Abstract
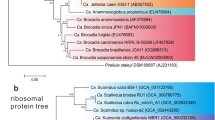
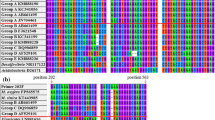
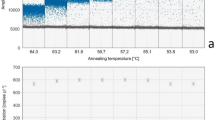
In this study, four real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primer sets were developed for the 16S rRNA genes of specific ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) found in activated sludge of sewage treatment systems. The primer sets target two of several sequence types of the Nitrosomonas oligotropha cluster, members within the Nitrosomonas communis cluster, and all members of the Nitrosomonas europaea–Nitrosococcus mobilis cluster. The detection limit of each primer set was in the range of 3×101–6×102 genes reaction−1. Reliable quantification of the target AOB DNA was obtained when the target AOB DNA comprised more than 0.1% of total AOB DNA in the sample. The application of the primer sets to samples taken from five sewage treatment systems showed that, in all systems, the majority of the AOB population was comprised of one sequence type of the N. oligotropha cluster (3.9±1.5×109–1.7±0.5×1010 cell l−1) and, in most systems, followed by members within the N. communis cluster (2.8±0.3×109–1.0±0.1×1010 cell l−1) or/and another sequence type of the N. oligotropha cluster (1.5±0.6×108–5.5±0.5×108 cell l−1). N. europaea–N. mobilis cluster arose solely in small numbers (4.9±0.8×108 cell l−1) in one system. Real-time PCR-amplified products obtained from genomic DNA extracted from samples were verified using clone library, and it revealed that only the target AOB DNA were PCR amplified, without amplification of the nontarget sequences.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aakra A, Utaker JB, Nes IF (1999) RFLP of rRNA genes and sequencing of the 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer region of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria: a phylogenetic approach. Int J Sys Bacteriol 49:123–130
Ballinger SJ, Head IM, Curtis TP, Godley AR (1998) Molecular microbial ecology of nitrification in an activated sludge process treating refinery wastewater. Water Sci Technol 37(4–5):105–108
Belser LW, Schmidt EL (1978) Diversity in the ammonia-oxidizing nitrifier population of a soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 36(4):584–588
Bollmann A, Laanbroek HJ (2001) Continuous culture enrichments of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria at low ammonium concentrations. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37:211–221
Dionisi HM, Layton AC, Harms G, Gregory IR, Robinson KG, Sayler GS (2002) Quantification of Nitrosomonas oligotropha-like ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and Nitrospira spp. from full-scale wastewater treatment plants by competitive PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):245–253
Gieseke A, Purkhold U, Wagner M, Amann R, Schramm A (2001) Community structure and activity dynamics of nitrifying bacteria in a phosphate-removing biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(3):1351–1362
Harms G, Layton AC, Dionisi HM, Gregory IR, Garrett VM, Hawkins SA, Robinson KG, Sayler GS (2003) Real-time PCR quantification of nitrifying bacteria in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 37:343–351
Hermansson A, Lindgren PE (2001) Quantification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in Arable soil by real-time PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(2):972–976
Juretschko S, Timmermann G, Schmid M, Schleifer KH, Pommerening-Roser A, Koops HP, Wagner M (1998) Combined molecular and conventional analyses of nitrifying bacterium diversity in activated sludge: Nitrosococcus mobilis and Nitrospira-like bacteria as dominant populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(8):3042–3051
Klappenbach JA, Saxman PR, Cole JR, Schmidt TM (2001) rrndb: the ribosomal RNA operon copy number database. Nucleic Acids Res 29(1):181–184
Koops HP, Pommerening-Roser A (2001) Distribution and ecophysiology of the nitrifying bacteria emphasizing cultured species. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 37:1–9
Koops HP, Purkhold U, Pommerening-Roser A, Timmermann G, Wagner M (2003) The lithoautotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. In: Dworkin M et al (eds) The prokaryotes: an evoluting electronic resource for the microbiological community. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kowalchuck GA, Stephen JR, De Boer W, Prosser JI, Embley TM, Woldendorp JM (1997) Analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the β subdivision of the class Proteobacteria in coastal sand dunes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequencing of PCR-amplified 16S ribosomal DNA fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(4):1489–1497
Kurata S, Kanagawa T, Yamada K, Torimura M, Yokomaku T, Kamagata Y, Kurane R (2001) Fluorescent quenching-based quantitative detection of specific DNA/RNA using BODIPYFL-labeled probe or primer. Nucleic Acids Res 29(6):e34
Limpiyakorn T, Shinihara Y, Kurisu F, Yagi O (2005) Communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge of various sewage treatment plants in Tokyo. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:205–117
Mobarry BK, Wagner M, Urbain V, Rittmann BE, Stahl DA (1996) Phylogenetic probes for analyzing abundance and spatial organization of nitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(6):2156–2162
Okano Y, Hristova KR, Leutenegger CM, Jackson LE, Denison RF, Gebreyesus B, Lebauer D, Scow KM (2004) Application of real-time PCR to study effects of ammonium on population size of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(2):1008–1016
Pommerening-Roser A, Rath G, Koops HP (1996) Phylogenetic diversity within the genus Nitrosomonas. Syst Appl Microbiol 19:344–351
Regan JM, Harrington GW, Noguera DR (2002) Ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria communities in a pilot-scale chloraminated drinking water distribution system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):73–81
Regan JM, Harrington GW, Baribeau H, De Leon R, Noguera DR (2003) Diversity of nitrifying bacteria in full-scale chloraminated distribution systems. Water Res 37:197–205
Schramm A, De Beer D, Wagner M, Amann R (1998) Identification and activities in situ of Nitrosospira and Nitrospira spp. as dominant population in nitrifying fluidized bed reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(9):3480–3485
Suwa Y, Imamura Y, Suzuki T, Tashiro T, Urushigawa Y (1994) Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria with different sensitivities to (NH4)2SO4 in activated sludges. Water Res 28(7):1523–1532
Wagner M, Rath G, Amann R, Koops HP, Schleifer KH (1995) In situ identification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 18:251–264
Wagner M, Rath G, Koops HP, Flood J, Amann R (1996) In situ analysis of nitrifying bacteria in sewage treatment plants. Water Sci Technol 34(1–2):237–244
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Tokyo Metropolitan Government for providing samples and data from the sewage treatment systems. We would also like to extend special thanks to Yoriko Sakamoto for providing laboratory assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Limpiyakorn, T., Kurisu, F. & Yagi, O. Development and application of real-time PCR for quantification of specific ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge of sewage treatment systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72, 1004–1013 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0366-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0366-x