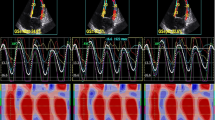
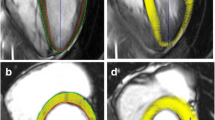
Abstract
Recently, the prevalence of infant Kawasaki disease (KD) has increased. However, the myocardial functional analysis of infant KD can be difficult and rarely reported. The purpose of this study was to investigate layer specific myocardial strain analysis for better assessment of the acute period in infant KD. The study retrospectively reviewed the echocardiographic data of 25 infant patients with KD at the acute phase. With advanced imaging, pulsed tissue Doppler velocity data, myocardial strain with three layers specific analysis was performed. Then the data were compared with 25 age-matched healthy control infants. The measures of longitudinal strain and radial strain were decreased in infant KD compared to healthy controls. The circumferential strain was significantly decreased in infant KD at all three myocardial layers, especially in the endocardial layer (KD: −20.5 ± 6.4 % vs. control: −25.6 ± 7.6 %, endocardium, p = 0.00001; −14.6 ± 4.4 % vs. −18.1 ± 4.0 %; middle myocardium, p = 0.01; −9.7 ± 3.3 % vs. −11.4 ± 3.8 %; epicardium, p = 0.04). The acute phase of infant KD demonstrated decreased myocardial strain measurement. Circumferential strain was the lowest in the endocardial layer. Further continuous long-term follow up for myocardial assessment should be recommended even after recovery with appropriate treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujiwara H, Hamashima Y (1978) Pathology of the heart in Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 61:100–107
Takahashi M (1989) Myocarditis in Kawasaki syndrome: A minor villain? Circulation 79:1398–1400
Kurotobi S, Kawakami N, Shimizu K et al (2005) Brain natriuretic peptide as a hormonal marker of ventricular diastolic dysfunction in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 26:425–430
Takeuchi D, Saji T, Takatsuki S, Fujiwara M (2007) Abnormal tissue Doppler images are associated with elevated plasma brain natriuretic peptide and increased oxidative stress in acute Kawasaki disease. Circ J 71:357–362
Terai M, Honda T, Yasukawa K, Higashi K, Hamada H, Kohno Y (2003) Prognostic impact of vascular leakage in acute Kawasaki disease. Circulation 108:325–330
Yu JJ, Kwak BO, Jeon YH, Park YM, Lee R, Chung S, Bae SH, Pyun BY (2009) Elevation of the index of left ventricular mass during the acute and subacute phase of Kawasaki disease, and its association with indexes of diastolic function. Cardiol Young 19:64–69
McCandless RT, Minich LL, Wilkinson SE, McFadden ML, Tani LY, Menon SC (2013) Myocardial strain and strain rate in Kawasaki disease. Eur Heart J 14:1061–1068
Dandel M, Hetzer R (2009) Echocardiographic strain and strain rate imaging: clinical applications. Int J Cardiol 132:11–24
Dahifar H, Ghorbani A (2005) Atypical Kawasaki disease in two infants younger than 6 months. J Res Med Sci 10(4):239–243
Freeman AF, Shulman ST (2006) Kawasaki disease: summary of the American Heart Association Guidelines. Am Fam Phys 74:1141–1148
Shulman ST, Mcauley JB, Pachman LM, Miller ML, Ruschhaupt DG (1987) Risk of coronary abnormalities due to Kawasaki disease in urban area with small Asian population. Am J Dis Child 141:420–425
Tseng CF, Fu YC, Fu LS, Hwang B, Chi CS (2001) Clinical spectrum of Kawasaki disease in infants. Chin Med J 64:168–173
Liu HC, Lo CW, Hwang B, Lee PC (2012) Clinical manifestations vary with different age spectrums in infants with Kawasaki disease. Sci World J 15:1–6
Burns JC, Wiggins JW, Toews WH (1986) Clinical spectrum of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than 6 months of age. J Pediatr 109:759–763
Rosenfeld EA, Corydon KE, Shulman ST, Mason W, Takahashi M, Kuroda C (1995) Kawasaki disease in infants less than one year of age. J Pediatr 126:524–529
Anderson MS, Todd JK, Glode MP (2005) Delayed diagnosis of Kawasaki disease syndrome: an analysis of the problem. Pediatrics 115:e428–e433
Chuang CH, Hsiao MH, Chiu CH, Huang YC, Lin TY (2006) Kawasaki disease in infants three months of age or younger. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 39:387–391
Moreno N, Mendez-Echevarria A, Inocencio J (2008) Coronary involvement in infants with Kawasaki disease treated with intravenous gamma-globulin. Pediatr Cardiol 29:31–35
Chang FY, Hwang B, Chen SJ, Lee PC, Meng CL, Lu JH (2006) Characteristics of Kawasaki disease in infants younger than six months of age. Pediatr Infect Dis 25:241–244
Manlhiot C, Yeung RS, Clarizia NA, Chahal N, McCrindle BW (2009) Kawasaki disease at the extremes of the age spectrum. Pediatrics 124:e410–e415
Joffe A, Kabani A, Jadavji T (1995) Atypical and complicated Kawasaki disease in infants—Do we need criteria? West J Med 162:322–327
Levy M, Koren G (1990) Atypical Kawasaki disease: analysis of clinical presentation and diagnostic clues. Pediatr Infect Dis J 9:122–126
Schuh S, Laxer RM, Smallhorn JF, Hilliard RI, Rowe RD (1988) Kawasaki disease with atypical presentation. Pediatr Infect Dis J 7:201–203
Friedman AD (1988) An atypical presentation of Kawasaki disease in an infant. Pediatr Dermatol 5:120–122
Reller M, DeCristofaro J, Schwartz DC (1984) Coronary aneurysms in a patient with atypical Kawaski disease and a streptococcal infection. Pediatr Cardiol 5:205–208
Kurotobi S, Kawakami N, Shimizu K et al (2005) Brain natriuretic peptide as a hormonal marker of ventricular diastolic dysfunction in children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 26:425–430
Takeuchi D, Saji T, Takatsuki S, Fujiwara M (2007) Abnormal tissue Doppler images are associated elevated plasma brain natriuretic peptide and increased oxidative stress in acute Kawasaki disease. Circ J 71:357–362
Arnold R, Goebel B, Ulmer HE, Gorenflo M, Poerner TC (2007) An exercise tissue Doppler and strain rate imaging study of diastolic myocardial dysfunction after Kawasaki syndrome in childhood. Cardiol Young 17:478–486
McCrindle BW, Li JS, Minich LL, Colan SD, Atz AM, Takahashi M (2007) Coronary artery involvement in children with Kawasaki disease: risk factors from analysis of serial normalized measurements. Circulation 116:174–179
Manlhiot C, Millar K, Golding F, McCrindle BW (2010) Improved classification of coronary artery abnormalities based only on coronary artery z-scores after Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 31:242–249
Dallaire F, Fournier A, Breton J, Nguyen TD, Spigelblatt L, Dahdah N (2012) Marked variations in serial coronary artery diameter measures in Kawasaki disease: a new indicator of coronary involvement. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 25:859–865
Moran AM, Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Parness IA, Spevak PJ, Burns JC, Colan SD (2000) Abnormal myocardial mechanics in Kawasaki disease: rapid response to gamma-globulin. Am Heart J 139(2 Pt 1):217–223
Hiraishi S, Yashiro K, Oguchi K, Kusano S, Ishii K, Nakazawa K (1981) Clinical course of cardiovascular involvement in the mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. Relation between clinical signs of carditis and development of coronary arterial aneurysm. Am J Cardiol 47(2):323–330
Yu JJ, Choi HS, Kim YB, Son JS, Kim YH, Ko JK, Park IS (2010) Analysis of left ventricular myocardial deformation by speckle tracking imaging during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 31:807–812
Newburger JW, Sanders SP, Burns JC, Parness IA, Beiser AS, Colan SD (1989) Left ventricular contractility and function in Kawasaki syndrome. Circulation 79:1237–1246
Henry WL, Ware J, Gardin JM, Hepner SI, McKay J, Weiner M (1987) Echocardiographic measurements in normal subjects: Growth-related changes that occur between infancy and early adulthood. Circulation 7:278–285
Printz BF, Sleeper LA, Newburger JW, Minich LL, Bradley T, Cohen MS, Frank D, Li JS, Margossian R, Shirali G, Takahashi M, Colan SD (2011) Noncoronary cardiac abnormalities are associated with coronary artery dilation and with laboratory inflammatory markers in acute Kawasaki disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 57:86–92
Lega JC, Bozio A, Cimaz R, Verier M, Floret D, Ducreux C, Reix P, Filippo S (2013) Extracoronary echocardiographic findings as predictors of coronary artery lesions in the initial phase of Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 98:97–102
No SJ, Kim DO, Choi KM, Eun LY (2013) Do predictors of incomplete Kawasaki disease exists for infants? Pediatr Cardiol 34:286–290
Acknowledgments
This research received no grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Lucy Youngmin Eun who wrote the first draft of manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eun, L.Y., Kim, J.H., Jung, J.W. et al. Myocardial Layers Specific Strain Analysis for the Acute Phase of Infant Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 37, 1404–1408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-016-1448-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-016-1448-x