Abstract
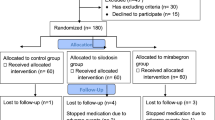
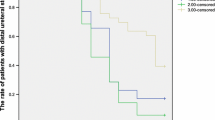
We performed a randomized, prospective study to assess the possible role of combined naftopidil and tolterodine for facilitating the spontaneous expulsion of intramural ureteral stones. A total of 76 patients with intramural ureter stones were included in the study from December 2007 to February 2011. Patients were randomized to one of three treatment groups. Group A patients received naftopidil 25 mg/day, group B patients received naftopidil 25 mg/day plus tolterodine 2 mg (twice a day), and group C patients received tolterodine 2 mg (twice a day). Both groups were followed up for 2 weeks. The stone expulsion rate and time and the number of pain episodes were obtained. Subjects rated the urgency associated with each micturition using the Urinary Sensation Scale (USS). Pain descriptions were recorded by the patients using the visual analog scale (VAS). A significant difference was shown for the expulsion rate between the group C and the other two groups (P < 0.001 by log rank test). In groups A, B and C, the mean number of pain episodes was 2.25 ± 0.90, 1.38 ± 1.37 and 1.54 ± 1.18, respectively. The USS score for groups A, B and C at 3 days was 2.32 ± 0.55, 1.4 ± 0.58 and 1.34 ± 0.49, respectively. It was 1.75 ± 0.44, 1.2 ± 0.41 and 1.22 ± 0.42, respectively, at 7 days. On the other hand, a statistically significant difference was found between groups A and B, and groups A and C in relation to the visual analog scale score on days 3 and 7, respectively. Treatment with naftopidil and tolterodine appears to be beneficial in intramural ureteral stones clearance, particularly in the intramural ureter with symptoms of vesical irritability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou SG, Lu JL, Hui JH (2011) Comparing efficacy of α1D-receptor antagonist naftopidil and α1A/D-receptor antagonist tamsulosin in management of distal ureteral stones. World J Urol 29:767–771
Dellabella M, Milanese G, Muzzonigro G (2003) Efficacy of tamsulosin in the medical management of juxtavesical ureteral stones. J Urol 170:2202–2205
Itoh Y, Kojima Y, Yasui T, Tozawa K, Sasaki S, Kohri K (2007) Examination of alpha 1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the human ureter. Int J Urol 14:749–753
Sigala S, Dellabella M, Milanese G et al (2004) Alpha-1adrenoceptor subtypes in men juxtavesical ureters: molecular and pharmacological characterization. Eur Urol 3:119
Cervenakov I, Fillo J, Mardiak J et al (2002) Speedy elimination of ureterolithiasis in lower part of ureters with the alpha-1 blocker—tamsulosin. Int Urol Nephrol 34:25–29
Canda AE, Turna B, Cinar GM, Nazli O (2007) Physiology and pharmacology of the human ureter: basis for current and future treatments. Urol Int 78:289–298
Sigala S, Dellabella M, Milanese G et al (2005) Evidence for the presence of α1 adrenoceptor subtypes in the human ureter. Neurourol Urodynam 24:142–148
Nishino Y, Masue T, Miwa K, Takahashi Y, Ishihara S, Deguchi T (2006) Comparison of two alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists, naftopidil and tamsulosin hydrochloride, in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized crossover study. BJU Int 97:747–751
Yilmaz E, Batislam E, Basar MM, Tuglu D, Ferhat M, Basar H (2005) The comparison and efficacy of 3 different alpha1-adrenergic blockers for distal ureteral stones. J Urol 713:2010–2012
Porpiglia F, Vaccino D, Billia M et al (2006) Corticosteroids and tamsulosin in the medical expulsive therapy for symptomatic distal ureter stones: single drug or association? Eur Urol 50:339–344
Takei R, Ikegaki I, Shibata K, Tsujimoto G, Asano T (1999) Naftopidil, a novel alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonist, displays selective inhibition of canine prostatic pressure and high affinity binding to cloned human alpha1-adrenoceptors. Jpn J Pharmacol 79:447–454
Hubner WA, Irby P, Stoller ML (1993) Natural history and current concepts for the treatment of small ureteral calculi. Eur Urol 24:172
Ueno A, Kawamura T, Ogawa A, Takayasu H (1977) Relation of spontaneous passage of ureteral calculi to size. Urology 10:544
Coll DM, Varanelli MJ, Smith RC (2002) Relationship of spontaneous passage of ureteral calculi to stone size and location as revealed by unenhanced helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:101
Shokeir AA (2001) Renal colic: pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Eur Urol 39:241–249
Borghi L, Meschi T, Amato F et al (1994) Nifedipine and methylprednisolone in facilitating ureteral stone passage: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Urol 152:1095
Porpiglia F, Destefanis P, Fiori C, Fontana D (2000) Effectiveness of nifedipine and deflazacort in the management of distal ureter stones. Urology 56:579
Morita T, Wada I, Saeki H, Tsuchida S, Weiss RM (1987) Ureteral urine transport: changes in bolus volume, peristaltic frequency, intraluminal pressure and volume of flow resulting from autonomic drugs. J Urol 137:132–135
Sun XZ, He L, Ge WH, Lv JL (2009) Efficacy of selective alpha1D-blocker naftopidil as medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteral stones. J Urol 181:1716–1720
Agrawal M, Gupta M, Gupta A, Agrawal A, Sarkari A, Lavania P (2009) Prospective randomized trial comparing efficacy of alfuzosin and tamsulosin in management of lower ureteral stones. Urology. 73:706–709
Al-Ansari Abdulla, Al-Naimi Abdulla, Alobaidy Abdulkader et al (2010) Efficacy of tamsulosin in the management of lower ureteral stones: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of 100 patients. Urology 75:4–7
Lv JL, Tang QN, Hui JH (2011) Efficacy of tolterodine for medical treatment of intramural ureteral stone with vesical irritability. Urol Res 39:213–216
Elinoff V, Bavendam T, Glasser DB et al (2006) Symptom-specific efficacy of tolterodine extended release in patients with overactive bladder: the IMPACT trial. Int J Clin Pract 60:745–751
Roberts R, Bavendam T, Glasser DB et al (2006) Tolterodine extended release improves patient-reported outcomes in overactive bladder: results from the IMPACT trial. Int J Clin Pract 60:752–758
Erturhan S, Erbagci A, Yagci F, Celik M, Solakhan M, Sarica K (2007) Comparative evaluation of efficacy of use of tamsulosin and/or tolterodine for medical treatment of distal ureteral stones. Urology 69(4):633–636
Brewster-Jordan JL, Guan Z, Green HL, et al. Establishing the content validity of the Urinary Sensation Scale (USS). Presented at a meeting of the international society for pharmacoeconomics and outcomes research, Washington, DC, 15–18 May 2005
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J.L., Tang, Q.L., De Liu, F. et al. Naftopidil and tolterodine in the medical expulsive therapy for intramural ureteral stones: a prospective randomized study. Urol Res 40, 757–762 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-012-0498-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-012-0498-7