Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the position of the peroneus longus (PL) tendon relative to the cuboid tuberosity and cuboid tunnel during ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion using ultrasound and MRI.
Materials and methods
The study population included two groups: 20 feet of 10 asymptomatic volunteers who underwent prospective dynamic ultrasound and 55 ankles found through retrospective review of routine ankle MRI examinations. The location of the PL tendon at the cuboid tuberosity and cuboid tunnel was designated as completely within the tunnel, indeterminate, or subluxed with respect to ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion.
Results
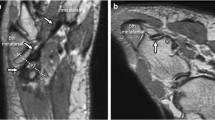
On dynamic ultrasound, the PL tendon was perched plantar to the cuboid tuberosity in dorsiflexion, and glided to enter the cuboid tunnel distal to the tuberosity in plantarflexion in all 20 feet. On the MRI evaluation, there was a statistically significant difference (p = 0.0006) in the location of the PL tendon between the ankles scanned in dorsiflexion and plantarflexion.
Conclusion
Based on our findings on ultrasound and MRI, the PL tendon can glide in and out of the cuboid tunnel along the cuboid tuberosity depending on ankle position. Thus, “subluxation” of the tendon as it curves to enter the cuboid tunnel, which to the best of our knowledge has not yet been described, should be recognized as a normal, position-dependent phenomenon and not be reported as pathology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patil V, Frisch NC, Ebraheim NA. Anatomical variations in the insertion of the peroneus (fibularis) longus tendon. Foot Ankle Int. 2007;28(11):1179–82.
Donovan A, Rosenberg ZS, Bencardino JT, Velez ZR, Blonder DB, Ciavarra GA, et al. Plantar tendons of the foot: MR imaging and US. Radiograph Rev Pub Radiol Soc North Am Inc. 2013;33(7):2065–85.
Fernandes R, Aguiar R, Trudell D, Resnick D. Tendons in the plantar aspect of the foot: MR imaging and anatomic correlation in cadavers. Skeletal Radiol. 2007;36(2):115–22.
Kelikian AS, Sarrafian SK, Sarrafian SK. Sarrafian’s anatomy of the foot and ankle: descriptive, topographical, functional. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott; 2011.
Sarrafian SK. Anatomy of the foot and ankle: descriptive, topographical, functional. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1993.
Gray H, Williams PL, Gray H. Gray’s anatomy. 37th ed. Edinburgh: Livingstone; 1989.
Clarke HD, Kitaoka HB, Ehman RL. Peroneal tendon injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19(5):280–8.
Scanlan RL, Gehl RS. Peroneal tendon injuries. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2002;19(3):419–31.
Brandes CB, Smith RW. Characterization of patients with primary peroneus longus tendinopathy: a review of twenty-two cases. Foot Ankle Int. 2000;21(6):462–8.
Sammarco GJ. Peroneus longus tendon tears: acute and chronic. Foot Ankle Int. 1995;16(5):245–53.
El Rassi G, Kouvalchouk JF, McFarland E. Isolated dislocation of the peroneus longus tendon over the calcaneal tubercle in an ice skater: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am Vol. 2012;94(7):e43.
Klos K, Vag T, Gras F, Konig V, Hofmann GO, Muckley T. Distal peroneal tendon dislocation: a case report. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(3):314–8.
Agur AMR, Grant JCB. Grant’s atlas of anatomy, 13th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott; 2013.
Lee KS, Ablove RH, Singh S, De Smet AA, Haaland B, Fine JP. Ultrasound imaging of normal displacement of the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon within the ulnar groove in 12 forearm-wrist positions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(3):651–5.
Jeantroux J, Becce F, Guerini H, Montalvan B, Le Viet D, Drapé J. Athletic injuries of the extensor carpi ulnaris subsheath: MRI findings and utility of gadolinium-enhanced fat-saturated T1-weighted sequences with wrist pronation and supination. Eur J Radiol. 2011;21:160–6.
Beitzel K, Kirchhoff C, Beitzel KI, Reiser MF, Kirchhoff S. In vivo evaluation of the kinematics of the long head of the biceps tendon within the pulley: a 3 T MRI motion analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(12):1719–25.
Nidecker A, Gückel C, von Hochstetter A. Imaging the long head of biceps tendon: a pictorial essay emphasizing magnetic resonance. Eur J Radiol. 1997;25(3):177–87.
Monteggia GB. Instituzini chirurgiche. Parte secondu. Milan, Italy; 1803; 336–41.
Safran MR, O’Malley Jr D, Fu FH. Peroneal tendon subluxation in athletes: new exam technique, case reports, and review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31(7 Suppl):S487–92.
Omey ML, Micheli LJ. Foot and ankle problems in the young athlete. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31(7 Suppl):S470–86.
Wang XT, Rosenberg ZS, Mechlin MB, Schweitzer ME. Normal variants and diseases of the peroneal tendons and superior peroneal retinaculum: MR imaging features. Radiograph Rev Pub Radiol Soc North Am Inc. 2005;25(3):587–602.
Raikin SM, Elias I, Nazarian LN. Intrasheath subluxation of the peroneal tendons. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(5):992–9.
Roaas A, Andersson GB. Normal range of motion of the hip, knee and ankle joints in male subjects, 30–40 years of age. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982;53:205–8.
Ahlberg A, Moussa M, Al Nahdi M. On geographical variations in the normal range of joint motion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;234:229–31.
Lundberg A, Goldie I, Kalin B, Selvik G. Kinematics of the ankle/foot complex, part 1: plantarflexion and dorsiflexion. Foot Ankle. 1989;9:194–200.
Valderrabano V, Hintermann B, Nigg BM, Stefanyshyn D, Stergiou P. Kinematic changes after fusion and total replacement of the ankle, part 1: range of motion. Foot Ankle Int. 2003;24:881–7.
Stauffer RN, Chao EY, Brewster RC. Force and motion analysis of the normal, diseased, and prosthetic ankle joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;127:189–96.
Lindsjo U, Danckwardt-Lilliestrom G, Sahlstedt B. Measurement of the motion range in the loaded ankle. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;199:68–71.
Boone DC, Azen SP. Normal range of motion of joints in male subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:756–9.
The authors have no financial disclosures to report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Source of funding
None
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stone, T.J., Rosenberg, Z.S., Velez, Z.R. et al. Subluxation of the peroneus long tendon in the cuboid tunnel: is it normal or pathologic? An ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging study. Skeletal Radiol 45, 357–365 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2293-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2293-3