Abstract
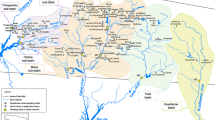
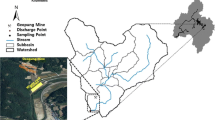
Work carried out at the abandoned copper (Cu) and sulphur (S) mine at Avoca (south east Ireland) has shown acid mine drainage (AMD) to be a multi-factor pollutant. It affects aquatic ecosystems by a number of direct and indirect pathways. Major impact areas are rivers, lakes, estuaries and coastal waters, although AMD affects different aquatic ecosystems in different ways. Due to its complexity, the impact of AMD is difficult to quantify and predict, especially in riverine systems. Pollutional effects of AMD are complex but can be categorized as (a) metal toxicity, (b) sedimentation processes, (c) acidity, and (d) salinization. Remediation of such impacts requires a systems management approach which is outlined. A number of working procedures which have been developed to characterise AMD sites, to produce surface water quality management plans, and to remediate mine sites and AMD are all discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 January 1996 · Accepted: 5 March 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gray, N. Environmental impact and remediation of acid mine drainage: a management problem. Environmental Geology 30, 62–71 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050133
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050133