Abstract
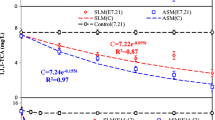
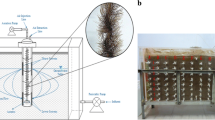
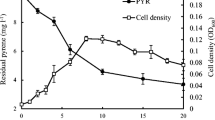
Aniline is of great environmental concern with regards to widespread occurrence in water and soil and increasing threat into the life forms. Bioremediation involving the use of degrading bacterium in the removal of aniline is the most promising process, yet inhibited under low temperature usually. In the present study, a new psychrotrophic bacterial strain isolated from groundwater, designated AN-1, was shown to be capable of aniline degradation in a concentration range of 135–2202 mg L−1 within 72 h at 10 °C. Strain AN-1 was proposed to be a Pseudomonas migulae group of bacteria based on the evolutionary relationship and the morphological and biochemical characteristics. The pH, NaH2PO4, and aniline concentration were used as independent variables to optimize the aniline removal by AN-1 at 10 °C, and a statistically significant (R 2 = 0.9230, p < 0.005) quadratic polynomial mathematical model was suggested. Moreover, an efficient biocomposite by assembling Fe3O4 nanoparticles onto the surface of AN-1 cells was constructed. Compared with free cells, the microbial cell/Fe3O4 biocomposite had the same biodegradation activity but exhibited remarkable reusability. This study highlights AN-1 might be a promising candidate for aniline removal from wastewater at low temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari F, Grigoriev P, Libor S, Tothill IE, Ramsden JJ (2009) DBT degradation enhancement by decorating Rhodococcus erythropolis IGST8 with magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(5):1505–1512
Bergauer P, Fonteyne P-A, Nolard N, Schinner F, Margesin R (2005) Biodegradation of phenol and phenol-related compounds by psychrophilic and cold-tolerant alpine yeasts. Chemosphere 59(7):909–918
Boon N, Goris J, De Vos P, Verstraete W, Top EM (2000) Bioaugmentation of activated sludge by an indigenous 3-chloroaniline-degrading Comamonas testosteroni strain, I2gfp. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(7):2906–2913
Heuer H, Krsek M, Baker P, Smalla K, Wellington EM (1997) Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(8):3233–3241
Jin Q, Hu Z, Jin Z, Qiu L, Zhong W, Pan Z (2012) Biodegradation of aniline in an alkaline environment by a novel strain of the halophilic bacterium, Dietzia natronolimnaea JQ-AN. Bioresour Technol 117:148–154
Jin HM, Choi EJ, Jeon CO (2013) Isolation of a BTEX-degrading bacterium, Janibacter sp. SB2, from a sea-tidal flat and optimization of biodegradation conditions. Bioresour Technol 145:57–64
Kahng H-Y, Kukor JJ, Oh K-H (2000) Characterization of strain HY99, a novel microorganism capable of aerobic and anaerobic degradation of aniline. Fems Microbiol Lett 190(2):215–221
Lee J, Isobe T, Senna M (1996) Preparation of ultrafine Fe3O4 particles by precipitation in the presence of PVA at high pH. J Colloid Interface Sci 177(2):490–494
Li Y, Liu Z, Zhao H, Xu Y, Cui F (2007) Statistical optimization of xylanase production from new isolated Penicillium oxalicum ZH-30 in submerged fermentation. Biochem Eng J 34(1):82–86
Li Y, Du X, Wu C, Liu X, Wang X, Xu P (2013) An efficient magnetically modified microbial cell biocomposite for carbazole biodegradation. Nanoscale Res Lett 8(1):1–5
Liu G-Q, Wang X-L (2007) Optimization of critical medium components using response surface methodology for biomass and extracellular polysaccharide production by Agaricus blazei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74(1):78–83
Morita R (1975) Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacterial Rev 39:144–167
Murakami S, Hayashi T, Maeda T, Takenaka S, Aoki K (2003) Cloning and functional analysis of aniline dioxygenase gene cluster, from Frateuria species ANA-18, That metabolizes aniline via an ortho-cleavage pathway of catechol. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67(11):2351–2358
Myers RH, Montgomery DC, Anderson-Cook CM (2009) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley & Sons, New York
O’Neill FJ, Bromley-Challenor KCA, Greenwood RJ, Knapp JS (2000) Bacterial growth on aniline: implications for the biotreatment of industrial wastewater. Water Res 34(18):4397–4409
Rao A, Bankar A, Kumar AR, Gosavi S, Zinjarde S (2013) Removal of hexavalent chromium ions by Yarrowia lipolytica cells modified with phyto-inspired Fe0/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Contam Hydrol 146:63–73
Robatjazi SM, Shojaosadati SA, Khalilzadeh R, Farahani EV, Balochi N (2012) Immobilization of magnetic modified Flavobacterium ATCC 27551 using magnetic field and evaluation of the enzyme stability of immobilized bacteria. Bioresour Technol 104:6–11
Sayyad SA, Panda BP, Javed S, Ali M (2007) Optimization of nutrient parameters for lovastatin production by Monascus purpureus MTCC 369 under submerged fermentation using response surface methodology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(5):1054–1058
Shan G, Xing J, Zhang H, Liu H (2005) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by microbial cells coated with magnetite nanoparticles. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(8):4497–4502
Tanaka T, Hachiyanagi H, Yamamoto N, Iijima T, Kido Y, Uyeda M, Takahama K (2009) Biodegradation of endocrine-disrupting chemical aniline by microorganisms. J Health Sci 55(4):625–630
Wang X, Gai Z, Yu B, Feng J, Xu C, Yuan Y, Lin Z, Xu P (2007) Degradation of carbazole by microbial cells immobilized in magnetic gellan gum gel beads. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(20):6421–6428
Xiao C, Ning J, Yan H, Sun X, Hu J (2009) Biodegradation of aniline by a newly isolated Delftia sp. XYJ6. Chin J Chem Eng 17(3):500–505
Xu P, Yu B, Li FL, Cai XF, Ma CQ (2006) Microbial degradation of sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles. Trends Microbiol 14(9):398–405
Zhu L, Lv M, Dai X, Xu X, Qi H, Yu Y (2012) Reaction kinetics of the degradation of chloroanilines and aniline by aerobic granule. Biochem Eng J 68:215–220
Zhuang R, Zhong W, Yao J, Chen H, Tian L, Zhou Y, Wang F, Bramanti E, Zaray G (2007) Isolation and characterization of aniline-degrading Rhodococcus sp. strain AN5. J Environ Sci Heal A 42(13):2009–2016
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41101226 and 41471252), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20110061120076), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Jilin University (No. 2013ZY02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 211 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YB., Qu, D., Wen, YJ. et al. Low-temperature biodegradation of aniline by freely suspended and magnetic modified Pseudomonas migulae AN-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 5317–5326 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6399-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6399-2