Abstract
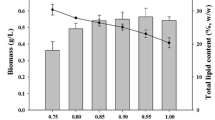
Microalgae harbor a not fully exploited industrial and environmental potential due to their high metabolic plasticity. In this context, a better understanding of the metabolism of microalgae and microalgal-bacterial consortia under stress conditions is essential to optimize any waste-to-value approach for their mass cultivation. This work constitutes a fundamental study of the mixotrophic metabolism under stress conditions of an axenic culture of Chlorella sorokiniana and a microalgal-bacterial consortium using carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorous mass balances. The hydrolysis of glucose into volatile fatty acids (VFA) during dark periods occurred only in microalgal-bacterial cultures and resulted in organic carbon removals in the subsequent illuminated periods higher than in C. sorokiniana cultures, which highlighted the symbiotic role of bacterial metabolism. Acetic acid was preferentially assimilated over glucose and inorganic carbon by C. sorokiniana and by the microalgal-bacterial consortium during light periods. N-NH4 + and P-PO4 −3 removals in the light stages decreased at decreasing duration of the dark stages, which suggested that N and P assimilation in microalgal-bacterial cultures was proportional to the carbon available as VFA to produce new biomass. Unlike microalgal-bacterial cultures, C. sorokiniana released P-PO4 −3 under anaerobic conditions, but this excretion was not related to polyhydroxybutyrate accumulation. Finally, while no changes were observed in the carbohydrate, lipid and protein content during repeated extended dark-light periods, nutrient deprivation boosted both C-acetate and C-glucose assimilation and resulted in significantly high biomass productivities and carbohydrate contents in both C. sorokiniana and the microalgal-bacterial cultures.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu AP, Fernandes B, Vicente AA, Teixeira J, Dragone G (2012) Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris using industrial dairy waste as organic carbon source. Bioresour Technol 118:61–66
Alcántara C, García-Encina PA, Muñoz R (2013) Evaluation of mass and energy balances in the integrated microalgae growth-anaerobic digestion process. Chem Eng J 221:238–246
Arbib Z, Ruiz J, Álvarez-Díaz P, Garrido-Pérez C, Perales JA (2014) Capability of different microalgae species for phytoremediation processes: wastewater tertiary treatment, CO2 bio-fixation and low cost biofuels production. Water Res 49:465–474
Asano T, Burton FL, Leverenz HL, Tsuchihashi R, Tchobanoglous G (2002) Metcalf and Eddy, wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bajekal SS, Dharmadhikari NS (2008) Use of polyphosphate accumulating organisms (PAO) for treatment of phosphate sludge. The 12th World Lake Conference: 918–922
Cade-Menun BJ, Paytan A (2010) Nutrient temperature and light stress alter phosphorus and carbon forms in culture-grown algae. Mar Chem 121:27–36
Cea-Barcía G, Buitrón G, Moreno G, Kumar G (2014) A cost-effective strategy for the bio-prospecting of mixed microalgae with high carbohydrate content: diversity fluctuations in different growth media. Bioresour Technol 163:370–373
Chu FF, Chu PN, Cai PJ, Li WW, Lam PKS, Zeng RJ (2013) Phosphorus plays an important role in enhancing biodiesel productivity of Chlorella vulgaris under nitrogen deficiency. Bioresour Technol 134:341–346
De Godos I, Vargas VA, Blanco S, García-González MC, Soto R, García-Encina PA, Becares E, Muñoz R (2010) A comparative evaluation of microalgae for the degradation of piggery wastewater under photosynthetic oxygenation. Bioresour Technol 101:5150–5158
De Philippis R, Ena A, Guastiini M, Sili C, Vincenzini M (1992) Factors affecting poly-β-hydroxybutyrate accumulation in cyanobacteria and in purple non-sulfur bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 103(2–4):187–194
Dean AP, Nicholson JM, Sigee DC (2008) Impact of phosphorus quota and growth phase on carbon allocation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an FTIR microspectroscopy study. Eur J Phycol 43(4):345–354
De-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2004) Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res 38(19):4222–4246
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, Washington DC, USA
Fanta SE, Hill WR, Smith TB, Roberts BJ (2010) Applying the light: nutrient hypothesis to stream periphyton. Freshw Biol 55:931–940
Feng P, Deng Z, Fan L, Hu Z (2012) Lipid accumulation and growth characteristics of Chlorella zofingiensis under different nitrate and phosphate concentrations. J Biosci Bioeng 114(4):405–410
Gómez C, Escudero R, Morales MM, Figueroa FL, Fernández-Sevilla JM, Acién FG (2013) Use of secondary-treated wastewater for the production of Muriellopsis sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(5):2239–2249
González CV, Cerón Mdel C, Acien FG, Segovia CS, Chisti Y, Fernández JM (2010) Protein measurements of microalgal and cyanobacterial biomass. Bioresour Technol 101:7587–7591
González-Fernández C, Ballesteros M (2012) Linking microalgae and cyanobacteria culture conditions and key-enzymes for carbohydrate accumulation. Biotechnol Adv 30(6):1655–1661
Guieysse B, Plouviez M, Coilhac M, Cazali L (2013) Nitrous oxide (N2O) production in axenic Chlorella vulgaris microalgae cultures: evidence, putative pathways, and potential environmental impacts. Biogeosciences 10(10):6737–6746
Harold FM (1966) Inorganic polyphosphates in biology: structure, metabolism, and function. Bacteriol Rev 30(4):772–794
He PJ, Mao B, Lü F, Shao LM, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2013) The combined effect of bacteria and Chlorella vulgaris on the treatment of municipal wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 146:562–568
Kamiya A, Kowallik W (1987) Photoinhibition of glucose uptake in Chlorella. Plant Cell Physiol 28:611–619
Kamiya A, Saitoh T (2002) Blue-light-control of the uptake of amino acids and of ammonia in Chlorella mutants. Physiol Plant 116:248–254
Kessler E, Oesterheld H (1970) Nitrification and induction of nitrate reductase in nitrogen deficient algae. Nature 228:287–288
Kim KH, Choi IS, Kim HM, Wi SG, Bae HJ (2014) Bioethanol production from the nutrient stress-induced microalga Chlorella vulgaris by enzymatic hydrolysis and immobilized yeast fermentation. Bioresour Technol 153:47–54
Kulaev I, Vagabov V, Kulakovskaya T (1999) New aspects of inorganic polyphosphate metabolism and function. J Biosci Bioeng 88(2):111–129
Li Y, Fei X, Deng X (2012) Novel molecular insights into nitrogen starvation induced triacylglycerols accumulation revealed by differential gene expression analysis in green algae Micractinium pusillum. Biomass Bioenergy 42:199–211
Liu ZY, Wang GC, Zhou BC (2008) Effect of iron on growth and lipid accumulation in Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour Technol 99(11):4717–4722
Markou G, Nerantzis E (2013) Microalgae for high-value compounds and biofuels production: a review with focus on cultivation under stress conditions. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1532–1542
Mesquita DP, Leal C, Cunha JR, Oehmen A, Amaral AL, Reis MA, Ferreira EC (2013) Prediction of intracellular storage polymers using quantitative image analysis in enhanced biological phosphorus removal systems. Anal Chim Acta 770:36–44
Muñoz R, Guieysse B (2006) Algal–bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: a review. Water Res 40(15):2799–2815
Panda B, Mallick N (2007) Enhanced poly-β-hydroxybutyrate accumulation in a unicellular cyanobacterium, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Lett Appl Microbiol 44(2):194–198
Pérez-García O, de-Bashan LE, Hernández JP, Bashan Y (2010) Efficiency of growth and nutrient uptake from wastewater by heterotrophic, autotrophic, and mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris immobilized with Azospirillum brasilense. J Phycol 46(4):800–812
Pérez-García O, Escalante FME, de-Bashan LE, Bashan Y (2011a) Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: metabolism and potential products. Water Res 45(1):11–36
Pérez-García RO, Bashan Y, Puente ME (2011b) Organic carbon supplementation of municipal wastewater is essential for heterotrophic growth and ammonium removing by the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. J Phycol 47(1):190–199
Powell N, Shilton AN, Pratt S, Chisti Y (2008) Factors influencing luxury uptake of phosphorus by microalgae in waste stabilization ponds. Environ Sci Technol 42(16):5958–5962
Powell N, Shilton A, Chisti Y, Pratt S (2009) Towards a luxury uptake process via microalgae—defining the polyphosphate dynamics. Water Res 43(17):4207–4213
Prajapati SK, Kaushik P, Malik A, Vijay VK (2013) Phycoremediation coupled production of algal biomass, harvesting and anaerobic digestion: possibilities and challenges. Biotechnol Adv 31(8):1408–1425
Sharma L, Mallick N (2005) Accumulation of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in Nostoc muscorum: regulation by pH, light–dark cycles, N and P status and carbon sources. Bioresour Technol 96(11):1304–1310
Sigee DC, Bahrami F, Estrada B, Webster RE, Dean AP (2007) The influence of phosphorus availability on carbon allocation and P quota in Scenedesmus subspicatus: a synchrotron-based FTIR analysis. Phycology 46(5):583–592
Simionato D, Block MA, La Rocca N, Jouhet J, Maréchal E, Finazzi G, Morosinotto T (2013) The response of Nannochloropsis gaditana to nitrogen starvation includes de novo biosynthesis of triacylglycerols, a decrease of chloroplast galactolipids, and reorganization of the photosynthetic apparatus. Eukaryot Cell 12(5):665–676
Sournia A (1978) Phytoplanton Manual. Museum National d’ Historie Naturelle, París. United Nations Educational. Scientific and Cultural Organization (Unesco)
Subashchandrabose SR, Ramakrishnan B, Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Naidu R (2011) Consortia of cyanobacteria/microalgae and bacteria: biotechnological potential. Biotechnol Adv 29(6):896–907
Takagi M, Karseno, Yoshida T (2006) Effect of salt concentration on intracellular accumulation of lipids and triacylglyceride in marine microalgae Dunaliella cells. J Biosci Bioeng 101(3):223–226
Venkata Mohan S, Devi MP, Subhash GV, Chandra R (2014) Algae oils as fuels. Biofuels from Algae, Elsevier 8:155–187
Zúñiga C, Morales M, Le Borgne S, Revah S (2011) Production of poly-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Methylobacterium organophilum isolated from a methanotrophic consortium in a two-phase partition bioreactor. J Hazard Mater 190(1–3):876–882
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the regional government of Castilla y León and the European Social Fund (Contract N° E-47-2011-0053564 and Project Ref. GR76). The financial support of the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and the National Institute for Agricultural Research and Technology and Food is also gratefully acknowledged (Project Ref. RTA2013-00056-C03-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(docx 45.1 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alcántara, C., Fernández, C., García-Encina, P.A. et al. Mixotrophic metabolism of Chlorella sorokiniana and algal-bacterial consortia under extended dark-light periods and nutrient starvation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 2393–2404 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6125-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6125-5