Abstract
Introduction
Stroke is a major health problem with important morbidity and mortality. Various risk factors and cardiovascular medication groups are known to have an influence on stroke incidence, but less is known about the relation between medication use and stroke severity.
Aim
To determine if relationships exist between the pre-stroke cardiovascular medication use and stroke severity.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on a database with anonymized data of 1974 patients with a suspected stroke, admitted to the Universitair Ziekenhuis (UZ) Brussel. Stroke severity was quantified using the National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS). Cardiovascular medication groups were first included in a multivariable linear regression model. Second, to obtain clinically interpretable results, all variables that were retained in the final linear regression model were introduced in a cumulative odds ordinal logistic regression model with proportional odds.
Results
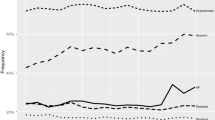
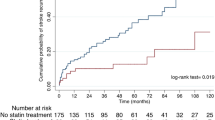
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), statins, and antiarrhythmics were significantly associated with stroke severity at the 10 % α level in a multivariable linear regression model, suggesting a possible effect of these medication groups on stroke severity. Only pre-stroke statin use showed a significant relationship with the NIHSS score in the ordinal logistic regression model with an adjusted odds ratio of 0.740 (95 % CI 0.580–0.944; p = 0.015).
Conclusion
Pre-stroke use of statins is significantly associated with lower stroke severity. No significant relationship was detected between pre-stroke use of other medication groups and stroke severity, defined by the NIHSS score.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thijs V, Dewilde S, Putman K, Pince H (2011) Cost of hospitalization for cerebrovascular disorders in Belgium. Acta Neurol Belg 111:104–110
Bejot Y, Benatru I, Rouaud O, Fromont A, Besancenot JP, Moreau T, Giroud M (2007) Epidemiology of stroke in Europe: geographic and environmental differences. J Neurol Sci 262:85–88
Meschia JF, Bushnell C, Boden-Albala B, Braun LT, Bravata DM, Chaturvedi S, Creager MA, Eckel RH, Elkind MS, Fornage M, Goldstein LB, Greenberg SM, Horvath SE, Iadecola C, Jauch EC, Moore WS, Wilson JA (2014) Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 45:3754–3832
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB (2014) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 129:e28–e292
Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R (2007) Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol 6:182–187
Bjorck S, Palaszewski B, Friberg L, Bergfeldt L (2013) Atrial fibrillation, stroke risk, and warfarin therapy revisited: a population-based study. Stroke 44:3103–3108
TESOEE Committee, TEW Committee (2008) Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc Dis 25:457–507
Artom N, Montecucco F, Dallegri F, Pende A (2014) Carotid atherosclerotic plaque stenosis: the stabilizing role of statins. Eur J Clin Investig 44:1122–1134
Castilla-Guerra L, Fernandez-Moreno Mdel C, Alvarez-Suero J (2009) Secondary stroke prevention in the elderly: new evidence in hypertension and hyperlipidemia. Eur J Intern Med 20:586–590
Krishnan A, Lopes RD, Alexander JH, Becker RC, Goldstein LB (2010) Antithrombotic therapy for ischemic stroke: guidelines translated for the clinician. J Thromb Thrombolysis 29:368–377
Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, Savelieva I, Atar D, Hohnloser SH, Hindricks G, Kirchhof P, Bax JJ, Baumgartner H, Ceconi C, Dean V, Deaton C, Fagard R, Funck-Brentano C, Hasdai D, Hoes A, Knuuti J, Kolh P, McDonagh T, Moulin C, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Vahanian A, Windecker S, Vardas P, Al-Attar N, Alfieri O, Angelini A, Blomstrom-Lundqvist C, Colonna P, De Sutter J, Ernst S, Goette A, Gorenek B, Hatala R, Heidbuchel H, Heldal M, Kristensen SD, Le Heuzey JY, Mavrakis H, Mont L, Filardi PP, Ponikowski P, Prendergast B, Rutten FH, Schotten U, Van Gelder IC, Verheugt FW (2012) 2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 33:2719–2747
Acciarresi M, De Luca P, Caso V, Agnelli G, D'Amore C, Alberti A, Venti M, Paciaroni M (2014) Acute stroke symptoms: do differences exist between sexes? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23:2928–2933
Dougu N, Takashima S, Sasahara E, Taguchi Y, Toyoda S, Hirai T, Nozawa T, Tanaka K, Inoue H (2011) Predictors of poor outcome in patients with acute cerebral infarction. J Clin Neurol 7:197–202
Appelros P, Nydevik I, Seiger A, Terent A (2002) Predictors of severe stroke: influence of preexisting dementia and cardiac disorders. Stroke 33:2357–2362
Di Carlo A, Lamassa M, Baldereschi M, Pracucci G, Consoli D, Wolfe CD, Giroud M, Rudd A, Burger I, Ghetti A, Inzitari D (2006) Risk factors and outcome of subtypes of ischemic stroke. Data from a multicenter multinational hospital-based registry. The European Community Stroke Project. J Neurol Sci 244:143–150
Phipps MS, Zeevi N, Staff I, Fortunato G, Kuchel GA, McCullough LD (2013) Stroke severity and outcomes for octogenarians receiving statins. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 57:377–382
Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Burn J, Warlow C (1991) Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 337:1521–1526
WHO. ATC/DDD Index. [Internet] Oslo, Norway: WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology; 2014 [updated 2013-12-19; cited 2014 2014-03-10]; Available from: http://www.whocc.no/.
Brott T, Adams HP Jr, Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, Spilker J, Holleran R, Eberle R, Hertzberg V et al (1989) Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke 20:864–870
Kwah LK, Harvey LA, Diong J, Herbert RD (2013) Models containing age and NIHSS predict recovery of ambulation and upper limb function six months after stroke: an observational study. J Physiother 59:189–197
Lakhan SE, Bagchi S, Hofer M (2010) Statins and clinical outcome of acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review. Int Arch Med 3:22
Kramer SF, Churilov L, Kroeders R, Pang MY, Bernhardt J (2013) Changes in activity levels in the first month after stroke. J Phys Ther Sci 25:599–604
Briggs DE, Felberg RA, Malkoff MD, Bratina P, Grotta JC (2001) Should mild or moderate stroke patients be admitted to an intensive care unit? Stroke 32:871–876
Adams HP Jr, Davis PH, Leira EC, Chang KC, Bendixen BH, Clarke WR, Woolson RF, Hansen MD (1999) Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: a report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology 53:126–131
Ottosen TP, Svendsen ML, Hansen ML, Brandes A, Andersen G, Husted SE, Johnsen SP (2014) Preadmission oral anticoagulant therapy and clinical outcome in patients hospitalised with acute stroke and atrial fibrillation. Dan Med J 61:A4904
Robinson JG, Smith B, Maheshwari N, Schrott H (2005) Pleiotropic effects of statins: benefit beyond cholesterol reduction? A meta-regression analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:1855–1862
Puccetti L, Pasqui AL, Pastorelli M, Bova G, Cercignani M, Palazzuoli A, Angori P, Auteri A, Bruni F (2002) Time-dependent effect of statins on platelet function in hypercholesterolaemia. Eur J Clin Investig 32:901–908
Horvath B, Marton Z, Alexy T, Kesmarky G, Toth K, Szapary L (2004) Short-term effects of atorvastatin on haemorheologic parameters, platelet aggregation and endothelium dysfunction in patients with hypercholesterolaemia. Eur Heart J 25:96
Laufs U, La Fata V, Plutzky J, Liao JK (1998) Upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by HMG CoA reductase inhibitors. Circulation 97:1129–1135
Mason RP, Walter MF, Jacob RF (2004) Effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on endothelial function: role of microdomains and oxidative stress. Circulation 109:II34–II41
Goldstein LB, Amarenco P, Zivin J, Messig M, Altafullah I, Callahan A, Hennerici M, MacLeod MJ, Sillesen H, Zweifler R, Michael K, Welch A (2009) Statin treatment and stroke outcome in the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) trial. Stroke 40:3526–3531
Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group (2002) MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol lowering with simvastatin in 20 536 high-risk individuals: a randomised placebocontrolled trial. The Lancet 360:7-22.
Moonis M, Kane K, Schwiderski U, Sandage BW, Fisher M (2005) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors improve acute ischemic stroke outcome. Stroke 36:1298–1300
Aboa-Eboule C, Binquet C, Jacquin A, Hervieu M, Bonithon-Kopp C, Durier J, Giroud M, Bejot Y (2013) Effect of previous statin therapy on severity and outcome in ischemic stroke patients: a population-based study. J Neurol 260:30–37
Sacco S, Toni D, Bignamini AA, Zaninelli A, Gensini GF, Carolei A (2011) Effect of prior medical treatments on ischemic stroke severity and outcome. Funct Neurol 26:133–139
Marti-Fabregas J, Gomis M, Arboix A, Aleu A, Pagonabarraga J, Belvis R, Cocho D, Roquer J, Rodriguez A, Garcia MD, Molina-Porcel L, Diaz-Manera J, Marti-Vilalta JL (2004) Favorable outcome of ischemic stroke in patients pretreated with statins. Stroke 35:1117–1121
Steckelings UM, Larhed M, Hallberg A, Widdop RE, Jones ES, Wallinder C, Namsolleck P, Dahlof B, Unger T (2011) Non-peptide AT2-receptor agonists. Curr Opin Pharmacol 11:187–192
Iwai M, Liu HW, Chen R, Ide A, Okamoto S, Hata R, Sakanaka M, Shiuchi T, Horiuchi M (2004) Possible inhibition of focal cerebral ischemia by angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation. Circulation 110:843–848
Li J, Culman J, Hortnagl H, Zhao Y, Gerova N, Timm M, Blume A, Zimmermann M, Seidel K, Dirnagl U, Unger T (2005) Angiotensin AT2 receptor protects against cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal injury. FASEB J 19:617–619
Sumners C, Horiuchi M, Widdop RE, McCarthy C, Unger T, Steckelings UM (2013) Protective arms of the renin-angiotensin-system in neurological disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 40:580–588
Danyel LA, Schmerler P, Paulis L, Unger T, Steckelings UM (2013) Impact of AT2-receptor stimulation on vascular biology, kidney function, and blood pressure. Integr Blood Press Control 6:153–161
Miyamoto N, Zhang N, Tanaka R, Liu M, Hattori N, Urabe T (2008) Neuroprotective role of angiotensin II type 2 receptor after transient focal ischemia in mice brain. Neurosci Res 61:249–256
Alhusban A, Fouda AY, Bindu P, Ishrat T, Soliman S, Fagan SC (2015) Compound 21 is pro-angiogenic in the brain and results in sustained recovery after ischemic stroke. J Hypertens 33:170–180
McCarthy CA, Vinh A, Broughton BR, Sobey CG, Callaway JK, Widdop RE (2012) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor stimulation initiated after stroke causes neuroprotection in conscious rats. Hypertension 60:1531–1537
Schrader J, Luders S, Kulschewski A, Hammersen F, Plate K, Berger J, Zidek W, Dominiak P, Diener HC (2005) Morbidity and mortality after stroke, eprosartan compared with nitrendipine for secondary prevention: principal results of a prospective randomized controlled study (MOSES). Stroke 36:1218–1226
Dahlöf B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Beevers G, de Faire U, Fyhrquist F, Ibsen H, Kristiansson K, Lederballe-Pedersen O, Lindholm LH, Nieminen MS, Omvik P, Oparil S, Wedel H (2002) Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 359:995–1003
Yusuf S, Teo KK, Pogue J, Dyal L, Copland I, Schumacher H, Dagenais G, Sleight P, Anderson C (2008) Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med 358:1547–1559
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F, Burnier M, Ambrosioni E, Caufield M, Coca A, Olsen MH, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Clement DL, Gillebert TC, Rosei EA, Anker SD, Bauersachs J, Hitij JB, Caulfield M, De Buyzere M, De Geest S, Derumeaux GA, Erdine S, Farsang C, Funck-Brentano C, Gerc V, Germano G, Gielen S, Haller H, Jordan J, Kahan T, Komajda M, Lovic D, Mahrholdt H, Ostergren J, Parati G, Perk J, Polonia J, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Ryden L, Sirenko Y, Stanton A, Struijker-Boudier H, Vlachopoulos C, Volpe M, Wood DA (2013) 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 34:2159–2219
Contributions of authors
S. Desmaele contributed to the design of the study and the analysis and interpretation of the data and drafted the manuscript. P. Cornu, S. Steurbaut, and AG. Dupont contributed to the design of the study and the interpretation of the data. They all critically revised the manuscript. K. Barbé contributed to the analysis and interpretation of the data and critically revised the manuscript. R. Brouns contributed to the data acquisition and to the interpretation of the data and critically revised the manuscript. All co-authors gave final approval to submit the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Source of funding
This work was supported in part by an unrestricted grant by Bayer NV-SA
Additional information
S. Steurbaut and A. G. Dupont joined the last authorship: both authors contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desmaele, S., Cornu, P., Barbé, K. et al. Relationship between pre-stroke cardiovascular medication use and stroke severity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72, 495–502 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-015-2001-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-015-2001-1