Abstract
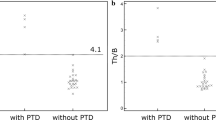
Therapy-induced autoimmunity may mediate the destruction of cancer cells. Previous studies have demonstrated that presence of autoimmune thyroid disorder is associated with favorable outcome in patients with solid cancer. Patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who achieved complete response on positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) after rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) therapy were enrolled in this study. The patients with and without diffuse thyroid uptake (DTU) were classified by PET/CT. A total of 270 patients were enrolled in this study. DTU related to autoimmune thyroiditis was present in 61 patients. The median time to DTU detection was 5.7 months (range, 0–21.3 months). High International Prognostic Index (IPI) score (progression-free survival [PFS], p = 0.001; overall survival [OS], p = 0.008), bulky mass ≥10 cm (PFS, p = 0.001; OS, p = 0.001), bone marrow involvement (PFS, p < 0.001; OS, p = 0.001), and DTU after R-CHOP therapy (PFS, p < 0.001; OS, p = 0.001) were significantly associated with PFS and OS. High IPI score (PFS, p = 0.003; OS, p = 0.014), BM involvement (PFS, p = 0.009; OS, p = 0.039), and DTU after R-CHOP therapy (PFS, p = 0.002; OS, p = 0.002) were independently associated with PFS and OS. DTU after R-CHOP therapy independently predicted favorable outcomes in patients with DLBCL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD (1998) New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: clinical features of the major histological subtypes. Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol 16:2780–2795
The Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Classification Project (1997) A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood 89:3909–3918
Reff ME, Carner K, Chambers KS, Chinn PC, Leonard JE, Raab R et al (1994) Depletion of B cells in vivo by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20. Blood 83:435–445
Nyman H, Adde M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Taskinen M, Berglund M, Amini RM et al (2007) Prognostic impact of immunohistochemically defined germinal center phenotype in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood 109:4930–4935
Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Choi WW, Perry KD, Smith LM, Shi X et al (2008) Addition of rituximab to standard chemotherapy improves the survival of both the germinal center B-cell-like and non-germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 26:4587–4594
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB et al (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363:711–723
Atkins MB, Mier JW, Parkinson DR, Gould JA, Berkman EM, Kaplan MM (1988) Hypothyroidism after treatment with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. N Engl J Med 318:1557–1563
Gogas H, Ioannovich J, Dafni U, Stavropoulou-Giokas C, Frangia K, Tsoutsos D et al (2006) Prognostic significance of autoimmunity during treatment of melanoma with interferon. N Engl J Med 354:709–718
Fong L, Small EJ (2008) Anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 antibody: the first in an emerging class of immunomodulatory antibodies for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol 26:5275–5283
Smyth PP, Shering SG, Kilbane MT, Murray MJ, McDermott EW, Smith DF et al (1998) Serum thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies, thyroid volume, and outcome in breast carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:2711–2716
Goldman MB, Monson RR, Maloof F (1992) Benign thyroid diseases and the risk of death from breast cancer. Oncology 49:461–466
Fiore E, Giustarini E, Mammoli C, Fragomeni F, Campani D, Muller I et al (2007) Favorable predictive value of thyroid autoimmunity in high aggressive breast cancer. J Endocrinol Invest 30:734–738
Spaepen K, Stroobants S, Dupont P, Vandenberghe P, Thomas J, de Groot T et al (2002) Early restaging positron emission tomography with (18) F-fluorodeoxyglucose predicts outcome in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Oncol 13:1356–1363
Haioun C, Itti E, Rahmouni A, Brice P, Rain JD, Belhadj K et al (2005) [18F] fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in aggressive lymphoma: an early prognostic tool for predicting patient outcome. Blood 106:1376–1381
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ et al (2007) Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:579–586
Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff K, Smithers DW, Tubiana M (1971) Report of the Committee on Hodgkin's Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res 31:1860–1861
Lister TA, Crowther D, Sutcliffe SB, Glatstein E, Canellos GP, Young RC et al (1989) Report of a committee convened to discuss the evaluation and staging of patients with Hodgkin's disease: Cotswolds meeting. J Clin Oncol 7:1630–1636
Karantanis D, Bogsrud TV, Wiseman GA, Mullan BP, Subramaniam RM, Nathan MA et al (2007) Clinical significance of diffusely increased 18F-FDG uptake in the thyroid gland. J Nucl Med 48:896–901
Liu Y (2009) Clinical significance of thyroid uptake on F18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med 23:17–23
Kim SS, Kim IJ, Kim SJ, Lee JY, Bae YT, Jeon YK et al (2012) Incidental diffuse thyroid 18F-FDG uptake related to autoimmune thyroiditis may be a favorable prognostic factor in advanced breast cancer. J Nucl Med 53:1855–1862
Kim SS, Kim SJ, Bae YT, Lee JY, Kim BH, Kim YK et al (2012) Factors associated with the development of new onset diffuse thyroid F18-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake after treatment of breast cancer in patients without a history of thyroid disease or thyroid dysfunction. Thyroid 22:53–58
Nakamoto Y, Tatsumi M, Hammoud D, Cohade C, Osman MM, Wahl RL (2005) Normal FDG distribution patterns in the head and neck: PET/CT evaluation. Radiology 234:879–885
Bohgaki T, Atsumi T, Koike T (2007) Multiple autoimmune diseases after autologous stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med 357:2734–2736
Ma J, Yu J, Tao X, Cai L, Wang J, Zheng SG (2010) The imbalance between regulatory and IL-17-secreting CD4+ T cells in lupus patients. Clin Rheumatol 29:1251–1258
Daikeler T, Tyndall A (2007) Autoimmunity following haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 20:349–360
Carlson K, Lönnerholm G, Smedmyr B, Oberg G, Simonsson B (1992) Thyroid function after autologous bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 10:123–127
Sanz J, Arriaga F, Montesinos P, Ortí G, Lorenzo I, Cantero S et al (2007) Autoimmune hemolytic anemia following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 39:555–561
Mackey JR, Desai S, Larratt L, Cwik V, Nabholtz JM (1997) Myasthenia gravis in association with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: clinical observations, therapeutic implications and review of literature. Bone Marrow Transplant 19:939–942
Matsushita T, Hasegawa M, Yanaba K, Kodera M, Takehara K, Sato S (2006) Elevated serum BAFF levels in patients with systemic sclerosis: enhanced BAFF signaling in systemic sclerosis B lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum 54:192–201
Groom J, Kalled SL, Cutler AH, Olson C, Woodcock SA, Schneider P et al (2002) Association of BAFF/BLyS overexpression and altered B cell differentiation with Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest 109:59–68
Mariette X, Roux S, Zhang J, Bengoufa D, Lavie F, Zhou T et al (2003) The level of BLyS (BAFF) correlates with the titre of autoantibodies in human Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 62:168–171
Anolik JH, Friedberg JW, Zheng B, Barnard J, Owen T, Cushing E et al (2007) B cell reconstitution after rituximab treatment of lymphoma recapitulates B cell ontogeny. Clin Immunol 122:139–145
Barrington SF, Mikhaeel NG, Kostakoglu L, Meignan M, Hutchings M, Müeller SP et al (2014) Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma: Consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J Clin Oncol 32:3048–3058
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by grants from the National R&D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (0920050)
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, MK., Chung, JS., Kim, SJ. et al. Diffuse thyroid 18F-FDG uptake after R-CHOP therapy predicts favorable outcome in patients with DLBCL. Ann Hematol 94, 995–1001 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-015-2311-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-015-2311-5