Abstract
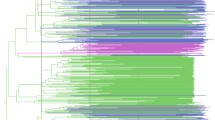
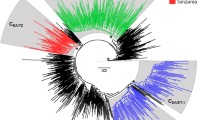
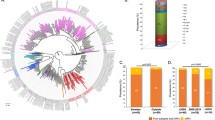
HIV, the cause of AIDS in humans, is characterized by great genetic heterogeneity. In particular, HIV-1 group M subtypes are responsible for most of the infections worldwide. We investigate the demographic history of HIV-1B and HIV-1C subtypes in South Africa and Brazil using both a parametric and a nonparametric approach based on coalescent theory. Our results show that although both subtypes are spreading exponentially in Brazil, the HIV-1C growth rate is about twice that of Brazilian HIV-1B or South African HIV-1C, providing evidence, for the first time, of a different epidemic potential between two HIV-1 subtypes. The present study not only may have important consequences for devising future vaccination and therapeutic strategies, but also offers additional evidence that skyline plots are indeed a simple and powerful tool for monitoring and predicting the behavior of viral epidemics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Bjorndal A Sonnerborg J Tscherning C Albert EM Fenyo (1999) ArticleTitlePhenotypic characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C isolates of Ethiopian AIDS patients AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 15 647–653 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjtFCrsbs%3D Occurrence Handle10331443
F Clavel M Guyader D Guetard M Salle L Montagnier M Alizon (1986) ArticleTitleMolecular cloning and polymorphism of the human immune deficiency virus type 2 Nature 324 691–695 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXnvFCmsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3025743
M Cornelissen R Burg Particlevan den F Zorgdrager V Lukashov J Goudsmit (1997) ArticleTitlePol gene diversity of five human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes: evidence for naturally occurring mutations that contribute to drug resistance, limited recombination patterns, and common ancestry for subtypes B and D J Virol 71 6348–6358 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXlsVKqtLg%3D Occurrence Handle9261352
Department of Health/Directorate Health Systems Research (2001) Seventh national HIV survey of woman attending antenatal clinics of the public health service of South Africa. October/November 2000. Directorate Health Systems Research. Department of Health, Pretoria, South Africa
AT Dumans MA Soares D Pieniazek ML Kalish V Vroey ParticleDe K Hertogs A Tanuri (2002) ArticleTitlePrevalence of protease and reverse transcriptase drug resistance mutations over time in drug-naive human immunodeficiency virus type 1-positive individuals in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46 3075–3079 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xmtl2kurk%3D Occurrence Handle12183276
J Esparza N Bhamarapravati (2000) ArticleTitleAccelerating the development and future availability of HIV-1 vaccines: why, when, where, and how? Lancet 355 2061–2066 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czjvFyktQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10885368
F Gao E Bailes DL Robertson Y Chen CM Rodenburg SF Michael LB Cummins LO Arthur M Peeters GM Shaw PM Sharp BH Hahn (1999) ArticleTitleOrigin of HIV-1 in the chimpanzee Pan troglodytes troglodytes Nature 397 436–441 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhtFOht7g%3D Occurrence Handle9989410
M Gordon T Oliveira ParticleDe K Bishop HM Coovadia L Madurai S Engelbrecht E Janse Rensburg Particlevan A Mosam A Smith S Cassol (2003) ArticleTitleMolecular characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C viruses from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa: implications for vaccine and antiretroviral control strategies J Virol 77 2587–2599 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvVGmug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12551997
RC Griffiths S Tavarè (1994) ArticleTitleSampling theory for neutral alleles in a varying environment Philos Trans. R Soc London Ser B 344 403–410 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqD1MfovFA%3D
BH Hahn GM Shaw SK Arya M Popovic RC Gallo F Wong-Staal (1984) ArticleTitleMolecular cloning and characterization of the HTLV-III virus associated with AIDS Nature 312 166–169 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhtlOg Occurrence Handle6095086
GM Jenkins A Rambaut OG Pybus EC Holmes (2002) ArticleTitleRates of molecular evolution in RNA viruses: a quantitative phylogenetic analysis J Mol Evol 54 156–165 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhtVCgurs%3D Occurrence Handle11821909
JFC Kingman (1982) ArticleTitleThe coalescent Stoch Proc Appl 13 235–248
B Korber M Muldoon J Theiler F Gao R Gupta A Lapedes BH Hahn S Wolinsky T Bhattacharya (2000) ArticleTitleTiming the ancestor of the HIV-1 pandemic strains Science 288 1789–1796 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFCisro%3D Occurrence Handle10846155
FE McCutchan (2000) ArticleTitleUnderstanding the genetic diversity of HIV-1 AIDS 14 S31–S44 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosFymsL8%3D Occurrence Handle11086847
M Peeters PM Sharp (2000) ArticleTitleGenetic diversity of HTV-1: the moving target AIDS 14 IssueIDSuppl 13 S129–S140 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXosFymsLw%3D Occurrence Handle11086856
OG Pybus A Rambaut (2002) ArticleTitleGENIE: estimating demographic history from molecular phylogenies Bioinformatics 18 1404–1405 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnvF2ru7o%3D Occurrence Handle12376389
OG Pybus A Rambaut PH Harvey (2000) ArticleTitleAn integrated framework for the inference of viral population history from reconstructed genealogies Genetics 155 1429–1437 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvgsVSnuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10880500
OG Pybus MA Charleston S Gupta A Rambaut EC Holmes PH Harvey (2001) ArticleTitleThe epidemic behavior of the hepatitis C virus Science 292 2323–2325 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkslSht78%3D Occurrence Handle11423661
A Rambaut (2000) ArticleTitleEstimating the rate of molecular evolution: incorporating non-contemporaneous sequences into maximum likelihood phylogenies Bioinformatics 16 395–399 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltFOlu7c%3D Occurrence Handle10869038
KE Robbins P Lemey OG Pybus HW Jaffe AS Youngpairoj TM Brown M Salemi A-M Vandamme ML Kalish (2003) ArticleTitleU.S. human immunodeficiency virus type 1 epidemic:date of origin, population history, and characterization of early strains J Virol 77 6359–6366 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktV2nsrc%3D Occurrence Handle12743293
DL Robertson JP Anderson JA Bradac et al. (2000) ArticleTitleHIV-1 nomenclature proposal Science 288 55–56 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXisVCqsLo%3D Occurrence Handle10766634
M Salemi M Lewis JF Egan WW Hall J Desmyter A-M Vandamme (1999) ArticleTitleDifferent population dynamics of human T cell lymphotropic virus type II in intravenous drug users compared with endemically infected tribes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96 13253–13258 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXns1Gmtrg%3D Occurrence Handle10557307
M Salemi K Strimmer WW Hall M Duffy E Delaporte S Mboup M Peeters A-M Vandamme (2001) ArticleTitleDating the common ancestor of SIVcpz and HIV-1 group M and the origin of HIV-1 subtypes using a new method to uncover clock-like molecular evolution FASEB J 15 276–278 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhsFentbc%3D Occurrence Handle11156935
MO Salminen JK Carr DS Burke FE McCutchan (1995) ArticleTitleIdentification of breakpoints in intergenotypic recombinants of HIV type 1 by bootscanning AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 11 1423– 1425 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitlKlsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8573403
Simon F, Mauclere P, Roques P, Loussert-Ajaka I, Muller-Trutwin MC, Sargosti S, Georges-Courbot MC, Barre-Sinoussi F, Brun-Vezinet F (1998) Indentification of a new human immunodeficiency virus type 1 distinct from group M and group O. Nat Med 4:1032–1037
MA Soares T Oliveira ParticleDe RM Brindeiro et al. (2003) ArticleTitleA specific subtype C of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 circulates in Brazil AIDS 17 11–21 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XpsVSrsrc%3D Occurrence Handle12478065
K Strimmer OG Pybus (2001) ArticleTitleExploring the demographic history of DNA sequences using the generalized skyline plot Mol Biol Evol 18 2298–2305 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXptFCrsLY%3D Occurrence Handle11719579
DL Swofford J Sullivan (2003) Phylogeny inference based on parsimony and other methods with PAUP* A-M Salemi M Vandame (Eds) The phylogenetic handbook—A practical approach to DNA and protein phylogeny Cambridge University Press New York
Y Tanaka K Hanada M Mizokami AET Yeo J Wai-Kuo Shih T Gojobori HJ Alter (2002) ArticleTitleA comparison of the molecular clock of hepatitis C virus in the United States and Japan predicts that hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in the United States will increase over the next two decades Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99 15584–15589 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjvVyl Occurrence Handle12438687
JD Thompson DG Higgins TJ Gibson (1994) ArticleTitleCLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice Nucleic Acids Res 22 4673– 4680 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitlSgu74%3D Occurrence Handle7984417
InstitutionalAuthorNameUN AIDS/WHO Working Group on Global HIV/AIDS and STD Surveillance (2000) Report on the global HIV/AIDS epidemic UN AIDS Geneva
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Flemish Funds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (FWO Grants G.0288.01 and KAN2002 1.5.193.02, Postdoctoral Onderzoeker Contract 530).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Reviewing Editor: Dr. Yves Van de Peer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salemi, M., de Oliveira, T., Soares, M.A. et al. Different Epidemic Potentials of the HIV-1B and C Subtypes. J Mol Evol 60, 598–605 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0206-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0206-5