Abstract
Objective
High-resolution real-time three-dimensional (3D) imaging of the moving wrist may provide novel insights into the pathophysiology of joint instability. The purpose of this work was to assess the feasibility of using retrospectively gated spiral computed tomography (CT) to perform four-dimensional (4D) imaging of the moving wrist joint.
Materials and methods
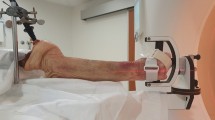
A cadaver forearm from below the elbow was mounted on a motion simulator which performed radioulnar deviation of the wrist at 30 cycles per minute. An electronic trigger from the simulator provided the “electrocardiogram” (ECG) signal required for gated reconstructions. Four-dimensional and 3D images were compared by a blinded observer for image quality and presence of artifacts.
Results
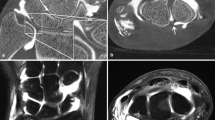
Image quality of 4D images was found to be excellent at the extremes of radial and ulnar deviation (end-motion phases). Some artifacts were seen in mid-motion phases.
Conclusion
4D CT musculoskeletal imaging is feasible. Four-dimensional CT may allow clinicians to assess functional (dynamic) instabilities of the wrist joint.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach S, Ropers D, Kuettner A, et al. Contrast-enhanced coronary artery visualization by dual-source computed tomography—initial experience. Eur J Radiol 2006; 57: 331–335.
Kopp AF, Ohnesorge B, Flohr T, et al. [Cardiac multidetector-row CT: first clinical results of retrospectively ECG-gated spiral with optimized temporal and spatial resolution]. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen BildgebVerfahr 2000; 172: 429–435.
Nikolaou K, Flohr T, Knez A, et al. Advances in cardiac CT imaging: 64-slice scanner. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2004; 20: 535–540.
Dewey M, Laule M, Krug L, et al. Multisegment and halfscan reconstruction of 16-slice computed tomography for detection of coronary artery stenoses. Invest Radiol 2004; 39: 223–229.
Dewey M, Muller M, Teige F, et al. Multisegment and halfscan reconstruction of 16-slice computed tomography for assessment of regional and global left ventricular myocardial function. Invest Radiol 2006; 41: 400–409.
Dewey M, Rutsch W, Schnapauff D, Teige F Hamm B. Coronary artery stenosis quantification using multislice computed tomography. Invest Radiol 2007; 42: 78–84.
Keall PJ, Starkschall G, Shukla H, et al. Acquiring 4D thoracic CT scans using a multislice helical method. Phys Med Biol 2004; 49: 2053–2067.
Nehmeh SA, Erdi YE, Pan T, et al. Four-dimensional (4D) PET/CT imaging of the thorax. Med Phys 2004; 31: 3179–3186.
Pan T, Lee TY, Rietzel E, Chen GT. 4D-CT imaging of a volume influenced by respiratory motion on multi-slice CT. Med Phys 2004; 31: 333–340.
Elgeti T, Proquitte H, Rogalla NE, et al. Evaluation of a reduced dose protocol for respiratory gated lung computed tomography in an animal model. Invest Radiol 2007; 42: 230–234.
Berdia S, Short WH, Werner FW, Green JK, Panjabi M. The hysteresis effect in carpal kinematics. J Hand Surg [Am] 2006; 31: 594 e1–594 e8.
Short WH, Werner FW, Fortino MD, Mann KA. Analysis of the kinematics of the scaphoid and lunate in the intact wrist joint. Hand Clin 1997; 13: 93–108.
Bachofen H, Hildebrandt J. Area analysis of pressure-volume hysteresis in mammalian lungs. J Appl Physiol 1971; 30: 493–497.
Watson H, Ottoni L, Pitts EC, Handal AG. Rotary subluxation of the scaphoid: a spectrum of instability. J Hand Surg [Br] 1993; 18: 62–64.
Werner FW, Short WH, Green JK. Changes in patterns of scaphoid and lunate motion during functional arcs of wrist motion induced by ligament division. J Hand Surg [Am] 2005; 30: 1156–1160.
Teoh LC, Yam AK. Anatomic reconstruction of the distal radioulnar ligaments: long-term results. J Hand Surg [Br] 2005; 30: 185–193.
Adams BD, Berger RA. An anatomic reconstruction of the distal radioulnar ligaments for posttraumatic distal radioulnar joint instability. J Hand Surg [Am] 2002; 27: 243–251.
Bickert B, Sauerbier M, Germann G. Scapholunate ligament repair using the Mitek bone anchor. J Hand Surg [Br] 2000; 25: 188–192.
Walsh JJ, Berger RA, Cooney WP. Current status of scapholunate interosseous ligament injuries. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2002; 10: 32–42.
Wolf JM, Weiss AP. Bone-retinaculum-bone reconstruction of scapholunate ligament injuries. Orthop Clin North Am 2001; 32: 241–246, viii.
Darlis NA, Weiser RW, Sotereanos DG. Partial scapholunate ligament injuries treated with arthroscopic debridement and thermal shrinkage. J Hand Surg [Am] 2005; 30: 908–914.
Watson HK, Weinzweig J, Zeppieri J. The natural progression of scaphoid instability. Hand Clin 1997; 13: 39–49.
Berger RA. The anatomy and basic biomechanics of the wrist joint. J Hand Ther 1996; 9: 84–93.
Camus EJ, Millot F, Lariviere J, Raoult S, Rtaimate M. Kinematics of the wrist using 2D and 3D analysis: biomechanical and clinical deductions. Surg Radiol Anat 2004; 26: 399–410.
Carelsen B, Bakker NH, Strackee SD, et al. 4D rotational X-ray imaging of wrist joint dynamic motion. Med Phys 2005; 32: 2771–2776.
Crisco JJ, Coburn JC, Moore DC, Akelman E, Weiss AP, Wolfe SW. In vivo radiocarpal kinematics and the dart thrower's motion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005; 87: 2729–2740.
Kobayashi M, Berger RA, Nagy L, et al. Normal kinematics of carpal bones: a three-dimensional analysis of carpal bone motion relative to the radius. J Biomech 1997; 30: 787–793.
Shim SS, Kim Y, Lim SM. Improvement of image quality with beta-blocker premedication on ECG-gated 16-MDCT coronary angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2005; 184: 649–654.
Tay S, Primak A, Fletcher J, Schmidt B, An KN, McCollough CH. Understanding the relationship of image quality to motion velocity in gated-CT imaging: preliminary work for 4D musculoskeletal imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2007 (in press).
Ohnesorge B, Flohr T, Becker C, et al. Cardiac imaging by means of electrocardiographically gated multisection spiral CT: initial experience. Radiology 2000; 217: 564–571.
Kyriakou Y, Kachelriebeta M, Knaup M, Krause JU, Kalender WA. Impact of the z-flying focal spot on resolution and artifact behavior for a 64-slice spiral CT scanner. Eur Radiol 2006; 16: 1206–1215.
Flohr T, Stierstorfer K, Raupach R, Ulzheimer S, Bruder H. Performance evaluation of a 64-slice CT system with z-flying focal spot. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen BildgebVerfahr 2004; 176: 1803–1810.
Taguchi K, Chiang BS, Hein IA. Direct cone-beam cardiac reconstruction algorithm with cardiac banding artifact correction. Med Phys 2006; 33: 521–539.
McCollough CH, Bruesewitz MR, Daly TR, Zink FE. Motion artifacts in subsecond conventional CT and electron-beam CT: pictorial demonstration of temporal resolution. Radiographics 2000; 20: 1675–1681.
Mori S, Endo M, Asakura H. Improvement in banding artefacts in four-dimensional computed tomography for radiotherapy planning. Phys Med Biol 2006; 51: 5231–5244.
Kaufmann R, Pfaeffle J, Blankenhorn B, Stabile K, Robertson D, Goitz R. Kinematics of the midcarpal and radiocarpal joints in radioulnar deviation: an in vitro study. J Hand Surg [Am] 2005; 30: 937–942.
Greuter MJ, Dorgelo J, Tukker WG, Oudkerk M. Study on motion artifacts in coronary arteries with an anthropomorphic moving heart phantom on an ECG-gated multidetector computed tomography unit. Eur Radiol 2005; 15: 995–1007.
Flohr TG, McCollough CH, Bruder H, et al. First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system. Eur Radiol 2006; 16: 256–68.
Taguchi K. Temporal resolution the evaluation of candidate algorithms for four-dimensional CT. Med Phys 2003; 30: 640–650.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Tay wishes to acknowledge financial support from Mayo Foundation, Rochester, MN, USA and National Medical Research Council, Singapore. The authors would like to thank Mr. Larry Berglund for the construction of the motion simulator and Ms Kristina Nunez for assistance with manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tay, SC., Primak, A.N., Fletcher, J.G. et al. Four-dimensional computed tomographic imaging in the wrist: proof of feasibility in a cadaveric model. Skeletal Radiol 36, 1163–1169 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-007-0374-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-007-0374-7