Abstract
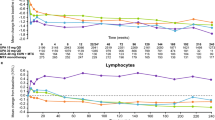
As a weak acid, methotrexate (MTX) is bound to serum albumin and has variable protein binding. The purpose of this study was to assess serum albumin’s relationship with MTX pharmacokinetics by comparing MTX clearance and toxicities between patients with normal serum albumin to those with hypoalbuminemia. This single-center retrospective study included adult patients with leukemia or lymphoma who received their first MTX at a dose ≥1 g/m2. Hypoalbuminemia was defined as serum albumin ≤3.4 g/dL. MTX clearance was defined as the first documented time the MTX level ≤0.05 μM. Fisher’s exact tests and Wilcoxon rank sum tests were used to examine differences in toxicities, and Cox proportional hazard regression was used to assess relationship with time to clearance. Of 523 patients identified, 167 patients were evaluable. One hundred thirty-five patients had normal serum albumin and 32 had hypoalbuminemia. Hypoalbuminemia was associated with a higher proportion of patients experiencing edema, ascites or pleural effusions (34 vs. 12 %, p = 0.006), and the concomitant use of nephrotoxic agents (41 vs. 20 %, p = 0.021). Hypoalbuminemia was associated with a significantly longer time to MTX clearance (median 96 vs. 72 h, p = 0.004). In addition, patients with hypoalbuminemia had a higher proportion of hyperbilirubinemia and significantly longer hospitalization (median 14 vs. 5 days, p < 0.001). In conclusion, hypoalbuminemia was associated with increased time to MTX clearance and increased length of hospitalization. High dose MTX is safe to administer in patients with low albumin levels, with appropriate leucovorin rescue, and good supportive care.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jolivet J, Cowan KH, Curt GA et al (1983) The pharmacology and clinical use of methotrexate. N Engl J Med 309:1094–1104
Kantarjian HM, O’Brien S, Smith TL et al (2000) Results of treatment with hyper-CVAD, a dose intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 18(3):547–561
Magrath I, Adde M, Venzon D et al (1996) Adults and children with small non-cleaved cell lymphoma have similar excellent outcome when treated with the same chemotherapy regimen. J Clin Oncol 14:925–934
Mead GM, Sydes MR, Walewski J et al (2002) An international evaluation of CODOX-M and CODOX-M alternating with IVAC in adult Burkitt’s lymphoma: results of United Kingdom lymphoma group LY06 study. Ann Oncol 13:1264–1274
Yamaguchi M, Kwong YL, Kim WS et al (2011) Phase II study of SMILE chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage IV, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: the NK-cell tumor study group study. J Clin Oncol 29:4410–4416
Paci A, Veal G, Bardin C, et al. (2014). Review of therapeutic drug monitoring of anticancer drugs part 1—cytotoxics. Eur J Cancer. 50:2010–2019
Bleyer WA (1978) The clinical pharmacology of methotrexate. Cancer 41:36–51
Stehle G, Sinn H, Wunder A, Schrenk HH, Schu¨Tt S, Heene DL, Maier-Borst W (1999) The loading rate determines tumor targeting of methotrexate-albumin conjugates in rats. Anticancer Drugs 8:677–685
Stehle G, Wunder A, Sinn H et al (1997) Pharmacokinetics of methotrexate-albumin conjugates in tumor bearing rats. Anticancer Drugs 8:835–844
Boldt J (2010) Use of albumin: an update. Br J Anaesth 104:276–284
Hartung G, Stehle G, Sinn H et al (1999) Phase I trial of methotrexate-albumin in a weekly intravenous bolus regimen in cancer patients. Clin Canc Res 5:753–759
Choi YH, Bae SK, Oh JM et al (2007) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous methotrexate in mutant Nagase analbuminemic rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 28:385–392
Alarcon GS, Kremer JM, Macaluso M et al (1997) Risk factors for methotrexate-induced lung injury in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 127:356–364
Wiczer T, Dotson E, Tuten A et al (2016) Evaluation of incidence and risk factors for high-dose methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity. J Oncol Pharm Pract 22:430–436
Evans WE, Pratt CB (1978) Effect of pleural effusion on high-dose methotrexate kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 23:68–72
Finfer S, Bellomo R, Boyce N et al (2004) A comparison of albumin and saline for fluid resuscitation in the intensive care unit. N Engl J Med 350:2247–2256
The Official Statement of the American Thoracic Society (2004) Evidence-based colloid use in the critically Ill: American thoracic society consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1247–1259
Guthrie RD Jr, Hines C Jr (1991) Use of intravenous albumin the critically ill patient. Am J Gastroenterol 86:255–263
Curtin JP, Koonings PP, Gutierrez M et al (1991) Ifosfamide-induced neurotoxicity. Gynecol Oncol 42(3):193–196
Kettle JK, Grauer D, Folker TL et al (2010) Effectiveness of exogenous albumin administration for the prevention of ifosfamide-induced encephalopathy. Pharmacotherapy 30:812–817
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reiss, S., Buie, L., Adel, N. et al. Hypoalbuminemia is significantly associated with increased clearance time of high dose methotrexate in patients being treated for lymphoma or leukemia. Ann Hematol 95, 2009–2015 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2795-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-016-2795-7