Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to compare clinical and quality of life outcomes following arthroscopic acetabular labral debridement between patients with different centre-edge (CE) angle.
Methods
A total of 79 patients who underwent hip labral debridement were enrolled in this study. Radiographic measurements of CE angle were collected, and patients were assigned into a normal group (25° < CE angle <40°, n = 68) and dysplasia group (CE angle <20°, n = 11). Clinical outcomes were evaluated by modified Harris Hip Score (mHHS), Hip Outcome Score (HOS) for activities of daily living (ADL) and sports and Short Form 12 (SF-12).
Results
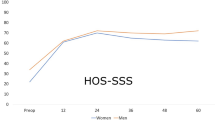
At the final follow-up, the normal group showed significant improvements in mHHS, HOS (ADL and sports) and SF-12 (P < 0.05). However, the dysplasia group revealed significant improvements in mHHS, HOS (ADL) and SF-12 physical component summary (PCS) (P < 0.05) and no significant changes in HOS sports and SF-12 mental component summary (MCS) (P > 0.05). Additionally, there was a greater improvement in clinical scores post-operatively in the normal group compared with the dysplasia group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Arthroscopic acetabular labral debridement resulted in significantly greater clinical and quality of life outcomes in patients with CE angle >25° compared with patients with CE angle < 20°.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben Tov T, Amar E, Shapira A, Steinberg E, Atoun E, Rath E (2014) Clinical and functional outcome after acetabular labral repair in patients aged older than 50 years. Arthroscopy 30(3):305–310
Groh MM, Herrera J (2009) A comprehensive review of hip labral tears. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2(2):105–117
Dezateux C, Rosendahl K (2007) Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Lancet 369:1541–1552
Harris-Hayes M, Royer NK (2011) Relationship of acetabular dysplasia and femoroacetabular impingement to hip osteoarthritis: a focused review. PM R 3:1055–1067
Lee HH, Klika AK, Bershadsky B, Krebs VE, Barsoum WK (2010) Factors affecting recovery after arthroscopic labral debridement of the hip. Arthroscopy 26(3):328–334
Haviv B, O’Donnell J (2011) Arthroscopic treatment for acetabular labral tears of the hip without bony dysmorphism. Am J Sports Med 39(Suppl 1):79S–84S
Mancini D, Fontana A (2014) Five-year results of arthroscopic techniques for the treatment of acetabular chondral lesions in femoroacetabular impingement. Int Orthop 38:2057–2064
Beutel BG, Collins JA, Garofolo G, Youm T (2015) Hip arthroscopy outcomes, complications, and traction safety in patients with prior lower-extremity arthroplasty. Int Orthop 39:13–18
Griffiths EJ, Khanduja V (2012) Hip arthroscopy: evolution, current practice and future developments. Int Orthop 36:1115–1121
Beaulé PE, O’Neill M, Rakhra K (2009) Acetabular labral tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:701–710
Tönnis D, Heinecke A (1999) Acetabular and femoral anteversion: relationship with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81:1747–1770
Tönnis D (1976) Normal values of the hip joint for the evaluation of x-rays in children and adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res 119:39–47
Wiberg G (1939) Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint with special reference to the complication of osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Scand 83(Suppl 58):28–38
Nötzli HP, Wyss TF, Stoecklin CH, Schmid MR, Treiber K, Hodler J (2002) The contour of the femoral head-neck junction as a predictor for the risk of anterior impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:556–560
Domb B, Hanypsiak B, Botser I (2012) Labral penetration rate in a consecutive series of 300 hip arthroscopies. Am J Sports Med 40(4):864–869
Philippon MJ, Schroder e Souza BG, Briggs KK (2010) Labrum: resection, repair and reconstruction. Sports Med Arthrosc 18:76–82
Krych AJ, Thompson M, Knutson Z, Scoon J, Coleman SH (2013) Arthroscopic labral repair versus selective labral debridement in female patients with femoroacetabular impingement: a prospective randomized study. Arthroscopy 29(1):46–53
Weiland DE, Philippon MJ (2005) Arthroscopic technique of femoroacetabular impingement. Oper Tech Orthop 15:256–260
Harris WH, Bourne RB, Oh I (1979) Intra-articular acetabular labrum: a possible etiological factor in certain cases of osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:510–514
Liang MH, Katz JN, Phillips C, Sledge C, Cats-Baril W (1991) The total hip arthroplasty outcome evaluation form of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Results of a nominal group process. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Task Force on Outcome Studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:639–646
Parvizi J, Bican O, Bender B, Mortazavi SM, Purtill JJ, Erickson J, Peters C (2009) Arthroscopy for labral tears in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a cautionary note. J Arthroplasty 24:110–113
Yamamoto Y, Ide T, Nakamura M, Hamada Y, Usui I (2005) Arthroscopic partial limbectomy in hip joints with acetabular hypoplasia. Arthroscopy 21:586–591
Byrd JWT, Jones KS (2000) Prospective analysis of hip arthroscopy with 2-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 16:578–587
Byrd JWT, Jones KS (2003) Hip arthroscopy in the presence of dysplasia. Arthroscopy 19(10):1055–1060
Matheney T, Kim YJ, Zurakowski D, Matero C, Millis M (2009) Intermediate to long-term results following the Bernese periacetabular osteotomy and predictors of clinical outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:2113–2123
Fujii M, Nakashima Y, Jingushi S, Yamamoto T, Noguchi Y, Suenaga E, Iwamoto Y (2009) Intraarticular findings in symptomatic developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 29(1):9–13
Ross JR, Zaltz I, Nepple JJ, Schoenecker PL, Clohisy JC (2011) Arthroscopic disease classification and interventions as an adjunct in the treatment of acetabular dysplasia. Am J Sports Med 39(Suppl):72S–78S
Henak CR, Abraham CL, Anderson AE, Maas SA, Ellis BJ, Peters CL, Weiss JA (2014) Patient-specific analysis of cartilage and labrum mechanics in human hips with acetabular dysplasia. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 22(2):210–217
Henak CR, Ellis BJ, Harris MD, Anderson AE, Peters CL, Weiss JA (2011) Role of the acetabular labrum in load support across the hip joint. J Biomech 44(12):2201–2206
Chegini S, Beck M, Ferguson SJ (2009) The effects of impingement and dysplasia on stress distributions in the hip joint during sitting and walking: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res 27:195–201
Crawford MJ, Dy CJ, Alexander JW, Thompson M, Schroder SJ, Vega CE, Patel RV, Miller AR, McCarthy JC, Lowe WR, Noble PC (2007) The biomechanics of the hip labrum and the stability of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 465:16–22
Akiyama K, Sakai T, Koyanagi J, Yoshikawa H, Sugamoto K (2011) Evaluation of translation in the normal and dysplastic hip using three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging and voxel-based registration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 19:700–710
Carreira DS, Mazzocca AD, Oryhon J, Brown FM, Hayden JK, Romeo AA (2006) A prospective outcome evaluation of arthroscopic Bankart repairs: minimum 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 34(5):771–777
Boykin RE, Patterson D, Briggs KK, Dee A, Philippon MJ (2013) Results of arthroscopic labral reconstruction of the hip in elite athletes. Am J Sports Med 41(10):2296–2301
Kutty S, Schneider P, Faris P, Kiefer G, Frizzell B, Park R, Powell JN (2012) Reliability and predictability of the centre-edge angle in the assessment of pincer femoroacetabular impingement. Int Orthop 36:505–510
Okano K, Yamaguchi K, Ninomiya Y, Matsubayashi S, Osaki M, Takahashi K (2013) Femoral head deformity and severity of acetabular dysplasia of the hip. Bone Joint J 95-B(9):1192–1196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Chen, S., Li, Y. et al. Effect of centre-edge angle on clinical and quality of life outcomes after arthroscopic acetabular labral debridement. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 40, 1427–1432 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2923-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2923-3