Abstract
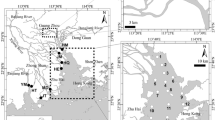
Occurrence of five endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs)—bisphenol-A (BPA), triclosan (TCS), 17α-ethinyl estradiol (EE2), benzophenone-3, and 4-methylbenzylidene camphor—were monitored in East Lake, the largest urban lake in China. Other than EE2, all selected EDCs were detected at least once in the lake water with concentrations ≤89.1 ng/L. EDCs were detected with greater occurrence in spring than in other seasons. In lake sediment, TCS was detected at the greatest concentration (30.9 ng g−1), whereas BPA and EE2 were not detected. Spatial distribution of the EDCs in the lake water and the lake sediment showed similar patterns, and greater EDC residuals were found from those sites with known wastewater input. The linear adsorption coefficients (K d) varied from 17.9 to 1,017 L kg−1 and were related to the octanol–water partition coefficient (K ow) values of the compounds. Photodegradation was a major process removing the EDCs from the lake water, and the presence of dissolved organic material and NO3 − in the lake water can accelerate the photodegradation process. Degradation of the EDCs in the lake sediment was relatively slow and occurred mainly due to the microbial processes. All compounds were found more persistent under anoxic conditions than under oxic conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anway MD, Cupp AS, Uzumcu M, Skinner MK (2005) Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science 308:1466–1469
Atkinson S, Marlatt V, Kimpe L, Lean DS, Trudeau V, Blais J (2011) Environmental factors affecting ultraviolet photodegradation rates and estrogenicity of estrone and ethinylestradiol in natural waters. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 60:1–7
Bahamonde PA, Tetreault GR, McMaster ME, Servos MR, Martyniuk CJ, Munkittrick KR (2014) Molecular signatures in rainbow darter (Etheostoma caeruleum) inhabiting an urbanized river reach receiving wastewater effluents. Aquat Toxicol 148:211–220
Birch S, McCaskie J (1999) Shallow urban lakes: a challenge for lake management. Hydrobiologia 395–396:365–378
Caliman FA, Gavrilescu M (2009) Pharmaceuticals, personal care products and endocrine disrupting agents in the environment—a review. Clean (Weinh) 37:277–303
Campbell CG, Borglin SE, Green FB, Grayson A, Wozei E, Stringfellow WT (2006) Biologically directed environmental monitoring, fate, and transport of estrogenic endocrine disrupting compounds in water: a review. Chemosphere 65:1265–1280
Chefetz B, Mualem T, Ben-Ari J (2008) Sorption and mobility of pharmaceutical compounds in soil irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 73:1335–1343
Chin Y-P, Miller PL, Zeng L, Cawley K, Weavers LK (2004) Photosensitized degradation of bisphenol A by dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 38:5888–5894
Chowdhury RR, Charpentier PA, Ray MB (2011) Photodegradation of 17β-estradiol in aquatic solution under solar irradiation: kinetics and influencing water parameters. J Photochem Photobiol A 219:67–75
Clara M, Strenn B, Saracevic E, Kreuzinger N (2004) Adsorption of bisphenol-A, 17β-estradiole and 17α-ethinylestradiole to sewage sludge. Chemosphere 56:843–851
Davey JC, Bodwell JE, Gosse JA, Hamilton JW (2007) Arsenic as an endocrine disruptor: effects of arsenic on estrogen receptor–mediated gene expression in vivo and in cell culture. Toxicol Sci 98:75–86
Dulin D, Mill T (1982) Development and evaluation of sunlight actinometers. Environ Sci Technol 16:815–820
Falconer IR, Chapman HF, Moore MR, Ranmuthugala G (2006) Endocrine-disrupting compounds: a review of their challenge to sustainable and safe water supply and water reuse. Environ Toxicol 21:181–191
Ge J, Liu M, Yun X, Yang Y, Zhang M, Li QX et al (2014) Occurrence, distribution and seasonal variations of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface waters of the East Lake, China. Chemosphere 103:256–262
Gong J, Ran Y, Chen D, Yang Y, Ma X (2009) Occurrence and environmental risk of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in surface waters of the Pearl River, South China. Environ Monit Assess 156:199–210
Jiang M, Wang L, Ji R (2010) Biotic and abiotic degradation of four cephalosporin antibiotics in a lake surface water and sediment. Chemosphere 80:1399–1405
Jin X, Xu Q, Huang C (2005) Current status and future tendency of lake eutrophication in China. Sci China C 48:948–954
Jin S, Yang F, Xu Y, Dai H, Liu W (2013) Risk assessment of xenoestrogens in a typical domestic sewage-holding lake in China. Chemosphere 93:892–898
Kameda Y, Kimura K, Miyazaki M (2011) Occurrence and profiles of organic sunblocking agents in surface waters and sediments in Japanese rivers and lakes. Environ Pollut 159:1570–1576
Karnjanapiboonwong A, Morse A, Maul J, Anderson T (2010) Sorption of estrogens, triclosan, and caffeine in a sandy loam and a silt loam soil. J Soil Sediment 10:1300–1307
Kawagoshi Y, Fujita Y, Kishi I, Fukunaga I (2003) Estrogenic chemicals and estrogenic activity in leachate from municipal waste landfill determined by yeast two-hybrid assay. J Environ Monit 5:269–274
Li W, Ma Y, Guo C, Hu W, Liu K, Wang Y et al (2007) Occurrence and behavior of four of the most used sunscreen UV filters in a wastewater reclamation plant. Water Res 41:3506–3512
Liu Z-H, Kanjo Y, Mizutani S (2009) Removal mechanisms for endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in wastewater treatment—physical means, biodegradation, and chemical advanced oxidation: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:731–748
Liu Y-S, Ying G-G, Shareef A, Kookana RS (2013) Degradation of six selected ultraviolet filters in aquifer materials under various redox conditions. Groundw Monit Remediat 33:79–88
Loftsson T, Össurardóttir Í, Thorsteinsson T, Duan M, Másson M (2005) Cyclodextrin solubilization of the antibacterial agents triclosan and triclocarban: effect of ionization and polymers. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 52:109–117
Mahler BJ, van Metre PC, Callender E (2006) Trends in metals in urban and reference lake sediments across the United States, 1970 to 2001. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1698–1709
Mayer T, Bennie D, Rosa F, Rekas G, Palabrica V, Schachtschneider J (2007) Occurrence of alkylphenolic substances in a Great Lakes coastal marsh, Cootes Paradise, ON, Canada. Environ Pollut 147:683–690
Nakada N, Shinohara H, Murata A, Kiri K, Managaki S, Sato N et al (2007) Removal of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) during sand filtration and ozonation at a municipal sewage-treatment plant. Water Res 41:4373–4382
Nélieu S, Kerhoas L, Sarakha M, Einhorn J (2004) Nitrite and nitrate induced photodegradation of monolinuron in aqueous solution. Environ Chem Lett 2:83–87
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (2002) Test no. 106: Adsorption-desorption using a batch equilibrium method. OECD, OECD Publishing
Peng X, Yu Y, Tang C, Tan J, Huang Q, Wang Z (2008) Occurrence of steroid estrogens, endocrine-disrupting phenols, and acid pharmaceutical residues in urban riverine water of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Sci Total Environ 397:158–166
Poiger T, Buser H-R, Balmer ME, Bergqvist P-A, Müller MD (2004) Occurrence of UV filter compounds from sunscreens in surface waters: regional mass balance in two Swiss lakes. Chemosphere 55:951–963
Pojana G, Gomiero A, Jonkers N, Marcomini A (2007) Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environ Int 33:929–936
Ribeiro C, Tiritan M, Rocha E, Rocha M (2009) Seasonal and spatial distribution of several endocrine-disrupting compounds in the Douro River Estuary, Portugal. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56:1–11
Rodil R, Moeder M, Altenburger R, Schmitt-Jansen M (2009) Photostability and phytotoxicity of selected sunscreen agents and their degradation mixtures in water. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1513–1524
Rosal R, Rodríguez A, Perdigón-Melón JA, Petre A, García-Calvo E, Gómez MJ et al (2010) Occurrence of emerging pollutants in urban wastewater and their removal through biological treatment followed by ozonation. Water Res 44:578–588
Sanchez-Prado L, Llompart M, Lores M, García-Jares C, Bayona JM, Cela R (2006) Monitoring the photochemical degradation of triclosan in wastewater by UV light and sunlight using solid-phase microextraction. Chemosphere 65:1338–1347
Sarmah AK, Northcott GL (2008) Laboratory degradation studies of four endocrine disruptors in two environmental media. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:819–827
Scalia S, Tursilli R, Iannuccelli V (2007) Complexation of the sunscreen agent, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor with cyclodextrins: effect on photostability and human stratum corneum penetration. J Pharm Biomed 44:29–34
Sidhu S, Gullett B, Striebich R, Klosterman J, Contreras J, DeVito M (2005) Endocrine disrupting chemical emissions from combustion sources: diesel particulate emissions and domestic waste open burn emissions. Atmos Environ 39:801–811
Stasinakis A, Mermigka S, Samaras V, Farmaki E, Thomaidis N (2012) Occurrence of endocrine disrupters and selected pharmaceuticals in Aisonas River (Greece) and environmental risk assessment using hazard indexes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1574–1583
Tan BLL, Hawker DW, Müller JF, Leusch FDL, Tremblay LA, Chapman HF (2007) Comprehensive study of endocrine disrupting compounds using grab and passive sampling at selected wastewater treatment plants in South East Queensland, Australia. Environ Int 33:654–669
Tuxen N, de Lipthay JR, Albrechtsen H-J, Aamand J, Bjerg PL (2002) Effect of exposure history on microbial herbicide degradation in an aerobic aquifer affected by a point source. Environ Sci Technol 36:2205–2212
United States Environmental Protection Agency (1998) Fate, transport and transformation test guidelines: OPPTS 835.2210 Direct photolysis rate in water by sunlight. EPA712-C-98-060
Vajda AM, Barber LB, Gray JL, Lopez EM, Bolden AM, Schoenfuss HL et al (2011) Demasculinization of male fish by wastewater treatment plant effluent. Aquat Toxicol 103:213–221
Venkatesan AK, Pycke BFG, Barber LB, Lee KE, Halden RU (2012) Occurrence of triclosan, triclocarban, and its lesser chlorinated congeners in Minnesota freshwater sediments collected near wastewater treatment plants. J Hazard Mater 229–230:29–35
Wang H, Wang C, Wu W, Wang Z (2002) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in surface sediments of Donghu Lake, Wuhan, Hubei, China. J Environ Sci Health A 37:499–507
Witorsch RJ, Thomas JA (2010) Personal care products and endocrine disruption: a critical review of the literature. Crit Rev Toxicol 40:1–30
Woodling JD, Lopez EM, Maldonado TA, Norris DO, Vajda AM (2006) Intersex and other reproductive disruption of fish in wastewater effluent dominated Colorado streams. Comp Biochem Physiol C 144:10–15
Wu C, Spongberg AL, Witter JD (2009) Adsorption and degradation of triclosan and triclocarban in soils and biosolids-amended soils. J Agric Food Chem 57:4900–4905
Yang Y, Huang X, Liu J (1998) Long-term changes in crustacean zooplankton and water quality in a shallow, eutrophic Chinese lake densely stocked with fish. Hydrobiologia 391:193–201
Yang T, Liu Q, Chan L, Liu Z (2007) Magnetic signature of heavy metals pollution of sediments: case study from the East Lake in Wuhan, China. Environ Geol 52:1639–1650
Yang Y, Zhang N, Xue M, Lu ST, Tao S (2011) Effects of soil organic matter on the development of the microbial polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) degradation potentials. Environ Pollut 159:591–595
Ying G-G, Kookana RS (2005) Sorption and degradation of estrogen-like-endocrine disrupting chemicals in soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2640–2645
Ying G-G, Kookana RS, Dillon P (2003) Sorption and degradation of selected five endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquifer material. Water Res 37:3785–3791
Ying G-G, Yu X-Y, Kookana RS (2007) Biological degradation of triclocarban and triclosan in a soil under aerobic and anaerobic conditions and comparison with environmental fate modelling. Environ Pollut 150:300–305
Yoon Y, Ryu J, Oh J, Choi B-G, Snyder SA (2010) Occurrence of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals, and personal care products in the Han River (Seoul, South Korea). Sci Total Environ 408:636–643
Zeng F, Cui K, Xie Z, Liu M, Li Y, Lin Y et al (2008) Occurrence of phthalate esters in water and sediment of urban lakes in a subtropical city, Guangzhou, South China. Environ Int 34:372–380
Zhang X, Zhang D, Zhang H, Luo Z, Yan C (2012) Occurrence, distribution, and seasonal variation of estrogenic compounds and antibiotic residues in Jiulongjiang River, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1392–1404
Zhao J-L, Ying G-G, Liu Y-S, Chen F, Yang J-F, Wang L (2010) Occurrence and risks of triclosan and triclocarban in the Pearl River system, South China: from source to the receiving environment. J Hazard Mater 179:215–222
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.41103064), the State Key Laboratory of Freshwater Ecology and Biotechnology (Grant No. 2014FBZ03), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Huang, X., Lin, J. et al. Occurrence and Fate of Selected Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in Water and Sediment from an Urban Lake. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68, 225–236 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0087-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0087-6