Abstract
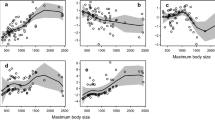
Determining trophic relationships within and among species can provide insight into the structure and function of an ecosystem, and can inform the development of multi-species monitoring and management plans. The goal of this study was to address the need for dietary and trophic information of two common and abundant skates in Prince William Sound (PWS), the Bering skate, Bathyraja interrupta, and longnose skate, Raja rhina. Based on identification and analysis of stomach content data, both species were found to be generalist predators with diets dominated by crustaceans and supplemented with teleosts. The primary source of dietary variability for each species was total length, with spatial variables (i.e., latitude, longitude, and depth) also explaining a large portion of total dietary variability in the Bering skate. However, only a small proportion of the total intraspecific dietary variation was accounted for among the analyzed variables, suggesting substantial individual-based differences in the feeding habits of each species. Trophic level estimates indicated that the Bering skate and longnose skates <100 cm total length (TL) were secondary consumers, whereas longnose skates ≥100 cm TL were more piscivorous, tertiary consumers. Significant interspecific dietary differences were also evident, suggesting trophic separation, likely as a function of skate size. Given their abundance and generalistic feeding behavior, PWS skates can provide a means of monitoring demersal community health; information about their foraging ecology will be valuable in gaining a better understanding of trophodynamics within the PWS food web.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsley SM, Ebert DA, Natanson LJ, Cailliet GM (2014) A comparison of age and growth of the Bering skate (Gil and Townsend, 1897). Fish Res 154:17–25
Ajaji TO (1982) Food and feeding habits of Raja species (Batoidei) in Carmarthen Bay, Bristol Channel. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 62:215–223. doi:10.1017/S0025315400020233
Albers WD, Anderson PJ (1985) Diet of Pacific cod, Gadus macrocephalus, and predation on the northern pink shrimp, Pandalus borealis, in Pavlof Bay, Alaska. Fish Bull 83:601–610
Amundsen PA, Gabler HM, Staldvik FJ (1996) A new approach to graphical analysis of feeding strategy from stomach contents data—modification of the Costello (1990) method. J Fish Biol 48:607–614. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1996.tb01455.x
Anderson MJ (2006) Distance-based test for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 62:245–253. doi:10.1111/j.1541-0420.2005.00440.x
Antonenko DV, Pushchina OI, Solomatov SF (2007) Distribution and some biological features of skate Bathyraja parmifera (Rajidae, Rajiformes) in the northwestern part of the Sea of Japan. J Ichthyol 47(4):279–287. doi:10.1134/S0032945207040042
Bang I, Mooers CNK (2003) The influence of several factors controlling the interactions between Prince William Sound, Alaska, and the Northern Gulf of Alaska. J Phys Oceanogra 33:19–36. doi:10.1175/1520-0485(2003)033<0019:TIOSFC>2.0.CO;2
Barbini SA, Lucifora LO (2011) Feeding habits of the Rio Skate, Rioraja agassizi (Chondrichthyes, Rajidae), from off Uruguay and north Argentina. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 91(6):1175–1184. doi:10.1017/S0025315410001529
Barbini SA, Lucifora LO (2012) Feeding habits of a large endangered skate from the south-west Atlantic: The spotback skate, Atlantoraja castelnaui. Mar Freshw Res 63(2):180–188. doi:10.1071/MF11170
Barbini SA, Lucifora LO (2016) Diet composition and feeding habits of the eyespot skate, Atlantoraja cyclophora (Elasmobranchii: Arhynchobatidae), off Uruguay and northern Argentina. Neotrop Ichthyol 14(3):e160032. doi:10.1590/1982-0224-20160032
Barbini SA, Scenna LB, Figueroa DE, Cousseau MB, Díaz de Astarloa JM (2010) Feeding habits of the Magellan skate: effects of sex, maturity stage, and body size on diet. Hydrobiologia 641:275–286. doi:10.1007/s10750-010-0090-5
Barry JP, Yoklavich MM, Cailliet GM, Ambrose DA, Antrim BS (1996) Trophic ecology of the dominant fishes in Elkhorn Slough, California, 1974–1980. Esturaries 19:115–138. doi:10.2307/1352657
Berestovskiy EG (1989) Feeding in the skates, Raja radiata and Raja fyllae, in the Barents and Norwegian Seas. Voprosy Ikhtiologii 29:994–1002. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2000.081
Bizzarro JJ (2015) Comparative resource utilization of eastern North Pacific skates (Rajiformes: Rajidae) with applications for ecosystem-based fisheries management. Dissertation, University of Washington, Seattle
Bizzarro JJ, Robinson HJ, Rinewalt CS, Ebert DA (2007) Comparative feeding ecology of four sympatric skate species off central California, USA. Environ Biol Fish 80:197–220. doi:10.1007/s10641-007-9241-6
Bizzarro JJ, Smith WD, Castillo–Géniz JL, Ocampo–Torres A, Márquez–Farías JF, Hueter RE (2009) The seasonal importance of small coastal sharks and rays in the artisanal elasmobranch fishery of Sinaloa, Mexico. Pan–Am J Aquat Sci 4:513–531. doi:10.1016/j.fishres.2011.01020
Bizzarro JJ, Broms KM, Logsdon MG, Ebert DA, Yoklavich MM, Kuhnz LA, Summers AP (2014) Spatial segregation in eastern North Pacific skate assemblages. PLoS One 9(10):e109907. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109907
Boldt JL, Haldorson LJ (2003) Seasonal and geographic variation in juvenile pink salmon diets in the northern Gulf of Alaska and Prince William Sound. Trans Am Fish Soc 132(6):1035–1052. doi:10.1577/T02-091
Boyle MD 2010. Trophic interactions of Bathyraja trachura and sympatric fishes. Masters thesis, California State University Monterey Bay, Monterey Bay
Braccini JM, Perez JE (2005) Feeding habits of the sandskate Psammobatis extenta (Garmin, 1913): sources of variation in dietary composition. Mar Freshw Res 56:395–403. doi:10.1071/MF04205
Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol Monogr 27:325–349. doi:10.2307/1942268
Brickle P, Laptikhovsky V, Bishop A (2003) Ontogenetic changes in the feeding habits and dietary overlap between three abundant rajid species on the Falkland Islands’ shelf. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 83:1119–1125. doi:10.1017/S0025315403008373h
Brown SC (2010) Diet composition of Bathyraja interrupta (Gill and Townsend, 1897) and Bathyraja aleutica (Gilbert, 1896), from the northern Gulf of Alaska continental shelf. Masters thesis, California State University Monterey Bay, Monterey Bay
Brown SC, Bizzarro JJ, Cailliet GM, Ebert DA (2012) Breaking with tradition: redefining measures for diet description with a case study of the Aleutian skate Bathyraja aleutica (Gilbert 1896). Environ Biol Fish 95:3–20. doi:10.1007/s10641-011-9959-z
Compagno LJV (1990) Alternative life-history styles of cartilaginous fishes in time and space. Environ Biol Fish 28:33–75. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-2065-1_3
Constable AJ (2011) Lessons from CCAMLR on the implementation of the ecosystem approach to managing fisheries. Fish Fish 12:138–151. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2979.2011.00410.x
Cortés E (1999) Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of sharks. ICES J Mar Sci 56:707–717. doi:10.1006/jmsc.1999.0489
Dolgov AV (2005) Feeding and food consumption by the Barents Sea Skates. J Northw Atl Fish Sci 35:495–503. doi:10.2960/J.v35.m523
Ebert DA (2003) Sharks, rays, and chimaeras of California. University of California Press, Berkeley
Ebert DA, Bizzarro JJ (2007) Standardized diet compositions and trophic levels of skates (Chondrichthyes: Rajiformes: Rajoidei). Environ Biol Fish 80:221–237. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9703-4_8
Ebert DA, Compagno LJV (2007) Biodiversity and systematics of skates (Chondrichthyes: Rajiformes: Rajoidei). Environ Biol Fish 80:111–124. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9703-4_2
Ebert DA, Winton MV (2010) Chondrichthyans of high latitude seas. In: Carrier J, Musick JA, Heithaus M (eds) Sharks and Their Relatives II: Biodiversity, Adaptive Physiology, and Conservation. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 115–158
Ebert DA, Cowley PD, Compagno LJV (1991) A preliminary investigation of the feeding ecology of skates (Batoidea: Rajidae) off the west coast of southern Africa. S Afr J Marine Sci 10:71–81. doi:10.2989/02577619109504621
Eggers DM (1977) Factors in interpreting the data obtained by diel sampling of food consumption for fiish. J Fish Res Board Canada 34:290–294
Elliot JM, Persson L (1978) The estimation of daily rates of food consumption for fish. J Animal Ecol 47:977–991
Farrugia TJ, Goldman KJ, Tribuzio C, Seitz AC (2016) First use of satellite tags to examine movement and habitat use of big skates Beringraja binoculata in the Gulf of Alaska. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 556:209–221. doi:10.3354/meps11842
Ferry LA, Cailliet GM (1996) Sample size and data analysis: are we characterizing and comparing diet properly? In: MacKinlay D, Shearer K (eds) Gutshop’96. Feeding ecology and nutrition in fish symposium proceedings, pp 71–80
Forman JS, Dunn MR (2012) Diet and scavenging habits of the smooth skate Dipturus innominatus. J Fish Biol 80(5):1546–1562. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2012.03255.x
Foy RJ, Norcross BL (1999) Spatial and temporal variability in the diet of juvenile Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi) in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Can J Zool 77(5):697–706. doi:10.1023/A:1007557509202
Gaichas S, Sagalkin N, Gburski C, Stevenson D, Swanson R (2005) Gulf of Alaska skates. In: NPFMC Stock assessment and fishery evaluation report, Anchorage, pp 881–896
Gaichas SK, Aydin KY, Francis RC (2010) Using food web model results to inform stock assessment estimates of mortality and production for ecosystem-based fisheries management. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 67:1490–1506. doi:10.1139/F10-071
Gill T, Townsend CH (1897) Diagnosis of new species of fishes found in Bering Sea. Proc Biol Soc Wash 11:231–234
Girard CF (1855) Characteristics of some cartilaginous fishes of the Pacific coast of North America. Proc Acad Nat Sci Phila 7(6):196–197
Hollowed AB, Aydin KY, Essington TE, Ianelli JN, Megrey BA, Punt AE, Smith ADM (2011) Experience with quantitative ecosystem assessment tools in the northeast Pacific. Fish Fish 12:189–208. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2979.2011.00413.x
Hyslop EJ (1980) Stomach contents analysis-a review of methods and their application. J Fish Biol 17:411–429. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1980.tb02775.x
Iverson SJ, Frost KJ, Lowry LF (1997) Fatty acid signatures reveal fine scale structure of foraging distribution of harbor seals and their prey in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 151:255–271. doi:10.3354/meps151255
Jennings S, Rice J (2011) Towards an ecosystem approach to fisheries in Europe: a perspective on existing progress and future directions. Fish Fish 12:125–137. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2979.2011.0
Jordan DS, Gilbert CH (1880) Description of a new species of ray, Raia rhina, from the coast of California. Proc U S Natl Mus 251–253. doi:10.5479/si.00963801.3-141.251
Koehn LE, Essington TE, Marshall KN, Kaplan IC, Sydeman WJ, Szoboszlai AI, Thayer JA (2016) Developing a high taxonomic resolution food web model to assess the functional role of forage fish in the California Current ecosystem. Ecol Model 335:87–100
Koen Alonso M, Crespo EA, Garcia NA, Pedraza SN, Mariotti PA, Berόn Vera B, Mora NJ (2001) Food habits of Dipturus chilensis (Pisces: Rajidae) off Patagonia, Argentina. ICES J Mar Sci 58:288–297. doi:10.1006/jmsc.2000.1010
Legendre P, Gallagher ED (2001) Ecological meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 129:271–280. doi:10.1007/s004420100716
Levin PS, Fogarty MJ, Muraswski SA, Fluharty D (2009) Integrated ecosystem assessments: developing the scientific basis for ecosystem-based management of the ocean. PLoS Biol 7(1):e1000014. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000014
Link JS, Garrison LP (2002) Trophic ecology of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua on the northeast US continental shelf. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 227:109–123. doi:10.3354/meps227109
Link JS, Sosebee K (2008) Estimates and implications of skate consumption in the Northeast U.S. continental shelf ecosystem. North Am J Fish Manag 28:649–662
Livingston PA, deReynier Y (1996) Groundfish food habits and predation on commercially important prey species in the eastern Bering Sea from 1990 to 1992. AFSC Processed Report 96–04, Seattle
Love MS, Mecklenburg CW, Mecklenburg TA, Thorsteinson LK (2005) Resource inventory of marine and estuarine fishes of the west coast of Alaska: a checklist of north Pacific and Arctic Ocean species from Baja California to the Alaska-Yukon border. USGS, Biological Resources Division, Seattle
Mabragaña E, Giberto DA (2007) Feeding ecology and abundance of two sympatic skates, the shortfin sand skate, Psammobatis normani McEachran, and the smallthorn sand skate P. rudsi Günther (Chondrichthyes, Rajidae), in the southwest Atlantic. ICES J Mar Sci 64:1–11. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsm078
Mabragaña E, Giberto DA, Bremec CS (2005) Feeding ecology of Bathyraja macloviana (Rajiformes, Arhynchobatidae): a polychaete-feeding skate from the South-west Atlantic. Sci Mar 69:405–413. doi:10.3989/scimar.2005.69n3405
McEachran JD, Musick JA (1975) Distribution and relative abundance of seven species of skates (Pisces: Rajidae) which occur between Nova Scotia and Cape Hatteras. Fish Bull 73:110–136
McEachran JD, Boeschand DF, Musick JA (1976) Food division within two sympatric species-pairs of skates (Pisces: Rajidae). Mar Biol 35:301–317. doi:10.1007/BF00386641
Morato T, Solà E, Grós MP, Menezes G (2003) Diets of thornback ray (Raja clavata) and tope shark (Galeorhinus galeus) in the bottom longline fishery of the Azores, northeastern Atlantic. Fish Bull 101:590–602
Muto EY, Soares LS, Goitein R (2001) Food resource utilization of the skates Rioraja agassizii (Müller & Henle, 1841) and Psammobatis extenta (Garman, 1913) on the continental shelf off Ubatuba, South-eastern Brazil. Braz J Biol 61(2):217–238. doi:10.1590/S0034-71082001000200005
Niebauer HJ, Royer TC, Weingartner TJ (1994) Circulation of Prince William Sound, Alaska. J Geophys Res 99(C7):14113–14126. doi:10.1029/94JC00712
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Henry M, Stevens H, Wagner H (2013) Vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.0–9. Available from: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Orlov AM (1998a) The diets and feeding habits of some deep-water benthic skates (Rajidae) in the Pacific waters off the Northern Kuril Islands and Southeastern Kamchatka. Alaska Fish Res Bull 5(1):1–17
Orlov AM (1998b) On feeding of mass species of deep-sea skates (Bathyraja spp., Rajidae) from the Pacific waters of the northern Kurils and southeastern Kamchatka. J Ichthyol 38(8):635–644
Orlov AM (2003) Diets, feeding habits, and trophic relations of six deep-benthic skates (Rajidae) in the western Bering Sea. AQUA 7(2):45–60
Ormseth OA (2015) Assessment of the skate stock complex in the Gulf of Alaska. NPFMC Gulf of Alaska SAFE, Anchorage, p 1497–1546
Patrick WS, Link JS (2015) Myths that continue to impede progress in ecosystem-based fisheries management. Fisheries 40:155–160. doi:10.1080/03632415.2015.1024308
Pedersen SA (1995) Feeding habits of starry ray (Raja radiata) in west Greenland waters. ICES J Mar Sci 52:43–53. doi:10.1016/1054-3139(95)80014-X
Pikitch EK, Santora C, Babcock EA, Bakun A, Bonfil R, Conover DO, Dayton P, Doukakis P, Fluharty D, Heneman B, Houde ED, Link J, Livingston PA, Mangel M, McAllister MK, Pope J, Sainsbury KJ (2004) Ecosystem-based fishery management. Science 305:346–347. doi:10.1126/science.1098222
Pinkas LM, Oliphant S, Iverson ILK (1971) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and Bonito in Californian waters. Calif Fish Game 152:1–105
Rice J (2011) Managing fisheries well: delivering the promises of an ecosystem approach. Fish Fish 12:209–231. doi:10.1111/j.1467-2979.2011.00416.x
Rinewalt CS, Ebert DA, Cailliet GM (2007) Food habits of the sandpaper skate, Bathyraja kincaidii (Garman, 1908) off central California: seasonal variation in diet linked to oceanographic conditions. Environ Biol Fish 80:147–163. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9703-4_4
Robinson HJ, Cailliet GM, Ebert DA (2007) Food habits of the longnose skate, Raja rhina (Jordan and Gilbert, 1880), in central California waters. Environ Biol Fish 80:165–179. doi:10.1007/s10641-007-9222-9
Royer TC, Vermersch JA, Weingartner TJ, Niebauer HJ, Muench RD (1990) Ocean circulation influencing the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Oceanography 3(2):3–10. doi:10.5670/oceanog.1990.01
Saulitis EL, Matkin CO, Heise K, Barrett Lennard L, Ellis GM (2000) Foraging strategies of sympatric killer whale (Orcinus orca) populations in Prince William Sound, Alaska. Mar Mamm Sci 16:94–109. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2000.tb00906.x
Scenna LB, García de la Rosa SB, Díaz de Astarloa JM (2006) Trophic ecology of the Patagonian skate, Bathyraja macloviana, on the Argentine continental shelf. ICES J Mar Sci 63:867–874. doi:10.1016/j.icesjms.2006.02.002
Smale MJ, Cowley PD (1992) The feeding ecology of skates (Batoidea: Rajidae) off the Cape South Coast, South Africa. S Afr J Mar Sci 12:823–834. doi:10.2989/02577619209504744
Stevenson DE, Orr JW, Hoff GR, McEachran JD (2007) Field guide to sharks, skates, and ratfish of Alaska. Sea Grant College Program, Fairbanks, AK
Treloar MA, Laurenson LJB, Stevens JD (2007) Dietary comparisons of six skate species (Rajidae) in south-eastern Australian waters. Enviorn Biol Fish 80:181–196. doi:10.1007/s10641-007-9233-6
Vaughan SL, Mooers CNK, Gay SM III (2001) Physical variability in Prince William Sound during the SEA Study (1994–98). Fish Oceanogr 10:58–80. doi:10.1046/j.1054-6006.2001.00034.x
Wakefield WW (1984) Feeding relationships within assemblages of nearshore and mid-continental shelf benthic fishes off Oregon. MS thesis. Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR
Wang J, Jin M, Patrick EV, Allen JR, Eslinger DL, Mooers CNK, Cooney RT (2001) Numerical simulations of the seasonal circulation patterns and thermohaline structures of Prince William Sound, Alaska. Fish Oceanogr 10:132–148. doi:10.1046/j.1054-6006.2001.00035.x
Wessel M, Rumble J, Goldman KJ, Russ E, Byerly M, Russ C (2014) Prince William Sound registration area E groundfish fisheries management report, 2009–2013. ADFG Fishery Management Report No. 14–42, Anchorage
Wetherbee BW, Cortés E, Bizzarro JJ (2012) Food consumption and feeding habits. In: Carrier JC, Musick JA, Heithaus MR (eds) Biology of sharks and their relatives. CRC Press, New York, pp 239–264
Yang MS, Dodd K, Hibpshman R, Whitehouse A (2006) Food habits of groundfishes in the Gulf of Alaska in 1999 and 2001. NMFS-AFSC-164, Seattle
Acknowledgements
We thank many people who helped to collect skates, including personnel of the National Marine Fisheries Service and the Alaska Department of Fish and Game, in particular, Ken Goldman, along with the many PSRC personnel. We are grateful to Dr. Peter Slattery for his help with amphipod identification and to Simon Brown for his assistance with prey identification and statistics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Financial support for this research was provided by the North Pacific Research Board project 621, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Marine Fisheries Service through the National Shark Research Consortium and the Pacific Shark Research Center, and the David and Lucile Packard Foundation. This is North Pacific Research Board publication 622.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the San Jose State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) under protocol #801.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: J. Carlson.
Reviewed by Undisclosed experts.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kemper, J.M., Bizzarro, J.J. & Ebert, D.A. Dietary variability in two common Alaskan skates (Bathyraja interrupta and Raja rhina). Mar Biol 164, 52 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3078-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3078-0