Abstract
Purpose
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) continues to be a significant complication after total joint arthroplasty. Diagnosis of PJI can be challenging and elusive in the absence of a gold standard. This purpose of this article is to review the current evidence on the utility of serum and synovial fluid biomarkers to help aid in the diagnosis of PJI with focusing on synovial fluid alpha-defensin.
Methods
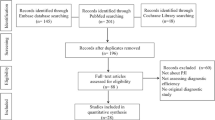
Articles and data for this review were identified by searches of PubMed and Ovid MEDLINE up to June 1, 2016. In addition, we manually reviewed the bibliographies of the retrieved articles for additional citations for references from relevant articles on the diagnosis of PJI.
Results
Serum biomarkers can be elevated in various inflammatory conditions. Synovial fluid biomarkers are more accurate for the diagnosis of PJI compared to serum biomarkers. Based on current available data, alpha-defensin is the most promising synovial fluid biomarker for the diagnosis of PJI and is commercially available.
Conclusions
Synovial fluid alpha-defensin could enhance our ability to identify PJI and incorporate into the diagnostic algorithm in the future. Large-scale studies are needed to provide more data for its significance for the diagnosis of PJI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Day JS, Lau E, Ong KL, Williams GR, Ramsey ML, Kurtz SM (2010) Prevalence and projections of total shoulder and elbow arthroplasty in the United States to 2015. J Shoulder Elb Surg / Am Shoulder Elb Surg 19:1115–1120. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2010.02.009
Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M (2007) Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:780–785. doi:10.2106/jbjs.f.00222
NIH (1995) NIH consensus conference: total hip replacement. NIH consensus development panel on total hip replacement. JAMA 273:1950–1956
Sperling JW, Kozak TK, Hanssen AD, Cofield RH (2001) Infection after shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 206–216
Widmer AF (2001) New developments in diagnosis and treatment of infection in orthopaedic implants. Clin Infect Dis Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am 33(Suppl 2):S94–106. doi:10.1086/321863
Spangehl MJ, Masri BA, O’Connell JX, Duncan CP (1999) Prospective analysis of preoperative and intraoperative investigations for the diagnosis of infection at the sites of two hundred and two revision total hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81:672–683
Matsen Ko L, Parvizi J (2016) Diagnosis of periprosthetic infection: novel developments. Orthop Clin North Am 47:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.ocl.2015.08.003
McArthur BA, Abdel MP, Taunton MJ, Osmon DR, Hanssen AD (2015) Seronegative infections in hip and knee arthroplasty: periprosthetic infections with normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level. Bone Joint J 97-b:939–944. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.97b7.35500
Shahi A, Deirmengian C, Higuera C, Chen A, Restrepo C, Zmistowski B, Parvizi J (2015) Premature therapeutic antimicrobial treatments can compromise the diagnosis of late periprosthetic joint infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473:2244–2249. doi:10.1007/s11999-015-4142-z
Arnold WV, Shirtliff ME, Stoodley P (2014) Bacterial biofilms and periprosthetic infections. Instr Course Lect 63:385–391
Parvizi J, Gehrke T, Chen AF (2013) Proceedings of the international consensus on periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Joint J 95-b:1450–1452. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.95b11.33135
Workgroup Convened by the Musculoskeletal Infection Society (2011) New definition for periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplast 26:1136–1138. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2011.09.026
Parvizi J, Zmistowski B, Berbari EF, Bauer TW, Springer BD, Della Valle CJ, Garvin KL, Mont MA, Wongworawat MD, Zalavras CG (2011) New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:2992–2994. doi:10.1007/s11999-011-2102-9
Gollwitzer H, Dombrowski Y, Prodinger PM, Peric M, Summer B, Hapfelmeier A, Saldamli B, Pankow F, von Eisenhart-Rothe R, Imhoff AB, Schauber J, Thomas P, Burgkart R, Banke IJ (2013) Antimicrobial peptides and proinflammatory cytokines in periprosthetic joint infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95:644–651. doi:10.2106/jbjs.l.00205
Bottner F, Wegner A, Winkelmann W, Becker K, Erren M, Gotze C (2007) Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and TNF-alpha: markers of peri-prosthetic infection following total joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:94–99. doi:10.1302/0301-620x.89b1.17485
Glehr M, Friesenbichler J, Hofmann G, Bernhardt GA, Zacherl M, Avian A, Windhager R, Leithner A (2013) Novel biomarkers to detect infection in revision hip and knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:2621–2628. doi:10.1007/s11999-013-2998-3
Hugle T, Schuetz P, Mueller B, Laifer G, Tyndall A, Regenass S, Daikeler T (2008) Serum procalcitonin for discrimination between septic and non-septic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26:453–456
Shah K, Mohammed A, Patil S, McFadyen A, Meek RM (2009) Circulating cytokines after hip and knee arthroplasty: a preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:946–951. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0562-3
Wirtz DC, Heller KD, Miltner O, Zilkens KW, Wolff JM (2000) Interleukin-6: a potential inflammatory marker after total joint replacement. Int Orthop 24:194–196
Deirmengian C, Hallab N, Tarabishy A, Della Valle C, Jacobs JJ, Lonner J, Booth RE Jr (2010) Synovial fluid biomarkers for periprosthetic infection. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:2017–2023. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1298-4
Frangiamore SJ, Siqueira MB, Saleh A, Daly T, Higuera CA, Barsoum WK (2016) Synovial cytokines AND the MSIS criteria are not useful for determining infection resolution after periprosthetic joint infection explantation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 474(7):1630–1639. doi:10.1007/s11999-016-4710-x
Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, Cameron A, Schiller K, Parvizi J (2014) Diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection: has the era of the biomarker arrived? Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:3254–3262. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3543-8
Greenwald GI, Ganz T (1987) Defensins mediate the microbicidal activity of human neutrophil granule extract against Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Infect Immun 55:1365–1368
Hazlett L, Wu M (2011) Defensins in innate immunity. Cell Tissue Res 343:175–188. doi:10.1007/s00441-010-1022-4
Lehrer RI, Ganz T (1992) Defensins: endogenous antibiotic peptides from human leukocytes. Ciba Found Symp 171:276–290, discussion 290–273
Agerberth B, Charo J, Werr J, Olsson B, Idali F, Lindbom L, Kiessling R, Jornvall H, Wigzell H, Gudmundsson GH (2000) The human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides LL-37 and alpha-defensins are expressed by specific lymphocyte and monocyte populations. Blood 96:3086–3093
Chalifour A, Jeannin P, Gauchat JF, Blaecke A, Malissard M, N’Guyen T, Thieblemont N, Delneste Y (2004) Direct bacterial protein PAMP recognition by human NK cells involves TLRs and triggers alpha-defensin production. Blood 104:1778–1783. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-08-2820
Ericksen B, Wu Z, Lu W, Lehrer RI (2005) Antibacterial activity and specificity of the six human {alpha}-defensins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:269–275. doi:10.1128/aac.49.1.269-275.2005
Verma C, Seebah S, Low SM, Zhou L, Liu SP, Li J, Beuerman RW (2007) Defensins: antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic development. Biotechnol J 2:1353–1359. doi:10.1002/biot.200700148
Rodriguez-Garcia M, Oliva H, Climent N, Garcia F, Gatell JM, Gallart T (2007) Human immature monocyte-derived dendritic cells produce and secrete alpha-defensins 1–3. J Leukoc Biol 82:1143–1146. doi:10.1189/jlb.0507295
Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, Gulati S, Citrano P, Booth RE Jr (2015) The Alpha-defensin test for periprosthetic joint infection responds to a wide spectrum of organisms. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473:2229–2235. doi:10.1007/s11999-015-4152-x
Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, Cameron A, Schiller K, Parvizi J (2014) Combined measurement of synovial fluid alpha-Defensin and C-reactive protein levels: highly accurate for diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96:1439–1445. doi:10.2106/jbjs.m.01316
Bingham J, Clarke H, Spangehl M, Schwartz A, Beauchamp C, Goldberg B (2014) The alpha defensin-1 biomarker assay can be used to evaluate the potentially infected total joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:4006–4009. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3900-7
Frangiamore SJ, Gajewski ND, Saleh A, Farias-Kovac M, Barsoum WK, Higuera CA (2016) Alpha-defensin accuracy to diagnose periprosthetic joint infection-best available test? J Arthroplasty 31:456–460. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2015.09.035
Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, Cameron A, Schiller K, Booth RE Jr, Parvizi J (2015) The alpha-defensin test for periprosthetic joint infection outperforms the leukocyte esterase test strip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 473:198–203. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3722-7
Frangiamore SJ, Saleh A, Grosso MJ, Kovac MF, Higuera CA, Iannotti JP, Ricchetti ET (2015) Alpha-defensin as a predictor of periprosthetic shoulder infection. J Shoulder Elb Surge / Am Shoulder Elb Surg 24:1021–1027. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2014.12.021
Frangiamore SJ, Saleh A, Kovac MF, Grosso MJ, Zhang X, Bauer TW, Daly TM, Ricchetti ET, Iannotti JP (2015) Synovial fluid interleukin-6 as a predictor of periprosthetic shoulder infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97:63–70. doi:10.2106/jbjs.n.00104
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance from librarians of Mercy Hospital, Springfield, Missouri, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for this paper as it is a review and not original research involving humans or animals.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial, institutional, or other relevant relationships that would constitute a potential competing interest with this review.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pupaibool, J., Fulnecky, E.J., Swords, R.L. et al. Alpha-defensin—novel synovial fluid biomarker for the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 40, 2447–2452 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3306-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3306-0