Abstract
Purpose
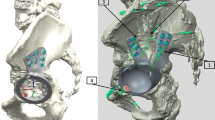
Modular acetabular reconstructive cups have been introduced in an attempt to offer initial rigid fixation by iliac lag screws and ischial pegs, to support bone grafts with a flanged metal socket, and to restore original hip center in acetabular revision. The purpose of this study was to clarify minimum ten year follow-up results of this cup system with morsellised allografts in revision cases.
Methods
We retrospectively investigated 54 acetabular revisions at a mean of 11 years (range, ten to 14 years). The indications were Paprosky’s type 2B (eight hip), 2C (eight hips), 3A (23 hips), 3B (nine hips), and 4 (six hips).
Results
Using aseptic loosening as the endpoints, the survival rate was 89.3 % (95 % CI 81–98). Radiographically, one type 3A hip, three type 3B hips and one type 4 hip showed aseptic loosening while no type 2 hips or no cemented cups showed loosening.
Conclusions
The modular reconstructive cups for acetabular revision showed bone stock restoration and stable implantation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comba F, Buttaro M, Pusso R, Piccaluga F (2006) Acetabular reconstruction with impacted bone allografts and cemented acetabular components. A 2- to 13-year follow-up study of 142 aseptic revisions. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:865–869
Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Cruz-Pardos A, Garcia-Rey E, Ortega-Chamarro J (2010) The survival and fate of acetabular reconstruction with impaction grafting for large defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:3304–3313
Jeffery M, Scott G, Freeman M (2003) Failure of an uncemented non-porous metal-backed prosthesis with augmentation using impacted allograft for acetabular revision. 12- to 17-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:182–186
Kawanabe K, Akiyama H, Onishi E, Nakamura T (2007) Revision total hip replacement using the Kerboull acetabular reinforcement device with morsellised or bulk graft. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:26–31
Okano K, Miyata N, Enomoto H, Osaki M, Shindo H (2010) Revision with impacted bone allografts and the Kerboull cross plate for massive bone defect of the acetabulum. J Arthroplasty 25:594–599
Oonishi H, Iwaki Y, Kin N, Kushitani S, Murata N, Wakitani S, Imoto K (1997) Hydroxyapatite in revision of total hip replacements with massive acetabular defects. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:87–92
Sakai T, Ohzono K, Nishii T, Miki H, Takao M, Sugano N (2010) Grafting with hydroxyapatite grannules for defects of acetabular bone at revision total hip replacement. A minimum ten-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92:1215–1221
Schreurs BW, Keurentjes JC, Gardeniers JWM, Verdonschot N, Slooff TJJH, Veth RPH (2009) Acetabular revision with impacted morsellised cancellous bone grafting and a cemented acetabular component. A 20-to 25-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:1148–1153
Sporer SM, O’Rourke M, Chong P, Paprosky WG (2005) The use of structural distal femoral allografts for acetabular reconstruction. Average 10-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:760–765
Sudo A, Hasegawa M, Fukuda A, Kawamura G, Muraki M, Uchida A (2007) Acetabular reconstruction using a cementless cup and hydroxyapatite granules. J Arthroplasty 22:828–832
Tanaka C, Shikata J, Ikenaga M, Takahashi M (2003) Acetabular reconstruction using a Kerboull-type acetabular reinforcement device and hydroxyapatite granules. A 3- to 8- year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 18:719–725
van Haaren EH, Heyligers IC, Alexander FGM, Wuisman PIJM (2007) High rate of failure of impaction grafting in large acetabular defects. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:296–300
Wang JW, Fong CY, Su YS, Yu HN (2006) Acetabular revision with morsellised allogenic bone graft and a cemented metal-backed component. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:586–591
Sadoghi P, Schröder C, Fottner A, Steinbrück A, Betz O, Müller PE, Jansson V, Hölzer A (2012) Application and survival curve of total hip arthroplasties: a systematic comparative analysis using worldwide hip arthroplasty registers. Int Orthop 36:2197–2203
Paprosky WG, Perona PG, Lawrence JM (1994) Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty: a six year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty 9:33–44
Babis GC, Sakellariou VI, Chatziantoniou AN, Soucacos PN, Megas P (2011) High complication rate in reconstruction of Paprosky type IIIa acetabular defects using an oblong implant with modular side plates and a hook. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:1592–1596
Friesenbichler J, Schwarzkopf R, Sadoghi P, Marwin SE, Glehr M, Maurer-Ertl W, Leithner A (2012) Failure rate of a rotating hinge knee design due to yoke fracture of the hinged tibial insert: a retrospective data analysis and review of the literature. Int Orthop 36:993–998
Lingaraj K, Teo YH, Bergman N (2009) The management of severe acetabular bone defects in revision hip arthroplasty using modular porous metal components. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:1555–1560
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty: an end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:737–755
Asayama I, Chamnongkich S, Simpson KJ, Kinsey TL, Mahoney OM (2005) Reconstructed hip joints position and abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:414–420
Nunn D, Freeman MAR, Hill PF, Evans SJW (1989) The measurement of migration of the acetabular component of hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br 71:629–631
Ochs BG, Schmid U, Rieth J, Ateschrang A, Weise K, Ochs U (2008) Acetabular bone reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A comparison of freeze-dried, irradiated and chemically-treated allograft vitalized with autologous marrow versus frozen non-irradiated allograft. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:1164–1171
DeLee JG, Charnley J (1976) Radiographic demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 121:20–32
Hoenig JM, Heisey DM (2001) The abuse of power: the pervasive fallacy of power calculations for data analysis. Am Stat 55:19–24
Takao M, Nakamura N, Ohzono K, Sakai T, Nishii T, Sugano N (2011) The results of a press-fit-only technique for acetabular fixation in hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty 26:562–568
van der Donk S, Buma P, Slooff TJJH, Gardeniers JWM, Schreurs BW (2002) Incorporation of morsellised bone grafts: a study of 24 acetabular biopsy specimens. Clin Orthop Relat Res 396:131–141
Winter E, Piert M, Volkmann R, Maurer F, Eingartner C, Weise K, Weller S (2001) Allogeneic cancellous bone graft and a Burch-Schneider ring for acetabular reconstruction in revision hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:862–867
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof Hideki Yoshikawa for technical support.
Conflict of interest
No competing interests declared. Each author certifies that he or she, or a member of their immediate family, has no commercial associations that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, T., Ohzono, K., Nishii, T. et al. Modular acetabular reconstructive cup in acetabular revision total hip arthroplasty at a minimum ten year follow-up. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 37, 605–610 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-1818-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-1818-4