Abstract
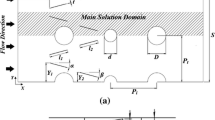
Delta winglet works better than other vortex generators in improving the performance of fin-tube heat exchangers. In this paper, Response Surface Approximation is used to study the effects of the fin pitch, the ratio of the longitudinal tube pitch to transverse tube pitch, the ratio of both sides V 1 , V h of delta winglets and the attack angle of delta winglets on the performance of fin-tube heat exchanger. Firstly, Twenty-nine numerical group experiments including five times repeated experiments at the central point are conducted. Then, the analyses of variable (ANOVA) and regression are performed to verify the accuracy of the polynomial coefficients. Finally, the optimization of the fin-tube heat exchanger using the Genetic Algorithm is conducted and the best performance of j/f (1/3) is found to be 0.07945, which is consistent with the numerical result.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiin-Yuh J, Mu-Cheng W, Wen-Jeng C (1996) Numerical and experimental studies of three-dimensional plate-fin and tube heat exchangers. Int J Heat Mass Transf 39:3083
Xi G, Ebisu T, Torikoshi K (1997) Differences in simulation with two-and three-dimensional models for finned tube heat exchangers. Transport Phenomena in Thermal Science and Process Engineering, Kyoto, Japan, pp 755–760
Tsai S, Sheu TW (1998) Some physical insights into a two-row finned-tube heat transfer. Comput Fluids 27:29–46
Wang C-C, Lo J, Lin Y-T, Wei C-S (2002) Flow visualization of annular and delta winlet vortex generators in fin-and-tube heat exchanger application. Int J Heat Mass Trans 45
Tao YB, He YL, Huang J, Wu ZG, Tao WQ (2007) Numerical study of local heat transfer coefficient and fin efficiency of wavy fin-and-tube heat exchangers. Int J Therm Sci 46:768–778
Tao YB, He YL, Huang J, Wu ZG, Tao WQ (2007) Three-dimensional numerical study of wavy fin-and-tube heat exchangers and field synergy principle analysis. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:1163–1175
Tao YB, He YL, Wu ZG, Tao WQ (2007) Three-dimensional numerical study and field synergy principle analysis of wavy fin heat exchangers with elliptic tubes. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 28:1531–1544
Qu Z, Tao W, He Y (2004) Three-dimensional numerical simulation on laminar heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics of strip fin surface with X-arrangement of strips. J Heat Transfer 126:697
Huisseune H, T’Joen C, De Jaeger P, Ameel B, De Schampheleire S, De Paepe M (2013) Influence of the louver and delta winglet geometry on the thermal hydraulic performance of a compound heat exchanger. Int J Heat Mass Transf 57:58–72
Bergles AE (2002) ExHFT for fourth generation heat transfer technology. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 26:335–344
Edwards FJ, GJRA (1974) The improvement of forces convection surface heat transfer using surfaces protrusions in the form of (A) cubes and (B) vortex generators. Proceedings of the 5th international conference on heat transfer, Tokyo vol. 2: pp. 244–248
Leu J-S, Wu Y-H, Jang J-Y (2004) Heat transfer and fluid flow analysis in plate-fin and tube heat exchangers with a pair of block shape vortex generators. Int J Heat Mass Transf 47:4327–4338
Gholami AA, Wahid MA, Mohammed HA (2014) Heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop for fin-and-tube compact heat exchangers with wavy rectangular winglet-type vortex generators. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 54:132–140
Wu JM, Tao WQ (2008) Numerical study on laminar convection heat transfer in a channel with longitudinal vortex generator. Part B: parametric study of major influence factors. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:3683–3692
Wu JM, Tao WQ (2008) Numerical study on laminar convection heat transfer in a rectangular channel with longitudinal vortex generator. Part A: verification of field synergy principle. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:1179–1191
Biswas G, Torii K, Fujii D, Nishino K (1996) Numerical and experimental determination of flow structure and heat transfer effects of longitudinal vortices in a channel flow. Int J Heat Mass Transf 39:3441–3451
Gentry MC, Jacobi AM (2002) Heat transfer enhancement by delta-wing-generated tip vortices in flat-plate and developing channel flows. J Heat Transfer 124:1158
Joardar A, Jacobi AM (2008) Heat transfer enhancement by winglet-type vortex generator arrays in compact plain-fin-and-tube heat exchangers. Int J Refrig 31:87–97
Li J, Wang S, Chen J, Lei Y-G (2011) Numerical study on a slit fin-and-tube heat exchanger with longitudinal vortex generators. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:1743–1751
Tian L, He Y, Tao Y, Tao W (2009) A comparative study on the air-side performance of wavy fin-and-tube heat exchanger with punched delta winglets in staggered and in-line arrangements. Int J Therm Sci 48:1765–1776
Du X, Feng L, Li L, Yang L, Yang Y (2014) Heat transfer enhancement of wavy finned flat tube by punched longitudinal vortex generators. Int J Heat Mass Transf 75:368–380
Wu XH, Zhang WH, Gou QP, Luo ZM, Lu YL (2014) Numerical simulation of heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics of composite fin. Int J Heat Mass Transf 75:414–424
Zhou G, Feng Z (2014) Experimental investigations of heat transfer enhancement by plane and curved winglet type vortex generators with punched holes. Int J Therm Sci 78:26–35
Xia HH, Tang GH, Shi Y, Tao WQ (2014) Simulation of heat transfer enhancement by longitudinal vortex generators in dimple heat exchangers. Energy 74:27–36
Wu XH, Zhang WH, Lu YL, Gou QP, Luo ZM (2014) Performance evaluation and optimization of semi-dimpled slit fin. Heat Mass Transf 50:1251–1259
Li M, Zhou W, Zhang J et al (2014) Heat transfer and pressure performance of a plain fin with radiantly arranged winglets around each tube in fin-and-tube heat transfer surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf 70:734–744
Wu JM, Tao WQ (2008) Numerical study on laminar convection heat transfer in a rectangular channel with longitudinal vortex generator. Part a: verification of field synergy principle. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51(5–6):1179–1191
Zhou G, Ye Q (2012) Experimental investigations of thermal and flow characteristics of curved trapezoidal winglet type vortex generators. Appl Therm Eng 37:241–248
Lei Y-G, He Y-L, Tian L-T, Chu P, Tao W-Q (2010) Hydrodynamics and heat transfer characteristics of a novel heat exchanger with delta-winglet vortex generators. Chem Eng Sci 65:1551–1562
Queipo NV, Haftka RT, Shyy W, Goel T, Vaidyanathan R, Kevin Tucker P (2005) Surrogate-based analysis and optimization. Prog Aerosp Sci 41:1–28
Van Doormaal J, Raithby G (1984) Enhancements of the SIMPLE method for predicting incompressible fluid flows. Numer Heat Trans 7:147–163
Kraus AD, Aziz A, Welty J (2002) Extended surface heat transfer. Wiley, New York
Bezerra MA, Santelli RE, Oliveira EP, Villar LS, Escaleira LA (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76:965–977
Yang X-S (2014) Chapter 5—genetic algorithms. In: Yang X-S (ed) Nature-inspired optimization algorithms. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 77–87
Gosselin L, Tye-Gingras M, Mathieu-Potvin F (2009) Review of utilization of genetic algorithms in heat transfer problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:2169–2188
Beigzadeh R, Rahimi M, Parvizi M (2013) Experimental study and genetic algorithm-based multi-objective optimization of thermal and flow characteristics in helically coiled tubes. Heat Mass Transf 49:1307–1318
Peng H, Ling X (2008) Optimal design approach for the plate-fin heat exchangers using neural networks cooperated with genetic algorithms. Appl Therm Eng 28:642–650
Xie GN, Sunden B, Wang QW (2008) Optimization of compact heat exchangers by a genetic algorithm. Appl Therm Eng 28:895–906
Yousefi M, Enayatifar R, Darus AN (2012) Optimal design of plate-fin heat exchangers by a hybrid evolutionary algorithm. Int Commun Heat Mass Transfer 39:258–263
Ghosh S, Ghosh I, Pratihar DK, Maiti B, Das PK (2011) Optimum stacking pattern for multi-stream plate-fin heat exchanger through a genetic algorithm. Int J Therm Sci 50:214–224
Ponce-Ortega JM, Serna-González M, Jiménez-Gutiérrez A (2009) Use of genetic algorithms for the optimal design of shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Appl Therm Eng 29:203–209
Guo J, Cheng L, Xu M (2009) Optimization design of shell-and-tube heat exchanger by entropy generation minimization and genetic algorithm. Appl Therm Eng 29:2954–2960
Hariharan NM, Sivashanmugam P, Kasthurirengan S (2012) Optimization of ther-moacoustic primemover using response surface methodology. HVAC&R Res 18:890–903
Acknowledgements
The present work is supported by the Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51476148) and Excellent Youth Foundation of He’nan Scientific Committee (154100510014) and Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Project of Zhengzhou City (131PLJRC640).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Liu, D., Zhao, M. et al. The optimization of fin-tube heat exchanger with longitudinal vortex generators using response surface approximation and genetic algorithm. Heat Mass Transfer 52, 1871–1879 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1709-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1709-x