Abstract
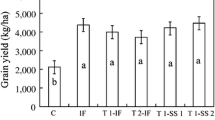
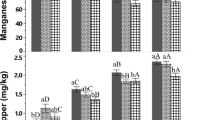
Variations in As, Ba, Bi, Cd, Co, Cu, Hg, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Se, Sn, Th, Tl, U, W, and Zn uptake were evaluated in young, middle-aged, and mature basil, tomato, zucchini, and sunflower plants grown in soils amended with 5, 10, and 20% by weight fly ash. Elements susceptible to uptake with increasing fly ash were As and Tl, with As exceeding potentially toxic levels in basil and zucchini. Temporal variations in element uptake included (1) increasing Ba and Cd concentrations in tomato and As, Ba, Cd, and Tl in zucchini, (2) decreasing Co concentrations in tomato, zucchini, and sunflower, Ni in zucchini, and Tl in basil, and (3) increasing As and Ni concentrations in basil and Pb in zucchini and sunflower during early growth followed by decreasing concentrations at maturity. Although most of the trace elements were below reported toxic levels, the elevated concentrations of As in plant tissue suggests that fly ash treatment programs can lead to potentially toxic accumulations of As, and thus, should be carefully monitored.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-El-Wafa MH, Awadallah RM, Rashed MN (1995) Major and trace elements in millet and soils of three different experimental farms. Pakistan J Sci Ind Res 38:414–419
Adriano DC (1986) Trace elements in the terrestrial environment. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Adriano DC, Page AL, Elseewi AA, Chang AC, Straughan I (1980) Utilization and disposal of fly ash and other coal residues in terrestrial ecosystems: a review. J Environ Qual 9:333–344
Adriano DC, Page AL, Elseewi AA, Chang AC (1982) Cadmium availability to sudangrass grown on soils amended with sewage sludge and fly ash. J Environ Qual 11:197–203
Brooks RR (1972) Geobotany and biogeochemistry in mineral exploration. Harper & Row, New York
Bunzl K, Trautmannsheimer M, Schramel P, Reifenhäuser W (2001) Availability of arsenic, copper, lead, thallium, and zinc to various vegetables grown in slag-contaminated soils. J Environ Qual 30:934–939
Combs GF, Barrows SA, Swader FN (1980) Biologic availability of selenium in corn grain produced on soil amended with fly ash. J Agric Food Chem 28:406–409
Dick WA, Chen L, Hao Y (2000) Beneficial uses of clean coal combustion by-products: soil amendment and coal refuse treatment examples and case studies. In: Vories KC, Throgmorton D (eds) Proceedings of the use and disposal of coal combustion by-products at coal mines: a technical interactive forum. US Depart Interior, Office Surface Mining, Alton, IL and Coal Res Center, Southern Illinois Univ, Carbondale, IL, pp 119–141
El-Mogazi D, Lisk DJ, Weinstein LH (1988) A review of physical, chemical, and biological properties of fly ash and effects on agricultural ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 74:1–37
Elseewi AA, Page AL (1984) Molybdenum enrichment of plants grown on fly ash-treated soils. J Environ Qual 13:394–398
Furr AK, Kelly WC, Bache CA, Gutenmann WH, Lisk DJ (1976) Multi-element uptake by vegetables and millet grown in pots on fly ash amended soil. J Agric Food Chem 24:885–888
Furr AK, Parkinson TF, Gutenmann WH, Pakkala IS, Lisk DJ (1978) Elemental content of vegetables, grains, and forages field-grown on fly ash amended soil. J Agric Food Chem 26:357–359
Ghuman GS, Menon MP, Chandra K, James J, Adriano DC, Sajwan KS (1994) Uptake of multi-elements by corn from fly ash-compost amended soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 72:285–295
Gissel-Nielsen B, Bertelsen F (1988) Inorganic element uptake by barley from soil supplemented with flue gas desulphurization waste and fly ash. Environ Geochem Health 10:21–25
Gough LP, Shacklette HT, Case AA (1979) Element concentrations toxic to plants, animals, and man. US Geol Surv Bull 1466:1–80
Korcak RF (1996) Coal combustion residues as soil amendments: surface coal mining. In: Chugh YP, Sangunett BM, Vories KC (eds) Coal combustion by-products associated with coal mining: interactive forum. Forum Proceed, Southern Illinois Univ, Carbondale, IL, pp 143–152
Korcak RF (1998) Agricultural uses of coal combustion by-products. In: Wright RJ, Millner PD, Korcak RF (eds) Agricultural uses of municipal, animal, and industrial by-products. US Depart Agric National Tech Info Center, Springfield, VA, pp 103–119
Levinson AA (1980) Introduction to exploration geochemistry. Applied Publ Ltd, Chicago
MacNicol RD, Beckett PHR (1985) Critical tissue concentrations of potentially toxic elements. Plant Soil 85:107–129
Menon MP, Ghuman GS, James J, Chandra K (1992) Effects of coal fly ash-amended composts on the yield and elemental uptake by plants. J Environ Sci Health A27:1127–1139
Pflughoeft-Hassett DF, Sondreal EA, Steadman EN, Eylands KE, Dockter BA (2000) Production of coal combustion by-products: processes, volumes, and variability. In: Vories KC, Throgmorton D (eds) Proceedings of the use and disposal of coal combustion by-products at coal mines: a technical interactive forum. US Depart Interior, Office Surface Mining, Alton, IL and Coal Res Center, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL, pp 7–14
Ransome LS, Dowdy RH (1987) Soybean growth and boron distribution in a sandy soil amended with scrubber sludge. J Environ Qual 16:171–175
Reimann C, de Caritat P (1998) Chemical elements in the environment. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Rose AW, Hawkes HE, Webb JS (1979) Geochemistry in mineral exploration. Academic Press, London
Severson RC, Shacklette HT (1988) Essential elements and soil amendments for plants: sources and use for agriculture. US Geol Surv Circ 1017:1–48
Sims JT, Vasilas BL, Ghodrati M (1995) Evaluation of fly ash as a soil amendment for the Atlantic Coastal Plain: II. Soil chemical properties and crop growth. Water Air Soil Pollut 81:363–372
Stewart B, Tyson SS (1996) Potential use of coal combustion by-product (CCB) in the eastern coal region: site characteristics. In: Chugh YP, Sangunett BM, Vories KC (eds) Coal combustion by-products associated with coal mining: interactive forum. Forum Proceed, Southern Illinois Univ, Carbondale, IL, pp 53–65
Vandecaveye SC, Horner GM, Keaton CM (1936) Unproductiveness of certain orchard soils as related to lead arsenate spray accumulations. Soil Sci 42:203–213
Ziemkiewicz PF, Skousen JG (1992) Prevention of acid mine drainage by alkaline addition. Green Lands 22:42–51
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank C. Amlaner, Jr., for offering the use of the greenhouse facility at Indiana State University, L. Lohman at Pfizer Inc. for providing the coal combustion by-products, and S. Short and D. Knight for their assistance in the greenhouse. This research was supported by a Surface Mining and Reclamation Technology (SMART) grant through the Indiana Division of Reclamation, Indiana Department of Natural Resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brake, S.S., Jensen, R.R. & Mattox, J.M. Effects of coal fly ash amended soils on trace element uptake in plants. Env Geol 45, 680–689 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0921-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0921-z