Abstract
Introduction
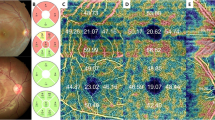
To investigate the association of quantitative 3-T diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) with retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness measured by optical coherence tomography (OCT) and clinical severity in detecting optic nerve degeneration in patients with primary closed-angle glaucoma.
Methods
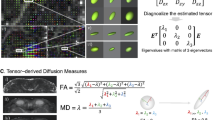
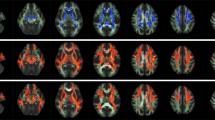
Twenty three patients (42 eyes; 9 men, 14 women) with primary closed-angle glaucoma and 20 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. Both DTI and OCT were performed on the optic nerves of all subjects. The mean diffusivity (MD), fractional anisotropy (FA), and eigenvalue maps were obtained for quantitative analysis. RNFL thickness and quantitative electrophysiology were also performed on all subjects. The association of quantitative DTI with RNFL thickness and glaucoma stage was analyzed.
Results
Compared with control nerves, the FA, λ‖, and λ⊥ values, and RNFL thickness in affected nerves decreased, while MD increased in patients with primary glaucoma (p < 0.05). There was a significant correlation between FA, MD, λ‖, and λ⊥ and the mean RNFL thickness (P < 0.01). The mean FA and λ⊥ values derived with DT MR imaging correlated well with glaucoma stage (P < 0.05), but the mean MD and λ‖ values did not correlate with glaucoma stage (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
DTI measurement could detect abnormality of the optic nerve in patients with glaucoma and may serve as a biomarker of disease severity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harwerth RS, Quigley HA (2006) Visual field defects and retinal ganglion cell losses in patients with glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 124:853–859
Lalezary M, Medeiros FA, Weinreb RN et al (2006) Baseline optical coherence tomography predicts the development of glaucomatous change in glaucoma suspects [J]. Am J Ophthalmol 142:576–582
Garaci FG, Bolacchi F, Cerulli A et al (2009) Optic nerve and optic radiation neurodegeneration in patients with glaucoma: in vivo analysis with 3-T diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 252:496–501
Trip SA, Wheeler-Kingshott C, Jones SJ et al (2006) Optic nerve diffusion tensor imaging in optic neuritis. NeuroImage 30:498–505
Wang MY, Qi PH, Shi DP (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging of the optic nerve in subacute anterior ischemic optic neuropathy at 3 T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1188–1194
Hodapp E, Parrish RK, Anderson DR (1993) Clinical decisions in glaucoma. Mosby, St. Louis
Parikh RS, Parikh S, Sekhar GC et al (2007) Diagnostic capability of optical coherence tomography (Stratus OCT 3) in early glaucoma. Ophthalmology 114:2238–2243
Zangwill LM, Williams J, Berry CC et al (2000) A comparison of optical coherence tomography and retinal nerve fiber layer photography for detection of nerve fiber layer damage in glaucoma. Ophthalmology 107:1309–1315
Greenberg G, Mikulis DJ, Ng K et al (2008) Use of diffusion tensor imaging to examine subacute white matter injury progression in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 89:S45–S50
Yucel YH, Kalichman MW, Mizisin AP et al (1999) Histomorphometric analysis of optic nerve changes in experimental glaucoma. J Glaucoma 8:38–45
Engelhorn T, Michelson G, Waerntges S et al (2012) A new approach to assess intracranial white matter abnormalities in glaucoma patients: changes of fractional anisotropy detected by 3T diffusion tensor imaging. Acad Radiol 19:485–488
Michelson G, Engelhorn T, Wärntges S, El Rafei A, Hornegger J, Doerfler A (2012) DTI parameters of axonal integrity and demyelination of the optic radiation correlate with glaucoma indices. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. doi:10.1007/s00417-011-1887-2
Alexander AL, Hasan K, Kindlmann G et al (2000) A geometric comparison of diffusion anisotropy measures. Magn Reson Med 44:283–291
Song SK, Sun SW, Ramsbottom MJ et al (2002) Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. NeuroImage 17:1429–1436
Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN et al (2010) Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer progression in glaucoma: a study on optical coherence tomography guided progression analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:217–222
Urcola JH, Hernández M, Vecino E (2006) Three experimental glaucoma models in rats: comparison of the effects of intraocular pressure elevation on retinal ganglion cell size and death. Exp Eye Res 83:429–437
Son JL, Soto I, Oglesby E et al (2010) Glaucomatous optic nerve injury involves early astrocyte reactivity and late oligodendrocyte loss. Glia 58:780–789
Pueyo V, Martin J, Fernandez J et al (2008) Axonal loss in the retinal nerve fiber layer in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 14:609–614
Taliantzis S, Papaconstantinou D, Koutsandrea C et al (2009) Comparative studies of RNFL thickness measured by OCT with global index of visual fields in patients with ocular hypertension and early open angle glaucoma. Clin Ophthalmol 3:373–379
Nucci C, Mancino R, Martucci A et al (2012) 3-T Diffusion tensor imaging of the optic nerve in subjects with glaucoma: correlation with GDx-VCC, HRT-III and Stratus optical coherence tomography findings. Br J Ophthalmol 96:976–980
Khong PL, Zhou LJ, Cheng OG, Chung B, Cheung RT, Wong V (2004) The evaluation of wallerian degeneration in chronic paediatric middle cerebral artery infarction using diffusion tensor MR imaging. Cerebrovasc Dis 18:240–247
Bolacchi F, Garaci FG, Martucci A et al (2012) Differences between proximal versus distal intraorbital optic nerve diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging properties in glaucoma patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:4191–4196
Techavipoo U, Okai AF, Lackey et al (2009) Toward a practical protocol for human optic nerve DTI with EPI geometric distortion correction. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:699–707
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yongming Dai, MRI Department of Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, for technical guidance. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81271534 and 81271565, the Distinguished Scholar in Scientific and Technical Innovation Foundation of Henan Province under Grant No. 074200510015, the Distinguished Young Scholar in Scientific and Technical Innovation Foundation of Henan Province under Grant No. 124100510016, and the Science and Technology Foundation of Public Health of Henan Province under Grant Nos. 201202018 and 201003095.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Tian and Dapeng Shi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, MY., Wu, K., Xu, JM. et al. Quantitative 3-T diffusion tensor imaging in detecting optic nerve degeneration in patients with glaucoma: association with retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and clinical severity. Neuroradiology 55, 493–498 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1133-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1133-1