Abstract
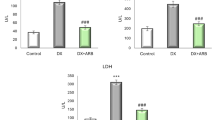
To evaluate the impact potential of nandrolone decanoate on DNA damage in multiple organs of Wistar rats by means of single-cell gel (comet) assay and micronucleus test. A total of 15 animals were distributed into three groups of five animals each as follows: control group = animal not exposed to nandrolone decanoate; experimental group = animals exposed to nandrolone decanoate for 24 h at 5 mg/kg subcutaneously; and experimental group = animals exposed to nandrolone decanoate for 24 h at 15 mg/kg subcutaneously. Significant statistical differences (p < 0.05) were noted in peripheral blood, liver, and heart cells exposed to nandrolone decanoate at the two doses evaluated. A clear dose–response relationship was observed between groups. Kidney cells showed genetic damage at only the highest dose (15 mg/kg) used. However, micronucleus data did not show remarkable differences among groups. In conclusion, the present study indicates that nandrolone decanoate induces genetic damage in rat blood, liver, heart, and kidney cells as shown by single-cell gel (comet) assay results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Shakra S, Alhalabi MS, Nachtman FC, Schemidt RA, Brusilow WS (1997) Anabolic steroids induce injury and apoptosis of differentiated skeletal muscle. J Neurosci Res 15(47):186–197
Alves MJ, Dos Santos MR, Dias RG, Akiho CA, Laterza MC, Rondon MU (2010) Abnormal neurovascular control in anabolic androgenic steroids users. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:865–871
Bronson FH (1996) Effects of prolonged exposure to anabolic steroids on the behavior of male and female mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:329–334
Califano J, Van Der Riet P, Westra W, Nawroz H, Clayman G, Piantadosi S et al (1996) Genetic progression model for head and neck cancer: Implications for field cancerization. Cancer Res 56:2488–2492
Dirix A, Knuttgen HE, Titell K (1988) Olympic book of sports medicine. Blackwell, London
do Carmo CA, Gonçalves AL, Salvadori DM, Maistro EL (2012) Nandrolone androgenic hormone presents genotoxic effects in different cells of mice. J Appl Toxicol 32:810–814
Fischer WH, Keiwan A, Schmitt E, Stopper H (2001) Increased formations of micronuclei alter hormonal stimulation of cell proliferation in human breast cancer cells. Mutagenesis 16:209–212
Fontana K, Aldrovani M, de Paoli F, Oliveira HC, de Campos Vidal B, da Cruz-Höfling MA (2008) Hepatocyte nuclear phenotype: The cross-talk between anabolic androgenic steroids and exercise in transgenic mice. Histol Histopathol 23:1367–1377
Hirotsu C, Tufik S, Ribeiro DA, Alvarenga TA, Andersen ML (2011) Genomic damage in the progression of chronic kidney disease in rats. Brain Behav Immun 25:416–422
Hurh YJ, Chen ZH, Na HK, Han SY, Surh YJ (2004) 2-Hydroxyestradiol induces oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in human mammary epithelial cells. J Toxicol Environ Health 67:1939–1953
Liehr JG (2000) Is estradiol a genotoxic mutagenic carcinogen? Endocr Rev 21:40–54
Martins RA, Gomes GA, Aguiar O Jr, Medalha CC, Ribeiro DA (2010) Chromosome damage and cytotoxicity in oral mucosa cells after 2 months of exposure to anabolic steroids (decadurabolin and winstrol) in weight lifting. Steroids 75:952–955
Metcalfe D, Watts E, Masters JP, Smith N (2012) Anabolic steroids in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. BMJ Open 22:2
Miller RC (1973) The micronucleus test as an in vivo cytogenetic method. Environ Health Perspect 6:167–170
Montisci M, El Mazloum R, Cecchetto G, Terranova C, Ferrara SD, Thiene G et al (2012) Anabolic androgenic steroids abuse and cardiac death in athletes: Morphological and toxicological findings in four fatal cases. Forensic Sci Int 217:e13–e18
Nishi EE, Campos RR, Bergamaschi CT, de Almeida VR, Ribeiro DA (2010) Vitamin C prevents DNA damage induced by renovascular hypertension in multiple organs of Wistar rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 29:593–599
Noguti J, Pereira VG, Martins AM, D’Almeida V, Ribeiro DA (2011) Genomic instability in blood cells from murine model of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. J Mol Histol 42:575–578
Olivie PL, Banath JP, Durand RE (1990) Heterogeneity in radiation-induced DNA damage and repair in tumor and normal cells measured using the comet assay. Radiat Res 112:86–94
Pitot HC (1993) The molecular biology of carcinogenesis. Cancer 72(Suppl 3):962–970
Pope JR, Katz DL (1988) Affective and psychotic symptoms associated with anabolic steroids use. Am J Psychiatry 145:487–490
Ribeiro DA, Grilli DG, Salvadori DM (2008) Genomic instability in blood cells is able to predict the oral cancer risk: An experimental study in rats. J Mol Histol 39:481–486
Scharhag J, Urhausen A, Kindermann W (2003) Anabolic steroid-induced echocardiographic characteristics of professional football players? J Am Coll Cardiol 42:588–589
Schuler M, Hasegawar L, Parks R, Metzler M, Eastmond DA (1998) Dose–response studies of the induction of hyperdiploidy and polyploidy by diethylstilbestrol and 17 β-estradiol in cultured human lymphocytes using multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. Environ Mol Mutagen 31:263–273
Stich HF, Parida BB, Brunnemann KD (1992) Localized formation of micronuclei in the oral mucosa and tobacco-specific nitrosamines in the saliva of “reverse” smokers, Khaini-tobacco chewers and gudakhu users. Int J Cancer 50:172–176
Su T, Pagliaro M, Schmidt PJ, Pickar D, Wolkowitz O, Rubinow DR (1993) Neuropsychiatric effects of anabolic steroids in male normal volunteers. JAMA 269:2760–2764
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H et al (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: Guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Torres-Bugarín O, Covarrubias-Bugarín R, Zamora-Perez AL, Torres-Mendoza BMG, García-Ulloa M, Martínez-Sandoval FG (2007) Anabolic androgenic steroids induce micronuclei in buccal mucosa cells of bodybuilders. Br J Sports Med 41:592–596
Wahnschaffe U, Bitsch A, Kielhorn J, Mangelsdorf I (2005) Mutagenicity testing with transgenic mice. Part 1: Comparison with the mouse bone marrow micronucleus test. Carcinogenesis 4:3
Zaugg M, Jamali NZ, Lucchinetti E, Xu W, Alam M, Shafiq SA et al (2001) Anabolic-androgenic steroids induce apoptotic cell death in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J Cell Physiol 187:90–95
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnologico and CAPES. D. A. R. is the recipient of fellowship from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pozzi, R., Fernandes, K.R., de Moura, C.F.G. et al. Nandrolone Decanoate Induces Genetic Damage in Multiple Organs of Rats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64, 514–518 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9848-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9848-2