Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the safety and efficacy of transarterial embolization of life-threatening arterial rupture in patients with vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (vEDS) in a single tertiary referral center.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed transarterial embolization for vEDS performed at our institution from 2000 to 2012. The indication of embolization was spontaneous arterial rupture or pseudoaneurysm with acute bleeding. All interventions used a percutaneous approach through a 5F or less introducer sheath. Embolic agents were microcoils and glue in 3 procedures, glue alone in 2, and microcoils alone in 2.
Results
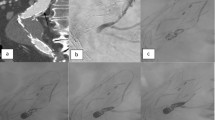
Five consecutive vEDS patients were treated by 7 embolization procedures (4 women, mean age 29.8 years). All procedures were successfully performed. Two patients required a second procedure for newly arterial lesions at a different site from the first procedure. Four of the five patients were still alive after a mean follow-up of 19.4 (range 1–74.7) months. One patient died of multiple organ failure 2 days after procedure. Minor procedural complications were observed in 3 procedures (43 %), all directly managed during the same session. Remote arterial lesions occurred after 3 procedures (43 %); one underwent a second embolization, and the other 2 were observed conservatively. Puncture site complication was observed in only one procedure (14 %).
Conclusion
Embolization for vEDS is a safe and effective method to manage life-threatening arterial rupture.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beighton P, De Paepe A, Steinmann B et al (1998) Ehlers–Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche. Ehlers–Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehlers–Danlos Support Group (UK). Am J Med Genet 77:31–37
Superti-Furga A, Steinmann B, Ramirez F, Byers PH (1989) Molecular defects of type III procollagen in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. Hum Genet 82:104–108
Perdu J, Boutouyrie P, Lahlou-Laforet K et al (2006) Vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Presse Med 35(12 Pt 2):1864–1875
Schievink WI, Limburg M, Oorthuys JW et al (1990) Cerebrovascular disease in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. Stroke 21:626–632
Schievink WI, Piepgras DG, Earnest FT, Gordon H (1991) Spontaneous carotid–cavernous fistulae in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. Case report. J Neurosurg 74:991–998
Pepin M, Schwarze U, Superti-Furga A, Byers PH (2000) Clinical and genetic features of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV, the vascular type. N Engl J Med 342:673–680
Zilocchi M, Macedo TA, Oderich GS et al (2007) Vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndrome: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:712–719
Freeman RK, Swegle J, Sise MJ (1996) The surgical complications of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Am Surg 62:869–873
Horowitz MB, Purdy PD, Valentine RJ, Morrill K (2000) Remote vascular catastrophes after neurovascular interventional therapy for type 4 Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:974–976
Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Dowd CF et al (1990) Treatment of carotid–cavernous fistulas associated with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Neurosurgery 26:1021–1027
Naidu SG, Chong BW, Huettl EA, Stone WM (2007) Percutaneous embolization of a lumbar pseudoaneurysm in a patient with type IV Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. J Vasc Surg 46:1036–1038
Iida Y, Obitsu Y, Komai H, Shigematsu H (2009) Successful coil embolization for rupture of the subclavian artery associated with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. J Vasc Surg 50:1191–1195
Matsushima K, Takara H (2009) Endovascular treatment for a spontaneous rupture of the posterior tibial artery in a patient with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV: report of a case. Surg Today 39:523–526
Kimura K, Sakai-Kimura M, Takahashi R et al (2010) Too friable to treat? Lancet 375(9725):1578
Hagspiel KD, Bonatti H, Sabri S et al (2011) Metachronous bilateral posterior tibial artery aneurysms in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34:413–418
Ong KT, Perdu J, De Backer J et al (2010) Effect of celiprolol on prevention of cardiovascular events in vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndrome: a prospective randomised, open, blinded-endpoints trial. Lancet 376(9751):1476–1484
Brooke BS, Arnaoutakis G, McDonnell NB, Black JH 3rd (2010) Contemporary management of vascular complications associated with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. J Vasc Surg 51:131–138
Lum YW, Brooke BS, Arnaoutakis GJ et al (2012) Endovascular procedures in patients with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome: a review of clinical outcomes and iatrogenic complications. Ann Vasc Surg 26:25–33
Casana R, Nano G, Dalainas I, Tealdi DG (2004) Endovascular treatment of hepatic artery aneurysm in a patient with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Case report. Int Angiol 23:291–295
Tonnessen BH, Sternbergh WC III, Mannava K, Money SR (2007) Endovascular repair of an iliac artery aneurysm in a patient with Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. J Vasc Surg 45:177–179
Khalique Z, Lyons OT, Clough RE et al (2009) Successful endovascular repair of acute type B aortic dissection in undiagnosed Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 38:608–609
Raval M, Lee CJ, Phade S et al (2012) Covered stent use after subclavian artery and vein injuries in the setting of vascular Ehlers–Danlos. J Vasc Surg 55:542–544
Kern MJ, Cohen M, Talley JD et al (1990) Early ambulation after 5 French diagnostic cardiac catheterization: results of a multicenter trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 15:1475–1483
Schoolman A, Kepes JJ (1967) Bilateral spontaneous carotid–cavernous fistulae in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Case report. J Neurosurg 26:82–86
Usinskiene J, Mazighi M, Bisdorff A, Houdart E (2006) Fatal peritoneal bleeding following embolization of a carotid–cavernous fistula in Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29:1104–1106
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, T., Frank, M., Pellerin, O. et al. Embolization of Life-Threatening Arterial Rupture in Patients with Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37, 77–84 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0640-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0640-0