–350
Efferth T, Sauerbrey A, Olbrich A, Gebhart E, Rauch P, Weber HO, Hengstler JG, Halatsch ME, Volm M, Tew KD, Ross DD, Funk JO (2003) Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell lines. Mol Pharmacol 64:382–394
Beekman AC, Barentsen AR, Woerdenbag HJ, Van UW, Pras N, Konings AW, el-Feraly FS, Galal AM, Wikstrom HV (1997) Stereochemistry-dependent cytotoxicity of some artemisinin derivatives. J Nat Prod 60:325–330
Li Y, Shan F, Wu JM, Wu GS, Ding J, Xiao D, Yang WY, Atassi G, Leonce S, Caignard DH, Renard P (2001) Novel antitumor artemisinin derivatives targeting G1 phase of the cell cycle. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:5–8
Willoughby JA Sr, Sundar SN, Cheung M, Tin AS, Modiano J, Firestone GL (2009) Artemisinin blocks prostate cancer growth and cell cycle progression by disrupting Sp1 interactions with the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) promoter and inhibiting CDK4 gene expression. J Biol Chem 284:2203–2213
Wu J, Feng Y, Xie D, Li X, Xiao W, Tao D, Qin J, Hu J, Gardner K, Judge SI, Li QQ, Gong J (2006) Unscheduled CDK1 activity in G1 phase of the cell cycle triggers apoptosis in X-irradiated lymphocytic leukemia cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(21):2538–2545
O’Neill PM, Barton VE, Ward SA (2010) The molecular mechanism of action of artemisinin—the debate continues. Molecules 15(3):1705–1721
Singh NP, Lai HC (2005) Synergistic cytotoxicity of artemisinin and sodium butyrate on human cancer cells. Anticancer Res 25:4325–4331
Chen T, Li M, Zhang R, Wang H (2009) Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis and sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to carboplatin therapy. J Cell Mol Med 13:1358–1370
Zhou HJ, Zhang JL, Li A, Wang Z, Lou XE (2009) Dihydroartemisinin improves the efficiency of chemotherapeutics in lung carcinomas in vivo and inhibits murine Lewis lung carcinoma cell line growth in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol
Hata T, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY, Koi M, Takagi A, Damdinsuren B, Yasui M, Fujie Y, Matsuzaki T, Hemmi H, Xu X, Kitani K, Seki Y, Takemasa I, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, Monden M (2005) Role of p21waf1/cip1 in effects of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 4:1585–1594
Tolis C, Peters GJ, Ferreira CG, Pinedo HM, Giaccone G (1999) Cell cycle disturbances and apoptosis induced by topotecan and gemcitabine on human lung cancer cell lines. Eur J Cancer 35:796–807
Escoubet-Lozach L, Lin IL, Jensen-Pergakes K, Brady HA, Gandhi AK, Schafer PH, Muller GW, Worland PJ, Chan KW, Verhelle D (2009) Pomalidomide and lenalidomide induce p21 WAF-1 expression in both lymphoma and multiple myeloma through a LSD1-mediated epigenetic mechanism. Cancer Res 69:7347–7356
Riganti C, Doublier S, Viarisio D, Miraglia E, Pescarmona G, Ghigo D, Bosia A (2009) Artemisinin induces doxorubicin resistance in human colon cancer cells via calcium-dependent activation of HIF-1alpha and P-glycoprotein overexpression. Br J Pharmacol 156:1054–1066
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. John Copier for helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. The authors would also like to thank Celgene Corps. for supplying thalidomide. Work at the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology was carried out in the Open Laboratory of Chemical Biology of the Institute of Molecular Technology for Drug Discovery and Synthesis with financial support from the Government of the HKSAR University Grants Committee Areas of Excellence Fund, Projects No. AoE P/10-01/01-02-I, AOE/P-10/01-2-II and the University Grants Council Grants No. HKUST 6493/06 M and 600507. Professor Krishna is funded by the European Commission projects ANTIMAL (Grant No. 018834) and MALSIG (Grant No. 223044). This work was funded by the cancer vaccine institute (http://www.cancervaccine.org.uk).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gravett, A.M., Liu, W.M., Krishna, S. et al. In vitro study of the anti-cancer effects of artemisone alone or in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67, 569–577 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1355-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1355-4