Abstract
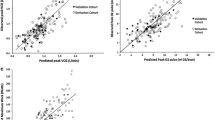
Maximal oxygen consumption (\( \dot{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\text{max}\)) is the “gold standard” by which to assess functional capacity; however, it is effort dependent. \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)@RER1.0 is defined when \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}={V}_{\text{CO}_{2}}\). Between December 22, 1997 and November 9, 2004, 305 pediatric subjects underwent cycle ergometer cardiopulmonary exercise testing, exercised to exhaustion, and reached a peak respiratory exchange ratio ≥1.10. Group 1 subjects achieved a peak \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}} \ge 80\%\) of predicted \( \dot{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\text{max}\); group 2 subjects achieved a peak \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}} \le 60\% \) of predicted \( \dot{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\text{max}\); and group 3 subjects achieved a peak \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\) between 61 and 79% of predicted \( \dot{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\text{max}\). Linear regression analysis was performed for \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)@RER1.0 as a function of predicted \( \dot{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\text{max}\) for group 1 subjects. A −2 SD regression line and equation was created. \( \text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)@RER1.0 data from groups 2 and 3 were plotted onto the normative graph. Contingency table and relative-risk analysis showed that an abnormal \( \text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)@RER1.0 predicted an abnormal peak \(\text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)(positive-predictive value 83%, negative-predictive value 85%, sensitivity 84%, and specificity 84%). \( \text{V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)@RER1.0 is a highly sensitive, specific, and predictive submaximal index of functional capacity. This submaximal index is easy to identify without subjectivity. This index may aid in the evaluation of subjects who cannot exercise to maximal parameters.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baba R, Nagashima M, Goto M, Nagano Y, Yokota M, Tauchi N et al (1996) Oxygen uptake efficiency slope: a new index of cardiorespiratory functional reserve derived from the relation between oxygen uptake and minute ventilation during incremental exercise. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:1567–1572
Baba R, Nagashima M, Nagano Y, Idoma M, Nishibata K (1999) Role of the oxygen uptake efficiency slope in evaluating exercise tolerance. Arch Dis Child 81:73–75
Cohen-Solal A, Benessiano J, Himbert D, Paillole C, Gourgon R (1991) Ventilatory threshold during exercise in patients with mild to moderate chronic heart failure: determination, relation with lactate threshold, and reproducibility. Int J Cardiol 30:321–327
Cooper DM, Weiler-Ravell D, Whipp BJ, Wasserman K (1984) Aerobic parameters of exercise as a function of body size during growth in children. J Appl Physiol 56:628–634
Dickstein K, Aarsland T, Svanes H, Barvik S (1993) A respiratory exchange ratio equal to 1 provides a reproducible index of submaximal cardiopulmonary exercise performance. Am J Cardiol 71:1367–1369
Gibbons RJ, Balady GJ, Beaslet JW et al (1997) ACC/AHA guidelines for exercise testing: executive summary. Circulation 96:343–354
Dickstein K, Barvik S, Aarsland T, Snapinn S, Karlsson J (1990) A comparison of methodologies in detection of the anaerobic threshold. Circulation 81(suppl II):II-38–II-46
Meyers J, Walsh D, Buchanan N, Froelicher V (1989) Can maximal cardiopulmonary capacity by recognized by a plateau in oxygen uptake? Chest 96:1312–1316
Milani RV, Lavie CJ, Mehra MR, Ventura HO (2006) Understanding the basics of cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Mayo Clin Proc 81:1603–1611
Taylor H, Buskirk E, Henschel A (1955) Maximal oxygen uptake as an objective measurement of cardiorespiratory performance. J Appl Physiol 8:73–80
Yeh MP, Gardner RM, Adams TD, Yanowitz FG, Crapo RO (1983) Anaerobic threshold: problems of determination and validation. J Appl Physiol 55:1178–1186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, C., Kazmucha, J., Kim, N. et al. \( {V}_{\text{O}_{2}}\)@RER1.0: A Novel Submaximal Cardiopulmonary Exercise Index. Pediatr Cardiol 31, 50–55 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-009-9544-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-009-9544-9