Abstract.
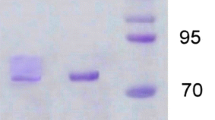
A recently isolated basidiomycete, Trametes sp. strain AH28-2, can be induced to produce a high level of laccases when grown on a cellobiose-asparagine liquid medium. After induction by kraft lignin, two major isozymes were detected in the fermentation supernatant of the fungus. The principal component laccase A, which accounts for about 85% of the total activity, can be purified to electrophoretic homogeneity by three chromatographic steps: DEAE-Sepharose FF, Superdex-200 and Mono-Q. The solution containing purified laccase is blue in color, and the ratio of absorbance at 280 nm to that at 600 nm is 22. The molecular mass of laccase A is estimated to be 62 kDa by SDS-PAGE, 57 kDa by FPLC, and measured as 58,522 Da by MALDI mass spectrum. Laccase A is a monomeric glycoprotein with a carbohydrate content of 11–12% and an isoelectric point of 4.2. The optimum pH and temperature for oxidizing guaiacol are 4.5 and 50°C, respectively. The half-life of the enzyme at 75°C is 27 min. The enzyme shows a good stability from pH 4.2 to pH 8.0. The K m values of the enzyme toward substrates 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothazoline-6-sulfonate) (ABTS), guaiacol and 2,6-dimethoxyphenol are 25, 420 and 25.5 µM, respectively, and the corresponding V max values are 670, 66.8, and 79 µM min–1 mg–1, respectively. Laccase A activity is strongly inhibited by 0.1 mM NaN3 or 0.1 mM cyanide. Two units of laccase A alone is able to completely oxidize 100 µmol 2,6-chlorophenol in 6 h. In the presence of 1 mM ABTS and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, 15.0 U laccase A is able to oxidize 45% and 70% of 50 µmol fluorene in 12 and 18 h, respectively. The laccase A gene was cloned by a PCR method, and preliminary analysis of its sequence indicates 87.0% similarity to the corresponding segment in the phenoloxidase gene from Coriolus hirsutus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, .Y., Tu, .X., Wang, .J. et al. Purification, molecular characterization and reactivity with aromatic compounds of a laccase from basidiomycete Trametes sp. strain AH28-2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60, 700–707 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1169-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1169-3