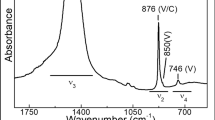
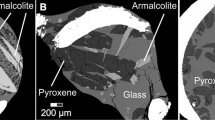
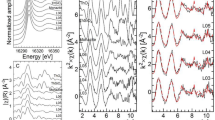
Abstract
In the context of radioactive waste repository in geological formation, kaolinite-metallic iron interaction in chlorine solution was conducted in batch experiments, under anoxic conditions at 90 °C during 9 months. After a mineralogical characterization at a global scale, products were analyzed at the micrometer and nanometer scales by X-ray absorption spectroscopic techniques (XAS and STXM). Absorption at Al, Si and Fe edges was investigated to have a complete overview of the distribution and status of constituting elements. Whereas Si K-edge results do not evidence significant evolution of silicon status, investigations at Al K-edge and Fe L-edges demonstrate variations at aggregate and particle scales of IVAl:VIAl and Fe2+:Fe3+ ratios. Spectroscopic data evidence the systematic crystallization of Fe-serpentines onto the remaining particles of kaolinite and the absence of pure species (kaolinite or Fe-serpentines). Combination of spatially resolved spectroscopic analyses and TEM-EDXS elemental distribution aims to calculate unit cell formulae of Fe-serpentines layers and abundance of each species in mixed particles. For most of the investigated particles, results reveal that the variations of particles composition are directly linked to the relative contributions of kaolinite and Fe-berthierine in mixed particles. However, for some particles, microscale investigations evidence crystallization of two other Fe-serpentines species, devoid of aluminum, cronstedtite and greenalite.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aja SU, Darby Dyar M (2002) The stability of Fe-Mg chlorites in hydrothermal solutions—I. Results of experimental investigations. Appl Geochem 17:1219–1239
Bailey SW (1988) Odinite, a new dioctahedral-trioctahedral Fe3+-rich 1:1 clay mineral. Clay Miner 23:237–247
Bardot F, Villiéras F, Michot LJ, François M, Gérard G, Cases JM (1998) High resolution gas adsorption study on illites permuted with various cations: assessment of surface energetic properties. J Dispers Sci Technol 19:739–759
Belin S, Briois V, Traverse A, Idir M, Moreno T, Ribbens M (2005) SAMBA a new beamline for X-ray absorption Spectroscopy in the 4–40 keV range. Phys Scripta T115:980–983
Brindley GW (1982) Chemical compositions of berthierines-a review. Clays Clay Miner 30:153–155
Briois V, Vantelon D, Villain F, Couzinet B, Flank AM, Lagarde P (2007) Combining two structural techniques on the micrometer scale: micro-XAS and micro-Raman spectroscopy. J Synchrotron Radiat 14:403–408
Calvert CC, Brown A, Brydson R (2005) Determination of the local chemistry of iron in inorganic and organic materials. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 143:173–187
Crocombette JP, Pollak M, Jollet F, Thromat N, Gautier-Soyer M (1995) X-Ray absorption spectroscopy at the Fe L2,3 threshold in iron oxides. Phys Rev B: Condens Matter 52:3143–3150
de Combarieu G, Barpoux P, Minet Y (2007) Iron corrosion in Callovo-Oxfordian argillite: from experiments to thermodynamic/kinetic modelling. Phys Chem Earth 32:346–358
Devaraju TC, Laajoki K, Subbarao G (2000) Retrograde chlorine-bearing greenalite from the iron-formation of Kudremukh, Karnataka, India. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie, Monatshefte 5:207–216
Farges F, Lefrère Y, Rossano S, Berthereau A, Calas G, Brown GE Jr (2004) The effect of redox state on the local structural environment of iron in silicate glasses: a combined XAFS spectroscopy, molecular dynamics, and bond valence study. J Non-Cryst Solids 334:176–188
Flank AM, Cauchon G, Lagard P, Bac S, Janousch M, Wetter R, Dubuisson JM, Idir M, Langlois F, Moreno T, Vantelon D (2006) LUCIA, a microfocus soft XAS beamline. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 246:269–274
Geiger CA, Henry DL, Bailey SW, Maj JJ (1983) Crystal structure of cronstedtite-2H2. Clays Clay Miner 31:97–108
Guggenheim S, Bailey SW (1989) An occurence of a modulated serpentine related to the greenalite-caryopilite series. Am Miner 74:637–641
Hitchcock AP (2001) Soft X-ray spectromicroscopy of polymers and biopolymer interfaces. J Synchrotron Radiat 8:66–71
Ildefonse Ph, Cabaret D, Sainctavit Ph, Calas G, Flank AM, Lagarde P (1998) Aluminium X_ray absorption near edge structure in model compounds and Earth’s surface minerals. Phys Chem Miner 25:112–121
Jacobsen C, Wirick S, Flynn G, Zimba C (2000) Soft X-Ray spectroscopy from image sequences with sub-100 nm spatial resolution. J Microsc 197:173–184
Kaznatcheev KV, Karunakaran Ch, Lanke UD, Urquhart SG, Obst M, Hitchcock AP (2007) Soft X-ray spectromicroscopy beamline at the CLS: commissioning results. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 582:96–99
Kogure T (2002) Identification of polytypic groups in hydrous phyllosilicates using electron back-scattering patterns. Am Miner 87:1678–1685
Kohler E (2001) Réactivité des mélanges synthétiques smectite/kaolinite et smectite/aluminium gel en présence d’un excès de fer métal. Dissertation (DRRT) Evry Val d’Essonne University
Lerotic M, Jacobsen C, Schäfer T, Vogt S (2004) Cluster analysis of soft X-ray spectromicroscopy data. Ultramicroscopy 100:35–57
Lerotic M, Jacobsen C, Gillow JB, Francis AJ, Wirick S, Vogt S, Maser J (2005) Cluster analysis in soft X-ray spectromicroscopy: finding the patterns in complex specimens. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom 144–147:1137–1143
Li D, Bancroft GM, Fleet ME, Feng XH (1995a) Silicon K-edge XANES spectra of silicate minerals. Phys Chem Miner 22:115–122
Li D, Bancroft GM, Fleet ME, Feng XH, Pan Y (1995b) Al K-edge XANES spectra of aluminosilicate minerals. Am Miner 80:432–440
Mermut AR, Cano AF (2001) Baseline studies of the clay mineral society source clays: chemical analyses of major elements. Clays Clay Miner 49:381–386
Miot J, Benzerara K, Morin G, Kappler A, Bernard S, Obst M, Férard C, Skouri-Panet F, Guigner JM, Posth N, Galvez M, Brown GE Jr, Guyot F (2009) Iron biomineralization by anaerobic neutrophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:696–711
Newville M (2001) EXAFS analysis using FEFF and FEFFIT. J Synchrotron Radiat 8:96–100
Newville M, Livin P, Yacoby Y, Rehr JJ, Stern EA (1993) Near-edge x-ray-absorption fine structure of Pb: a comparison of theory and experiment. Phys Rev B: Condens Matter 47:14126–14131
Perronnet M (2004) Réactivité des matériaux argileux dans un contexte de corrosion métal. Application au stockage des déchets radioactifs en site argileux. PhD Thesis INPL Nancy
Ravel B, Newville M (2005) ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J Synchrotron Radiat 12:537–541
Rivard C, Pelletier M, Michau N, Razafitianamaharavo A, Bihannic I, Abdelmoula M, Ghanbaja J, Villiéras F (2013) Berthierine-like mineral formation and stability during the interaction of kaolinite with metallic iron at 90°C under anoxic and oxidant conditions. Am Miner 98: xxx–xxx (In Press)
Schlegel ML, Bataillon C, Benhamida K, Blanc C, Menut D, Lacour JL (2008) Metal corrosion and argillite transformation at the water-saturated, high-temperature iron-clay interface: a microscopic-scale study. Appl Geochem 23:2619–3263
Shaw SA, Peak D, Hendry J (2009) Investigation of acidic dissolution of mixed clays between pH 1.0 and −3.0 using Si and Al X-ray absorption near edge structure. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:4151–4165
Teo BK (1986) EXAFS: basic principles and data analysis. Inorganic chemistry concepts, vol 9. Springer, Berlin
Van Aken PA, Liebscher B (2002) Quantification of ferrous/ferric ratios in minerals: new evaluation schemes of Fe-L2,3 electron energy-loss near-edge spectra. Phys Chem Miner 29:188–200
Van der Laan G, Kirkman IW (1992) 2p absorption spectra of 3d transition metal compounds in tetrahedral and octahedral symmetry. J Phys: Condens Matter 4:4189–4204
Vantelon D, Montarges-Pelletier E, Michot LJ, Briois V, Pelletier M, Thomas F (2003) Iron distribution in the octahedral sheet of dioctahedral smectites. An Fe K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Phys Chem Miner 30:44–53
Wasinger E, de Groot FMF, Hedman B, Hodgson KO, Solomon EI (2003) L-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy of Non-Heme Iron sites: experimental determination of differential orbital covalency. J Am Chem Soc 125:12894–12906
Wilke M, Farges F, Petit PE, Brown GE Jr, Martin F (2001) Oxidation state and coordination of Fe in minerals: an Fe K-Xanes spectroscopic study. Am Miner 86:714–730
WWW-MINCRYST (2012) Crystallographic and crystallochemical database for minerals and their structural analogues. http://database.iem.ac.ru/mincryst
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Andra (Agence nationale pour la gestion des déchets radioactifs—French national radioactive waste management agency). The STXM data were collected at the Canadian Light Source, which is supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the National Research Council Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Province of Saskatchewan, Western Economic Diversification Canada, and the University of Saskatchewan. We also thank SOLEIL facility for financial and technical supports. This work could not have been done without the collaboration of LUCIA beamline staff Nicolas Tercera, Anne-Marie Flank and Pierre Lagarde. We also thank Valérie Briois from SAMBA beamline for collecting data at Fe K-edge on her “home beamtime”. We gratefully thank Jaafar Ghanbaja for TEM investigations. A special thanks goes to Yves Moëlo who provided berthierine sample and to Markus Plaschke who kindly shared Fe–L edges data on reference samples so that we could operate validation tests on the fitting procedure of Fe–L spectra.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivard, C., Montargès-Pelletier, E., Vantelon, D. et al. Combination of multi-scale and multi-edge X-ray spectroscopy for investigating the products obtained from the interaction between kaolinite and metallic iron in anoxic conditions at 90 °C. Phys Chem Minerals 40, 115–132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-012-0552-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-012-0552-6