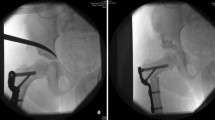
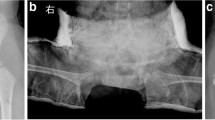
Abstract
Purpose
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is an effective procedure for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH); however, it is sometimes difficult to complete for severe cases because of femoral head dislocation, dysplasia of the acetabulum and the femur, disparity in limb length, soft tissue contraction, and muscular atrophy. We aimed at exploring the efficiency of the techniques of release and balance of soft tissues and reconstruction of true socket THA for patients with severe DDH.
Methods
From January 2000 to January 2009, 46 adult patients with severe DDH (50 hips) were included in this study. According to the classification system, there were 26 type III and 24 type IV. Among them there were 32 women and 14 men, aged from 38 to 77 years. THA was performed via a lateral approach. All acetabular sockets were reconstructed at the original anatomical location following a meticulous technique of soft tissue release and balance around the hip to restore limb length, to strengthen the abductor and improve its function.
Results
All patients had restoration of limb length (range, 2.5–5.5 cm; 30 limbs of more than 4 cm) without injury to the sciatic nerve. One postoperative dislocation occurred due to slight enlargement of the angle of abduction of the acetabulum. The follow-up ranged from 2.2 to 11.5 years (median 6.4 years) in 46 patients, and the Harris score increased from 40.2 preoperatively to 86.5 (P = 0.027). All hips were pain free with good function at the latest follow-up.
Conclusion
The meticulous techniques of soft tissue release and balance can be recommended to ensure anatomical reconstruction of the true acetabular socket and to improve abductor function during arthroplasty for DDH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novacheck TF (1996) Developmental dysplasia of hip. Pediatr Clin N Am 3:829–848
Delimar D, Cicak N, Klobucar H, Pećina M, Korzinek K (2002) Acetabular roof reconstruction with pedicled iliac graft. Int Orthop 26:344–348
Delimar D, Bićanić G, Pećina M, Korzinek K (2004) Acetabular roof reconstruction with pedicled iliac graft: early clinical experience. Int Orthop 28(5):319–320
Hendrich C, Engelmaier F, Mehling I, Sauer U, Kirschner S, Martell JM (2007) Cementless acetabular reconstruction and structural bone-grafting in dysplastic hips. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:54–67
Koulouvaris P, Stafylas K, Xenakis T (2008) Cementless modular centroid reconstruction cup in young adults with congenital dysplasia of the hip. J Arthroplasty 23:79–85
Liu Q, Zhou YX, Xu HJ, Tang J, Guo SJ, Tang QH (2009) Safe zone for transacetabular screw fixation in prosthetic acetabular reconstruction of high developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:2880–2885
Shen B, Yang J, Wang L, Zhou ZK, Kang PD, Pei FX (2009) Midterm results of hybrid total hip arthroplasty for treatment of osteoarthritis secondary to developmental dysplasia of the hip-Chinese experience. J Arthroplasty 24:1157–1163
Krych AJ, Howard JL, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME, Berry DJ (2009) Total hip arthroplasty with shortening subtrochanteric osteotomy in Crowe type-IV developmental dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:2213–2221
Nagoya S, Kaya M, Sasaki M, Tateda K, Kosukegawa I, Yamashita T (2009) Cementless total hip replacement with subtrochanteric femoral shortening for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:1142–1147
Reikerås O, Haaland JE, Lereim P (2010) Femoral shortening in total hip arthroplasty for high developmental dysplasia of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:1949–1955
Howie CR, Ohly NE, Miller B (2010) Cemented total hip arthroplasty with subtrochanteric osteotomy in dysplastic hips. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:3240–3247
Bicanic G, Delimar D, Delimar M, Pecina M (2009) Influence of the acetabular cup position on hip load during arthroplasty in hip dysplasia. Int Orthop 33:397–402
Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS (1979) Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:15–23
Fukui K, Kaneuji A, Sugimori T, Ichiseki T, Matsumoto T (2011) A radiological study of the true anatomical position of the acetabulum in Japanese women. Hip Int 21:311–316
Farrell CM, Springer BD, Haidukewych GJ, Morrey BF (2005) Motor nerve palsy following primary total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:2619–2625
Eggli S, Hankemayer S, Müller ME (1999) Nerve palsy after leg lengthening in total replacement arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81:843–845
Ito H, Tanino H, Yamanaka Y, Nakamura T, Matsuno T (2011) Hybrid total hip arthroplasty using specifically-designed stems for patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip. A minimum five-year follow-up study. Int Orthop 35:1289–1294
Holzapfel BM, Greimel F, Prodinger PM, Pilge H, Nöth U, Gollwitzer H, Rudert M (2012) Total hip replacement in developmental dysplasia using an oval-shaped cementless press-fit cup. Int Orthop 36(7):1355–1361
Bolder SB, Melenhorst J, Gardeniers JW (2001) Cemented total hip arthroplasty with impacted morcellized bone-grafts to restore acetabular bone defects in congenital hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty 16:164–169
Linde F, Jensen J (1998) Socket loosening in arthroplasty for congenital dislocation of the hip. Acta Orthop Scand 59:254–257
Harley JM, Wilkinson JA (1987) Hip replacement for adults with unreduced congenital dislocation. A new surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br 69:752–755
Reikeraas O, Lereim P, Gabor I (1996) Femoral shortening in total arthroplasty for completely dislocated hips: 3–7 year results in 25 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 67:33–36
Neumann D, Thaler C, Dorn U (2012) Femoral shortening and cementless arthroplasty in Crowe type 4 congenital dislocation of the hip. Int Orthop 36(3):499–503
Delimar D, Bicanic G, Korzinek K (2008) Femoral shortening during hip arthroplasty through a modified lateral approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(8):1954–1958
Kerboull M, Hamadouche M, Kerboull L (2001) Total hip arthroplasty for the treatment of ankylosed hips: a five to twenty-one-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 16(8 Supp1):170–176
Sener N, Tözün IR, Aşik M (2002) Femoral shortening and cementless arthroplasty in high congenital dislocation of the hip. J Arthroplasty 17:41–48
Zhang H, Zhou YX, Huang Y (2005) Acetabular medial wall displacement osteotomy in total hip arthroplasty: a technique to optimize the acetabular reconstruction in acetabular dysplasia (in Chinese). Zhonghua Gu Ke Za Zhi 25:223–226
Paavilainen T, Hoikka V, Solonen KA (1990) Cementless total replacement for severely dysplastic or dislocated hips. J Bone Joint Surg Br 72:205–211
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest in our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Li, Sh., Lou, Lm. et al. The techniques of soft tissue release and true socket reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 1795–1801 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1622-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1622-6