Abstract
Purpose
Sonidegib prevents activation of the Hedgehog signal transduction pathway. This PK-QT analysis has been performed to test for potential prolongation of the QT/QTc interval during extended use, and to understand the exposure-QT relationship for sonidegib in patients and in healthy volunteers (HV).
Methods
A pooled analysis of the change in QT interval corrected for heart rate according to Fridericia’s formula was conducted across four patient studies from a total of 341 patients (n = 211, 102, 21, and 7 from the phase II pivotal study A2201, study X2101, study X1101, and study B2209, respectively), and across four healthy volunteer studies from a total of 204 healthy volunteers (n = 146, 36, 16, and 6 from study A2114, study A1102, study A2108, and study A2110, respectively). A PK/ECG subgroup of 62 patients from the pivotal study A2201 was also analyzed to assess the QT prolongation risk at steady-state exposures. Sonidigib PK and ECG data were matched to determine the change from baseline in QTcF using a linear mixed-effect model.
Results
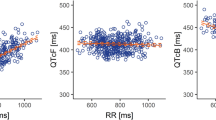
Clinical data indicate sonidegib does not cause QTc prolongation. ΔQTcF at steady-state concentrations for both 200 and 800-mg doses were all below 5 ms.
The highest mean ΔQTcF at steady state was −3.9 ms at week 17 pre-dose in the sonidegib 200-mg group and 2.7 ms at 2-h post-dose in the sonidegib 800-mg group. The upper one-sided 95 % confidence interval of the estimated ΔQTcF at steady-state concentrations from the linear mixed-effect models were all <10 ms. No cases of ventricular arrhythmia or torsades de pointes and no deaths associated with QT prolongation have been reported in the sonidegib clinical development program.
Conclusions
Based on these analyses, there is no evidence of QT prolongation associated with sonidegib 200 or 800 mg in solid tumor patients and HV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan S, Wu X, Jiang J, Gao W, Wan Y, Cheng D, Han D, Liu J, Englund NP, Wang Y, Peukert S, Miller-Moslin K, Yuan J, Guo R, Matsumoto M, Vattay A, Jiang Y, Tsao J, Sun F, Pferdekamper AC, Dodd S, Tuntland T, Maniara W, Kelleher JF 3rd, Yao YM, Warmuth M, Williams J, Dorsch M (2010) Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective smoothened antagonist. ACS Med Chem Lett 1(3):130–134. doi:10.1021/ml1000307
Ruiz-Gomez A, Molnar C, Holguin H, Mayor F Jr, de Celis JF (2007) The cell biology of Smo signalling and its relationships with GPCRs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768(4):901–912. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.09.020
Scales SJ, de Sauvage FJ (2009) Mechanisms of Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30(6):303–312. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2009.03.007
Novartis. (2015) ODOMZO® (sonidegib) capsules, for oral use: US Prescribing Information.
Agency EM (2005) The clinical evaluation of QT/QTc interval prolongation and proarrhythmic potential for non-antiarrythmic drugs. Available from: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500002879.pdf.
ICH (2005) The clinical evaluation of interval prolongation and proarrhythmic potential for non-antiarrhythmic drugs E14. Available from:www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E14/E14_Guideline.pdf.
Migden MR, Guminski A, Gutzmer R, Dirix L, Lewis KD, Combemale P, Herd RM, Kudchadkar R, Trefzer U, Gogov S, Pallaud C, Yi T, Mone M, Kaatz M, Loquai C, Stratigos AJ, Schulze HJ, Plummer R, Chang AL, Cornelis F, Lear JT, Sellami D, Dummer R (2015) Treatment with two different doses of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (BOLT): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind phase 2 trial. The Lancet Oncology 16(6):716–728. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(15)70100-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
The studies and analysis reported here were sponsored and performed by Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation. Michelle Quinlan, Jocelyn Zhou, and Dalila Sellami are all employees of Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation. Eunju Hurh was an employee of Novartis Pharmaceutical at the time of this work. Medical writing support was provided by Tina Patrick, Novartis Ireland Ltd.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quinlan, M., Zhou, J., Hurh, E. et al. Exposure-QT analysis for sonidegib (LDE225), an oral inhibitor of the hedgehog signaling pathway, for measures of the QT prolongation potential in healthy subjects and in patients with advanced solid tumors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72, 1427–1432 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-016-2128-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-016-2128-8