Abstract
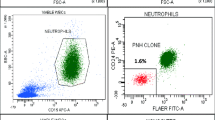
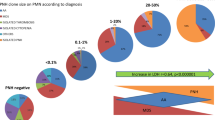
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is characterized by absence of CD55 and CD59 from the surface of affected cells. PNH has been associated with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). The aim of our study was to estimate the prevalence of the PNH clone in MDS patients by detecting CD55 and CD59 deficiency. We studied 90 MDS patients: 19 patients with RA, 15 with refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts (RARS), 18 with refractory anemia with excess of blasts (RAEB), 17 with refractory anemia with excess of blasts in transformation (RAEB-t), and 21 with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML). Twenty healthy individuals were also studied as the control group. We studied the PNH clone on granulocytes of these patients with the aid of flow cytometry. CD55- and CD59-deficient granulocytic populations were detected in 15.5% of MDS patients compared to 2.8% of normal individuals. Among the subgroups of the study, significant difference was present in three cases: (1) between CMML and control, (2) between CMML and RA, and (3) between CMML and RARS. These data indicate a possible association between PNH phenotype and MDS. MDS patients of worse prognosis (CMML) express more strongly the PNH clone compared to those of better prognosis (RA and RARS). Perhaps, the examination of MDS patients for the PNH clone by flow cytometry could provide us with a valuable prognostic tool.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meletis J, Michali E, Samarkos M et al (1997) Detection of “PNH red cell” populations in haematological disorders using the sephacryl gel test micro typing system. Leuk Lymphoma 28:177–182
Rosse WF, Ware RE (1995) The molecular basis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood 86:3277–3286
Bessler M, Mason PJ, Hillmen P et al (1994) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria is caused by somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene. EMBO J 13:110–117
Longo L, Bessler M, Beris P, Swirsk D, Luzzatto L (1994) Myelodysplasia in a patient with pre-existing paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: a clonal disease originating from within a clonal disease. Br J Haematol 87:401–403
Van Kamp H, Smit JW, van den Berg E, Halie MR, Vellenga E (1994) Myelodysplasia following paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: evidence for the emergency of a separate clone. Br J Haematol 87:399–400
Young NS, Calado RT, Scheinberg P (2006) Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Blood 108:2509–2519
Okamoto M, Shichishima T, Noji H, Ikeda K, Nakamura A, Akutsu K, Maruyama Y (2006) High frequency of several PIG-A mutations in patients with aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia 20:627–634
Nakakuma H, Nagakura S, Iwamoto N et al (1995) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clone in bone marrow of patients with pancytopenia. Blood 85:1371–1376
Luzzatto L, Familusi JB, Williams CKO, Junnid TA, Rotoli B, Alfinito F (1979) The PNH abnormality in myeloproliferative disorders: association of PNH and acute erythremic myelosis in two children. Haematologica 64:13–30
Omura GA (1981) Coexistence of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol 11:439–441
Christou T, Subramanian S, Fung C (1987) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria preceding malignant lymphoma. Arch Intern Med 147:377–379
Hernandez-Campo PM, Almeida J, Sanchez ML, Malvezzi M, Orfao A (2006) Normal patterns of expression of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins on different subsets of peripheral blood cells: a frame of reference for the diagnosis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 70:71–81
Rotoli B, Luzzatto L (1989) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Bailliere’s Clin Haematol 2:113–138
Kwong YL, Lee CP, Chan TK, Chan LC (1994) Flow cytometric measurement of glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol-linked surface proteins on blood cells of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Clin Pathol 102:30–35
Kishimoto T et al (eds) (1996) Leukocyte typing VI: white cell differentiation antigens. Garland Publishing, New York, pp 519–520, 521–522
Oelschlaegel U, Besson I, Arnoulet C et al (2001) A standardized flow cytometric method for screening paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) measuring CD55 and CD59 expression on erythrocytes and granulocytes. Clin Lab Haematol 23:81–90
Luzzatto L, Bessler M (1993) The dual pathogenesis of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Curr Opin Hematol 3:101–110
Rotoli B, Luzzatto L (1989) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Semin Hematol 26:201–207
Iwanaga M, Furukava K, Amenomori T et al (1998) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 102:465–476
Wang H, Chuhjo T, Yasue S, Omine M, Nakao S (2002) Clinical significance of a minor population of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria-type cells in bone marrow failure syndrome. Blood 100:3897–3902
Dunn DE, Tanawattanacharoen P, Boccuni P et al (1999) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells in patients with bone marrow failure syndromes. Ann Intern Med 131:401–408
Meletis J, Terpos E, Samarkos M et al (2001) Detection of CD55 and/or CD59 deficient red cell populations in patients with aplastic anemia, myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders. Haematologia 31:7–16
Araten DJ, Nafa K, Pakdeesuwan K, Luzzatto L (1999) Clonal populations of hematopoietic cells with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria genotype and phenotype are present in normal individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5209–5214
Yamaguchi M, Machii T, Azenishi Y et al (2000) Detection of small populations of CD59-deficient erythrocytes in patients with aplastic anemia or myelodysplastic syndrome and normal individuals. Blood Cells Mol Diseases 26:247–254
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr Christina Aggouridaki for the clinical and laboratory support, and Mrs. Aglaia Naoum and Mrs. Margarita Tsouka for their skilled technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaiafa, G., Papadopoulos, A., Ntaios, G. et al. Detection of CD55- and CD59-deficient granulocytic populations in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Ann Hematol 87, 257–262 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0420-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0420-5