Abstract
Background
MRI is a sensitive tool for the evaluation of synovitis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Objective
The purpose of this study was to introduce a novel MRI-based score for synovitis in children and to examine its inter- and intraobserver variability in a multi-centre study.
Materials and methods
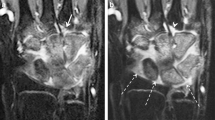
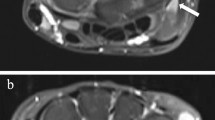
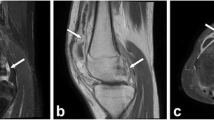
Wrist MRI was performed in 76 children with JIA. On postcontrast 3-D spoiled gradient-echo and fat-suppressed T2-weighted spin-echo images, joint recesses were scored for the degree of synovial enhancement, effusion and overall inflammation independently by two paediatric radiologists. Total-enhancement and inflammation-synovitis scores were calculated.
Results
Interobserver agreement was poor to moderate for enhancement and inflammation in all recesses, except in the radioulnar and radiocarpal joints. Intraobserver agreement was good to excellent. For enhancement and inflammation scores, mean differences (95 % CI) between observers were −1.18 (−4.79 to 2.42) and −2.11 (−6.06 to 1.83). Intraobserver variability (reader 1) was 0 (−1.65 to 1.65) and 0.02 (−1.39 to 1.44).
Conclusion
Intraobserver agreement was good. Except for the radioulnar and radiocarpal joints, interobserver agreement was not acceptable. Therefore, the proposed scoring system requires further refinement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ravelli A, Martini A (2007) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 369:767–778
Cassidy JT, Petty RE, Laxer RM et al (2005) Textbook of pediatric rheumatology, 5th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia
Martini A, Lovell DJ (2010) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: state of the art and future perspectives. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1260–1263
Breedveld F (2011) The value of early intervention in RA-a window of opportunity. Clin Rheumatol 30(Suppl 1):S33–39
Lovell DJ, Giannini EH, Reiff A et al (2000) Etanercept in children with polyarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 342:763–769
Lovell DJ, Ruperto N, Goodman S et al (2008) Adalimumab with or without methotrexate in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 359:810–820
Ruperto N, Lovell DJ, Quartier P et al (2008) Abatacept in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled withdrawal trial. Lancet 372:383–391
Nistala K, Babar J, Johnson K et al (2007) Clinical assessment and core outcome variables are poor predictors of hip arthritis diagnosed by MRI in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:699–702
Lamer S, Sebag GH (2000) MRI and ultrasound in children with juvenile chronic arthritis. Eur J Radiol 33:85–93, Review
Brown AK, Quinn MA, Karim Z et al (2006) Presence of significant synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis patients with disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-induced clinical remission: evidence from an imaging study may explain structural progression. Arthritis Rheum 54:3761–3773
Østergaard M, Peterfy C, Conaghan P et al (2003) OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol 30:1385–1386
Haavardsholm EA, Ostergaard M, Ejbjerg BJ et al (2005) Reliability and sensitivity to change of the OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score in a multireader, longitudinal setting. Arthritis Rheum 52:3860–3867
Conaghan P, Lassere M, Østergaard M et al (2003) OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 4: an international multicenter longitudinal study using the RA-MRI Score. J Rheumatol 30:1376–1379
Malattia C, Damasio MB, Pistorio A et al (2011) Development and preliminary validation of a paediatric-targeted MRI scoring system for the assessment of disease activity and damage in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:440–446
Hodgson RJ, O’Connor P, Moots R (2008) MRI of rheumatoid arthritis—image quantitation for the assessment of disease activity, progression and response to therapy. Rheumatology 47:13–21
Konig H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ et al (1990) Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology 176:473–477
Malattia C, Damasio MB, Basso C et al (2010) Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of disease activity in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:178–185
Workie DW, Graham TB, Laor T et al (2007) Quantitative MR characterization of disease activity in the knee in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a longitudinal pilot study. Pediatr Radiol 37:535–543
Boers M, Brooks P, Strand CV et al (1998) The OMERACT filter for outcome measures in rheumatology. J Rheumatol 25:198–199
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P et al (2004) International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
Ejbjerg B, McQueen F, Lassere M et al (2005) The EULAR-OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas: the wrist joint. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 1):i23–i47
Donner A, Eliasziw M (1987) Sample size requirements for reliability studies. Stat Med 6:441–448
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Deyo RA, Diehr P, Patrick DL (1991) Reproducibility and responsiveness of health status measures: statistics and strategies for evaluation. Control Clin Trials 12(Suppl 4):142S–158S
Swinscow TDV (1997) Statistics at square one, 9th edn. Revised by Campbell MJ, University of Southampton. BMJ Publishing Group, Southampton, London, p 78
Gaffney K, Cookson J, Blades S et al (1998) Quantitative assessment of the rheumatoid synovial microvascular bed by gadolinium-DTPA enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Rheum Dis 57:152–157
Konig H, Sieper J, Wolf KJ (1990) Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology 176:473–477
Ostergaard M, Klarlund M, Lassere M et al (2001) Interreader agreement in the assessment of magnetic resonance images of rheumatoid arthritis wrist and finger joints—an international multicenter study. J Rheumatol 28:1143–1150
Bird P, Joshua F, Lassere M et al (2005) Training and calibration improve inter-reader reliability of joint damage assessment using magnetic resonance image scoring and computerized erosion volume measurement. J Rheumatol 32:1452–1458
Ejbjerg BJ, Vestergaard A, Jacobsen S et al (2005) The smallest detectable difference and sensitivity to change of magnetic resonance imaging and radiographic scoring of structural joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis finger, wrist, and toe joints: a comparison of the OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score applied to different joint combinations and the Sharp/van der Heijde radiographic score. Arthritis Rheum 52:2300–2306
Acknowledgement
Supported by a grant from the European Union, Health-e-Child Integrated Project (IST-2004-027749).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damasio, M.B., Malattia, C., Tanturri de Horatio, L. et al. MRI of the wrist in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: proposal of a paediatric synovitis score by a consensus of an international working group. Results of a multicentre reliability study. Pediatr Radiol 42, 1047–1055 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2392-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-012-2392-4