Abstract
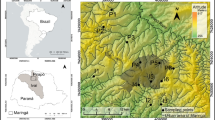
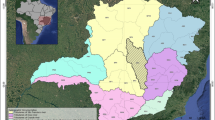
Nutrient enrichment in streams due to land use is increasing globally, reducing water quality and causing eutrophication of downstream fresh and coastal waters. In temperate developed countries, the intensive use of fertilizers in agriculture is a main driver of increasing nutrient concentrations, but high levels and fast rates of urbanization can be a predominant issue in some areas of the developing world. We investigated land use in the highly urbanized tropical State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. We collected total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and inorganic nutrient data from 35 independent watersheds distributed across the State and characterized land use at a riparian and entire watershed scales upstream from each sample station, using ArcGIS. We used regression models to explain land use influences on nutrient concentrations and to assess riparian protection relationships to water quality. We found that urban land use was the primary driver of nutrient concentration increases, independent of the scale of analyses and that urban land use was more concentrated in the riparian buffer of streams than in the entire watersheds. We also found significant thresholds that indicated strong increases in nutrient concentrations with modest increases in urbanization reaching maximum nutrient concentrations between 10 and 46% urban cover. These thresholds influenced calculation of reference nutrient concentrations, and ignoring them led to higher estimates of these concentrations. Lack of sewage treatment in concert with urban development in riparian zones apparently leads to the observation that modest increases in urban land use can cause large increases in nutrient concentrations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JD (2004) Landscapes and riverscapes: the influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 35:257–284
Andrade TMB, Camargo PB, Silva DML, Piccolo MC, Vieira SA, Alves LF, Joly CA, Martinelli LA (2011) Dynamics of dissolved forms of carbon and inorganic Nitrogen in small watersheds of the coastal atlantic forest in Southeast Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut 214:393–408
Bernhardt ES, Palmer MA (2007) Restoring streams in an urbanizing world. Freshw Biol 52:738–751
Biggs T, Dunne T, Martinelli L (2004) Natural controls and human impacts on stream nutrient concentrations in a deforested region of the Brazilian Amazon basin. Biogeochemistry 68:227–257
Biggs TW, Dunne T, Domingues TF, Martinelli LA (2002) Relative influence of natural watershed properties and human disturbance on stream solute concentrations in the southwestern Brazilian Amazon basin. Water Resour Res 38:25–21-25-16
Blinn CR, Kilgore MA (2001) Riparian management practices: a summary of state guidelines. J For 99:11–17
Booth DB, Jackson CR (1997) Urbanization of aquatic systems: degradation thresholds, stormwater detection, and the limits of mitigation jawra. J Am Water Resour Assoc 33:1077–1090
Booth DB, Roy AH, Smith B, Capps KA (2016) Global perspectives on the urban stream syndrome. Freshw Sci 35:412–420
Brabec E, Schulte S, Richards PL (2002) Impervious surfaces and water quality: a review of current literature and its implications for watershed planning. J Plan Lit 16:499–514
Bustamante MMC, Martinelli LA, Pérez T, Rasse R, Ometto JHB, Pacheco FS, Lins SRM, Marquina S (2015) Nitrogen management challenges in major watersheds of South America. Environ Res Lett 10:065007
Capps KA, Bentsen CN, Ramírez A (2016) Poverty, urbanization, and environmental degradation: urban streams in the developing world. Freshw Sci 35:429–435
Carpenter SR, Caraco NF, Correll DL, Howarth RW, Sharpley AN, Smith VH (1998) Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecol Appl 8:559–568
Castillo MM (2010) Land use and topography as predictors of nutrient levels in a tropical catchment. Limnologica 40:322–329
Clark EA (1998) Landscape variables affecting livestock impacts on water quality in the humid temperate zone. Can J Plant Sci 78:181–190
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. APHA American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Cunha D, Dodds W, Carmo Calijuri M (2011) Defining nutrient and biochemical oxygen demand baselines for tropical rivers and streams in São Paulo State (Brazil): a comparison between reference and impacted sites. Environ Manage 48:945
Daniel MHB et al. (2002) Effects of urban sewage on dissolved oxygen, dissolved inorganic and organic carbon, and electrical conductivity of small streams along a gradient of Urbanization in the Piracicaba River Basin. Water Air Soil Pollut 136:189–206
Diaz RJ, Rosenberg R (2008) Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 321:926–929
Dodds WK, Smith VH, Zander B (1997) Developing nutrient targets to control benthic chlorophyll levels in streams: a case study of the Clark Fork River. Water Res 31:1738–1750
Dodds WK (2003) Misuse of inorganic N and soluble reactive P concentrations to indicate nutrient status of surface waters. J N Am Benthol Soc 22:171–181
Dodds WK, Oakes RM (2004) A technique for establishing reference nutrient concentrations across watersheds affected by humans. Limnol Oceanogr 2:333–341
Dodds WK, Oakes RM (2006) Controls on nutrients across a prairie stream watershed: land use and riparian cover effects. Environ Manage 37:634–646
Dodds WK, Smith VH, Lohman K (2006) Nitrogen and phosphorus relationships to benthic algal biomass in temperate streams. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 63:1190–1191
Dodds WK, Clements WH, Gido K, Hilderbrand RH, King RS (2010) Thresholds, breakpoints, and nonlinearity in freshwaters as related to management. J N Am Benthol Soc 29:988–997
Dodds WK, Whiles MR (2010) Freshwater ecology: concepts and environmental applications of limnology, 2nd edn.. Academic Press, Burlington
Dodds WK, Smith VH (2016) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters 6:155–164
Downing JA, Mcclain M, Twilley R, Melack JM, Elser J, Rabalais NN, Lewis WM, Turner RE, Corredor J, Soto D, Yanez-Arancibia A, Kopaska JA, Howarth RW (1999) The impact of accelerating land-use change on the N-cycle of tropical aquatic ecosystems: current conditions and projected changes. Biogeochemistry 46:109–148
Filoso S et al. (2003) Land use and nitrogen export in the Piracicaba River basin, Southeast Brazil. Biogeochemistry 65:275–294
Filoso S, Martinelli LA, Howarth RW, Boyer EW, Dentener F (2006) Human activities changing the nitrogen cycle in Brazil. In: Martinelli LA, Howarth RW (eds) Nitrogen cycling in the Americas: natural and anthropogenic influences and controls. Springer, Dordrecht, p 61–89
Foley JA, DeFries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coe MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Monfreda C, Patz JA, Prentice IC, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309:570–574
Germer S, Neill C, Vetter T, Chaves J, Krusche AV, Elsenbeer H (2009) Implications of long-term land-use change for the hydrology and solute budgets of small catchments in Amazonia. J Hydrol 364:349–363
Grimm NB, Faeth SH, Golubiewski NE, Redman CL, Wu J, Bai X, Briggs JM (2008) Global change and the ecolog of cities. Science 319:756–760
Groffman PM, Baron JS, Blett T, Gold AJ, Goodman I, Gunderson LH, Levinson BM, Palmer MA, Paerl HW, Peterson GD, Poff NL, Rejeski DW, Reynolds JF, Turner MG, Weathers KC, Wiens J (2006) Ecological thresholds: the key to successful environmental management or an important concept with no practical application? Ecosystems 9:1–13
Gücker B, Silva RCS, Graeber D, Monteiro JAF, Brookshire ENJ, Chaves RC, Boëchat IG (2016) Dissolved nutrient exports from natural and human-impacted Neotropical catchments. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 25:378–390
Howarth RW (1988) Nutrient limitation of net primary production in marine ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 19:89–110
IBGE (2006a) Censo Agropecuario 2006 Brasil, Grandes Regiones y Unidades de la Federación
IBGE (2006b) Censo Agropecuario, Agricultura Familiar Primeiros Resultados
IBGE (2010) Censo Demografico http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/default.shtm
Johnson LB, Richards C, Host GE, Arthur JW (1997) Landscape influences on water chemistry in midwestern stream ecosystems. Freshw Biol 37:193–208
Kummu M, de Moel H, Ward PJ, Varis O (2011) How close do we live to water? A global analysis of population distance to freshwater bodies. PLoS One 6:e20578
Leal CG, Pompeu PS, Gardner TA, Leitão RP, Hughes RM, Kaufmann PR, Zuanon J, de Paula FR, Ferraz SFB, Thomson JR, Mac NallyJoice R, Ferreira J, Barlow J (2016) Multi-scale assessment of human-induced changes to Amazonian instream habitats. Landsc Ecol 31:1725–1745
Lehner B, Verdin K, Jarvis A (2006) HydroSHEDS Technical Documentation Version 1.0
Lewis Jr WM (1986) Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses from a nutrient-poor tropical moist forest. Ecology 67:1275–1282
Meyer JL, Paul MJ, Taulbee WK (2005) Stream ecosystem function in urbanizing landscapes. J N Am Benthol Soc 24:602–612
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystem and human well-being: wetland and water synthesis. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC
Neill C, Deegan LA, Thomas SM, Cerri CC (2001) Deforestation for pasture alters nitrogen and phosphorus in small Amazonian streams. Ecol Appl 11:1817–1828
Neill C, Deegan LA, Thomas SM, Haupert CL, Krusche AV, Ballester VM, Victoria RL (2006) Deforestation alters the hydraulic and biogeochemical characteristics of small lowland Amazonian streams. Hydrol Process 20:2563–2580
Nürnberg GK (1996) Trophic state of clear and colored, soft- and hardwater lakes with special consideration of nutrients, anoxia, phytoplankton and fish. J Lake Reserv Manage 12:432–447
Omernik JM, Abernathy AR, Male LM (1981) Stream nutrient levels and proximity of agricultrual and forest land to streams: some relationships. J Soil Water Conserv 36:227–231
Paerl HW, Fulton RS, Moisander PH, Dyble J (2001) Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. Sci World J 1:76–113
Paerl HW, Otten TG (2013) Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: causes, consequences, and controls. Microb Ecol 65:995–1010
Paerl HW, Hall NS, Peierls BL, Rossignol KL (2014) Evolving paradigms and challenges in estuarine and coastal eutrophication dynamics in a culturally and climatically stressed world. Estuar Coasts 37:243–258
Paul MJ, Meyer JL (2001) Streams in the urban landscape. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 32:333–365
Ramírez A, De Jesús-Crespo R, Martinó-Cardona DM, Martínez-Rivera N, Burgos-Caraballo S (2009) Urban streams in Puerto Rico: what can we learn from the tropics? J N Am Benthol Soc 28:1070–1079
Ribeiro MC, Metzger JP, Martensen AC, Ponzoni FJ, Hirota MM (2009) The Brazilian Atlantic forest: how much is left, and how is the remaining forest distributed? Implications for conservation. Biol Conserv 142:1141–1153
Secchi S, Gassman PW, Jha M, Kurkalova L, Kling CL (2011) Potential water quality changes due to corn expansion in the Upper Mississippi River Basin. Ecol Appl 21:1068–1084
Silva DML, Camargo PB, Mcdowell WH, Vieira I, Salomão MSMB, Martinelli LA (2012) Influence of land use changes on water chemistry in streams in the State of São Paulo, southeast Brazil. Anais Acad Bras Cienc 84:919–930
Silva JSO, da Cunha Bustamante MM, Markewitz D, Krusche AV, Ferreira LG (2011) Effects of land cover on chemical characteristics of streams in the Cerrado region of Brazil. Biogeochemistry 105:75–88
Smith RA, Alexander RB, Schwarz GE (2003) Natural background concentrations of nutrients in streams and rivers of the conterminous United States. Environ Sci Technol 37:2039–3047
Smith VH (2003) Eutrophication of freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems. A global problem. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:126–139
Smith VH, Schindler DW (2009) Eutrophication science: where do we go from here? Trends Ecol Evol 24:201–207
UNFPA (2007) State of world population 2007: unleashing the potential of urban growth United Nations Population Fund. http://www.unfpaorg/swp/2007/presskit/pdf/sowp2007_engpdf
Uriarte M, Yackulic CB, Lim Y, Arce-Nazario JA (2011) Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: a multi-scale analysis. Landsc Ecol 26:1151–116
Wenger SJ et al. (2009) Twenty-six key research questions in urban stream ecology: an assessment of the state of the science. J N Am Benthol Soc 28:1080–1098
Acknowledgements
First author was supported by the CAPES/FAPERJ scholarship process n. E-26/100.018/2015. We thank Marcelo de Souza of the ANA (Agencia Nacional de Aguas) for providing data on water quality for the State of Rio de Janeiro, Dr. Marcellus M. Caldas for helpful comments on the manuscript and two anonymous reviewers for the valuable comments that improved our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tromboni, F., Dodds, W. Relationships Between Land Use and Stream Nutrient Concentrations in a Highly Urbanized Tropical Region of Brazil: Thresholds and Riparian Zones. Environmental Management 60, 30–40 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-017-0858-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-017-0858-8