Abstract
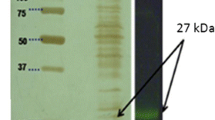
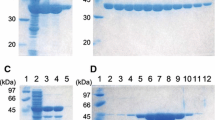
In this study, we report the cloning, recombinant expression, and biochemical characterization of a heat-stable CMP-N-acylneuraminic acid (NeuAc) synthetase from Clostridium thermocellum ATCC 27405. A high throughput electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS)-based assay demonstrates that the enzyme has an absolute requirement for a divalent cation for activity and reaches maximum activity in the presence of 10 mM Mn2+. The enzyme is active at pH 8–13 in Tris–HCl buffer and at 37–60 °C, and maximum activity is observed at pH 9.5 and 50 °C in the presence of 0.2 mM dithiothreitol. In addition to NeuAc, the enzyme also accepts the analog N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc) as a substrate. The apparent Michaelis constants for cytidine triphosphate and NeuAc or NeuGc are 240 ± 20, 130 ± 10, and 160 ± 10 μM, respectively, with corresponding turnover numbers of 3.33, 2.25, and 1.66 s−1, respectively. An initial velocity study of the enzymatic reaction indicates an ordered bi–bi catalytic mechanism. In addition to demonstration of a thermostable and substrate-tolerant enzyme, confirmation of the biochemical function of a gene for CMP-NeuAc synthetase in C. thermocellum also opens the question of the biological function of CMP-NeuAc in such nonpathogenic microorganisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angata T, Varki A (2002) Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related alpha-keto acids: an evolutionary perspective. Chem Rev 102:439–469
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bravo IG, Barrallo S, Ferrero MA, Rodriguez-Aparicio LB, Martinez-Blanco H, Reglero A (2001) Kinetic properties of the acylneuraminate cytidylyltransferase from Pasteurella haemolytica A2. Biochem J 358:585–598
Bravo IG, Garcia-Vallve S, Romeu A, Reglero A (2004) Prokaryotic origin of cytidylyltransferases and alpha-ketoacid synthases. Trends Microbiol 12:120–127
Canganella F, Wiegel J (1993) The potential of thermophilic clostridia in biotechnology. In: Wood DR (ed) The clostridia and biotechnology. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, MA, pp 393–429
Chokhawala HA, Yu H, Chen X (2007) High-throughput substrate specificity studies of sialidases by using chemoenzymatically synthesized sialoside libraries. ChemBioChem 8:194–201
Demian AL, Newcomb M, Wu JHD (2005) Cellulose, clostridia, and ethanol. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 69:124–154
Gilbert M, Bayer R, Cunningham AM, DeFrees S, Gao Y, Watson DC, Young NM, Wakarchuk WW (1998) The synthesis of sialylated oligosaccharides using a CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase/sialyltransferase fusion. Nat Biotechnol 16:769–772
Haft RF, Wessels MR, Mebane MF, Conaty N, Rubens CE (1996) Characterization of cpsF and its product CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase, a group B streptococcal enzyme that can function in K1 capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 19:555–563
Ishige K, Hamamoto T, Shiba T, Noguchi T (2001) Novel method for enzymatic synthesis of CMP-NeuAc. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:1736–1740
Kean EL (1991) Sialic acid activation. Glycobiology 1:441–447
Kittelmann M, Klein T, Kragl U, Wandrey C, Ghisalba O (1995) CMP-N-acetyl neuraminic acid synthetase from Escherichia coli: fermentation production and application for the preparative synthesis of CMP-neuraminic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:59–67
Knorst M, Fessner W-D (2001) CMP-sialate synthetase from Neisseria meningitidis-overexpression and application to the synthesis of oligosaccharides containing modified sialic acids. Adv Synth Catal 343:698–710
Liu JL-C, Shen C-J, Ichikawa Y, Rutan JF, Zapata C, Vann WF, Wong C-H (1992) Overproduction of CMP-sialic acid synthetase for organic synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 114:3901–3910
Martinez J, Steenbergen S, Vimr E (1995) Derived structure of the putative sialic acid transporter from Escherichia coli predicts a novel sugar permease domain. J Bacteriol 177:6005–6010
Mizanur RM, Zea CJ, Pohl NL (2004) Unusually broad substrate tolerance of a heat-stable archaeal sugar nucleotidyltransferase for the synthesis of sugar nucleotides. J Am Chem Soc 126:15993–15998
Mizanur RM, Jaipuri FA, Pohl NL (2005) One-step synthesis of labeled sugar nucleotides for protein O-GlcNAc modification studies by chemical function analysis of an archaeal protein. J Am Chem Soc 127:836–837
Mosimann SC, Gilbert M, Dombroswki D, To R, Wakarchuk W, Strynadka NCJ (2001) Structure of a sialic acid-activating synthetase, CMP-acylneuraminate synthetase in the presence and absence of CDP. J Biol Chem 276:8190–8196
Plumbridge J, Vimr E (1999) Convergent pathways for utilization of the amino sugars N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylmannosamine, and N-acetylneuraminic acid by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 181:47–54
Rodriguez-Aparicio LB, Luengo JM, Gonzalez-Clemente C, Reglero A (1992) Purification and characterization of the nuclear cytidine 5′-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 267:9257–9263
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, NY
Samuels NM, Gibson BW, Miller SM (1999) Investigation of the kinetic mechanism of cytidine 5′monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase from Haemophilus ducreyi with new insights on rate limiting steps from product inhibition analysis. Biochemistry 38:6195–6203
Schauer R (2000) Achievements and challenges of sialic acid research. Glycoconj J 17:485–499
Shames SL, Simon ES, Christopher CW, Schmid W, Whitesides GM, Yang LL (1991) CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase of Escherichia coli: high level expression, purification and use in the enzymatic synthesis of CMP-N- acetylneuraminic acid and CMP-neuraminic acid derivatives. Glycobiology 1:187–191
Tullius MV, Munson Jr RS, Wang J, Gibson BW (1996) Purification, cloning, and expression of a cytidine 5′-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase from Haemophilus ducreyi. J Biol Chem 271:15373–15380
Tullius MV, Vann WF, Gibson BW (1999) Covalent modification of Lys19 in the CTP binding site of cytidine 5′-monophosphate N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase. Protein Sci 8:666–675
Vimr ER, Troy FA (1985) Identification of an inducible catabolic system for sialic acids (Nan) in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 164:845–853
Vimr E, Lichtensteiger L (2002) To sialylate, or not to sialylate: that is the question. Trends Microbiol 10:254–257
Vimr E, Lichtensteiger C, Steenbergen S (2000) Sialic acid metabolism’s dual function in Haemophilus influenzae. Mol Microbiol 36:1113–1123
Warren L, Blacklow RS (1962) The biosynthesis of cytidine 5′-monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid by an enzyme from N. meningitidis. J Biol Chem 237:3527–3534
Yu H, Chokhawala H, Karpel R, Yu H, Wu B, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Jia Q, Chen X (2005) A multifunctional Pasteurella multocida sialyltransferase: a powerful tool for the synthesis of sialoside libraries. J Am Chem Soc 127:17618–17619
Yu H, Huang S, Chokhawala H, Sun M, Zheng H, Chen X (2006) Highly efficient chemoenzymatic synthesis of naturally occurring and non-natural α-2,6-linked sialosides: a P. damsella α-2,6-sialyltransferase with extremely flexible donor-substrate specificity. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3938–3944
Yu H, Yu H, Karpel R, Chen X (2004) Chemoenzymatic synthesis of CMP-sialic acid derivatives by a one-pot two-enzyme system: comparison of substrate flexibility of three microbial CMP-sialic acid synthetases. Bioorg Med Chem 12:6427–6435
Zea CJ, Pohl NL (2004) General assay for sugar nucleotidyltransferases using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 328:196–202
Acknowledgements
We thank a Shimadzu University Research Grant and the Herman Frasch Foundation (American Chemical Society) for their support of this research. N.L.P. is a Cottrell Scholar of Research Corporation and an Alfred P. Sloan Foundation Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizanur, R.M., Pohl, N.L. Cloning and characterization of a heat-stable CMP-N-acylneuraminic acid synthetase from Clostridium thermocellum . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76, 827–834 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1053-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1053-2