Abstract
Purpose
We have previously demonstrated doxorubicin-induced urokinase (uPA) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression in human H69 small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) cells by a microarray technique using Human Cancer Chip version 2, in which 425 human "cancer-related" genes are spotted on the plates. The microarray analysis also revealed a significant induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and doxorubicin-induced macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) expression was demonstrated by an RNase protection assay. We extended the study by testing the effects of doxorubicin on the induction of TNF-α, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1 in other types of lung carcinoma cells.
Methods
We investigated the effects of doxorubicin on the expression of TNF-α, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1 in 12 human lung carcinoma cell lines, including five SCLC, three adenocarcinoma and four squamous cell carcinoma cells. The surface expression of their receptors was also investigated.
Results
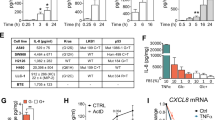
TNF-α was significantly induced in three cell lines, H69, SBC-7 (SCLC) and PC-9 (adenocarcinoma), uPA in five cell lines, H69, SBC-7, EBC-1 (squamous cell), EBC-2 (squamous cell), and Sq-1 (squamous cell), IL-8 in three cell lines, H69, PC-9 and EBC-1, and MCP-1 in five cell lines, H69, SBC-3 (SCLC), SBC-7, PC-9 and Sq-1. In H69 cells, TNF-α antigen levels were increased approximately fivefold in the conditioned medium of doxorubicin-treated cells, in parallel with an increase in mRNA levels. As with uPA and IL-8, the maximum induction was observed at the "sublethal" concentrations of 2 and 4 μM at which cell growth was slightly inhibited 24 h after treatment. Furthermore, the cells did not express receptors including types I and II TNF-α receptors, uPA receptor (uPAR), C-x-C-chemokine receptor-1 (CXCR-1), or C-C-chemokine receptor-2, corresponding to TNF-α, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1, respectively, that were induced by doxorubicin in the cells, although SBC-7 cells expressed uPAR, and EBC-1 cells expressed CXCR-1.
Conclusions
TNF-α, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1 induced and secreted from tumor cells upon doxorubicin stimulation may activate surrounding cells expressing the receptors such as neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages in a paracrine fashion. TNF-α is a major proinflammatory cytokine, and IL-8 and MCP-1 are major chemoattractants for neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages, respectively. Furthermore, uPA activates matrix metalloproteinase 9 which can truncate and activate IL-8. Thus, the simultaneous induction of TNF-α, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1 may enhance the interaction between tumor and inflammatory/immune cells, and augment cytotoxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- C-C:
-
Cysteine-cysteine
- C-x-C:
-
Cysteine-x-cysteine
- CCR-2:
-
C-C chemokine receptor-2
- CXCR-1:
-
C-x-C chemokine receptor-1
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- IL-1:
-
Interleukin-1
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-8:
-
Interleukin-8
- MCP-1:
-
Macrophage chemoattractant protein-1
- MTT:
-
(3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SCLC:
-
Small-cell lung cancer
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TNFRI :
-
Type I tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor
- TNFRII:
-
Type II tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor
- uPA:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator
- uPAR:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
References
Aggarwal BB, Natarajan K (1996) Tumor necrosis factors: developments during the last decade. Eur Cytokine Netw 7:93
Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B (1994) Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol 55:97
Bussolino F, Camussi G, Baglioni C (1988) Synthesis and release of platelet-activating factor by human vascular endothelial cells treated with tumor necrosis factor or interleukin 1 alpha. J Biol Chem 263:11856
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Lijnen R, Baes M, Lemaitre V, Tipping P, Drew A, Eeckhout Y, Shapiro S, Lupu F, Collen D (1997) Urokinase-generated plasmin activates matrix metalloproteinases during aneurysm formation. Nat Genet 17:439
De Larco JE, Wuertz BR, Manivel JC, Furcht LT (2001) Progression and enhancement of metastatic potential after exposure of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Res 61:2857
Duan Z, Feller AJ, Penson RT, Chabner BA, Seiden MV (1999) Discovery of differentially expressed genes associated with paclitaxel resistance using cDNA array technology: analysis of interleukin (IL) 6, IL-8, and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in the paclitaxel-resistant phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 5:3445
Ehrke MJ, Verstovsek S, Maccubbin DL, Ujhazy P, Zaleskis G, Berleth E, Mihich E (2000) Protective specific immunity induced by doxorubicin plus TNF-alpha combination treatment of EL4 lymphoma-bearing C57BL/6 mice. Int J Cancer 87:101
Evans CP, Stapp EC, Dall'Era MA, Juarez J, Yang JC (2001) Regulation of u-PA gene expression in human prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 94:390
Feng L, Xia Y, Garcia GE, Hwang D, Wilson CB (1995) Involvement of reactive oxygen intermediates in cyclooxygenase-2 expression induced by interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest 95:1669
Fisher DE (1994) Apoptosis in cancer therapy: crossing the threshold. Cell 78:539
Furutani Y, Nomura H, Notake M, Oyamada Y, Fukui T, Yamada M, Larsen CG, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K (1989) Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for human monocyte chemotactic and activating factor (MCAF). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 159:249
Hiraki A, Kaneshige T, Kiura K, Ueoka H, Yamane H, Tanaka M, Harada M (1999) Loss of HLA haplotype in lung cancer cell lines: implications for immunosurveillance of altered HLA class I/II phenotypes in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5:933
Inoue K, Slaton JW, Kim SJ, Perrotte P, Eve BY, Bar-Eli M, Radinsky R, Dinney CP (2000) Interleukin 8 expression regulates tumorigenicity and metastasis in human bladder cancer. Cancer Res 60:2290
Kiguchi T, Niiya K, Shibakura M, Miyazono T, Shinagawa K, Ishimaru F, Kiura K, Ikeda K, Nakata Y, Harada M (2001) Induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by the anthracycline antibiotic in human RC-K8 lymphoma and H69 lung-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 93:792
Koch AE, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL, Harlow LA, DiPietro LA, Elner VM, Elner SG, Strieter RM (1992) Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science 258:1798
Kramer B, Wiegmann K, Kronke M (1995) Regulation of the human TNF promoter by the transcription factor Ets. J Biol Chem 270:6577
Kudoh K, Ramanna M, Ravatn R, Elkahloun AG, Bittner ML, Meltzer PS, Trent JM, Dalton WS, Chin KV (2000) Monitoring the expression profiles of doxorubicin-induced and doxorubicin-resistant cancer cells by cDNA microarray. Cancer Res 60:4161
Larsen CG, Anderson AO, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Matsushima K (1989) The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science 243:1464
Laster SM, Wood JG, Gooding LR (1988) Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptotic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J Immunol 141:2629
Lee LF, Hellendall RP, Wang Y, Haskill JS, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Ting JP (2000) IL-8 reduced tumorigenicity of human ovarian cancer in vivo due to neutrophil infiltration. J Immunol 164:2769
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ (2001) The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104:487
Montovani A, Sozzani S, Proost P, van Damme J (1996) The monocyte chemoattractant protein family. In: Horuk R (ed) Chemoattractant ligands and their receptors: pharmacology and toxicology: basic and clinical aspects, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, p 169
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55
Mueller H (1998) Tumor necrosis factor as an antineoplastic agent: pitfalls and promises. Cell Mol Life Sci 54:1291
Muller I, Jenner A, Bruchelt G, Niethammer D, Halliwell B (1997) Effect of concentration on the cytotoxic mechanism of doxorubicin—apoptosis and oxidative DNA damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 230:254
Nawroth PP, Bank I, Handley D, Cassimeris J, Chess L, Stern D (1986) Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med 163:1363
Niiya K, Shinbo M, Ozawa T, Hayakawa Y, Sakuragawa N (1995) Modulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression by inflammatory cytokines in human pre-B lymphoma cell line RC-K8. Thromb Haemost 74:1511
Nokihara H, Nishioka Y, Yano S, Mukaida N, Matsushima K, Tsuruo T, Sone S (1999) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene modification of multidrug-resistant human lung cancer enhances antimetastatic effect of therapy with anti-P-glycoprotein antibody in SCID mice. Int J Cancer 80:773
Pober JS, Gimbrone MA Jr, Lapierre LA, Mendrick DL, Fiers W, Rothlein R, Springer TA (1986) Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol 137:1893
Powis G (1989) Free radical formation by antitumor quinones. Free Radic Biol Med 6:63
Rebbaa A, Chou PM, Emran M, Mirkin BL (2001) Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in caspase-8-deficient neuroblastoma cells is mediated through direct action on mitochondria. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 48:423
Rizzardini M, Carelli M, Cabello Porras MR, Cantoni L (1994) Mechanisms of endotoxin-induced haem oxygenase mRNA accumulation in mouse liver: synergism by glutathione depletion and protection by N-acetylcysteine. Biochem J 304 (Pt 2):477
Roebuck KA (1999) Regulation of interleukin-8 gene expression. J Interferon Cytokine Res 19:429
Sambrook J, Fritsh EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Schmitt M, Harbeck N, Thomssen C, Wilhelm O, Magdolen V, Reuning U, Ulm K, Hofler H, Janicke F, Graeff H (1997) Clinical impact of the plasminogen activation system in tumor invasion and metastasis: prognostic relevance and target for therapy. Thromb Haemost 78:285
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C, Chilvers ER, Dransfield I, Donnelly SC, Strieter R, Haslett C (1999) Extracellular matrix proteins protect small cell lung cancer cells against apoptosis: a mechanism for small cell lung cancer growth and drug resistance in vivo. Nat Med 5:662
Shibakura M, Niiya K, Kiguchi T, Kitajima I, Niiya M, Asaumi N, Huh NH, Nakata Y, Harada M, Tanimoto M (2003) Induction of IL-8 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by doxorubicin in human small cell lung carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 103:380
Strieter RM, Polverini PJ, Arenberg DA, Walz A, Opdenakker G, Van Damme J, Kunkel SL (1995) Role of C-X-C chemokines as regulators of angiogenesis in lung cancer. J Leukoc Biol 57:752
Takaki T, Hiraki A, Uenaka A, Gomi S, Itoh K, Udono H, Shibuya A, Tsuji T, Sekiguchi S, Nakayama E (1998) Variable expression on lung cancer cell lines of HLA-A2-binding MAGE-3 peptide recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int J Oncol 12:1103
Ueda A, Ishigatsubo Y, Okubo T, Yoshimura T (1997) Transcriptional regulation of the human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene. Cooperation of two NF-kappaB sites and NF-kappaB/Rel subunit specificity. J Biol Chem 272:31092
Watts GS, Futscher BW, Isett R, Gleason-Guzman M, Kunkel MW, Salmon SE (2001) cDNA microarray analysis of multidrug resistance: doxorubicin selection produces multiple defects in apoptosis signaling pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:434
Xing RH, Rabbani SA (1999) Transcriptional regulation of urokinase (uPA) gene expression in breast cancer cells: role of DNA methylation. Int J Cancer 81:443
Yoshida S, Ono M, Shono T, Izumi H, Ishibashi T, Suzuki H, Kuwano M (1997) Involvement of interleukin-8, vascular endothelial growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor in tumor necrosis factor alpha-dependent angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 17:4015
Yoshimura T, Matsushima K, Tanaka S, Robinson EA, Appella E, Oppenheim JJ, Leonard EJ (1987) Purification of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor that has peptide sequence similarity to other host defense cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:9233
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid (no. 12771476) for Encouragement of Young Scientists (to M.S.) and a Grant-in-Aid (no. 10670937) for Scientific Research (C) (to K.N.) from the Ministry of Education, Sciences, Sports and Culture, Japan. Northern blotting was carried out in the Radioisotope Center of Okayama University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niiya, M., Niiya, K., Kiguchi, T. et al. Induction of TNF-α, uPA, IL-8 and MCP-1 by doxorubicin in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 52, 391–398 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0665-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0665-1