Abstract
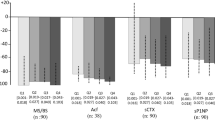
The aim of this work was to evaluate the response of different biochemical bone markers to tiludronate administration in Paget’s disease of bone. Ten patients (five men and five women), 56–77 years old (67 ± 6.5), were treated for 3 months with tiludronate tablets (400 mg/day). Bone formation markers: alkaline phosphatase (AP), bone alkaline phosphatase (bAP), osteocalcin (BGP), and procollagen I carboxyterminal propeptide (PICP) in serum; and bone resorption markers: serum cross-linked carboxyterminal telopeptides of type I collagen (ICTP), urinary hydroxyproline/creatinine (Hyp/Cr), pyridinoline/Cr (Pyr/Cr), and alpha-1 collagen chain products degradation (CrossLaps) were assessed. Samples were taken before and at monthly intervals for 3 months after treatment began. The results of the present work show that serum AP and bAP are sensitive and reliable biochemical markers of bone formation in the follow-up of tiludronate in this disease. Serum PICP shows less sensitivity than serum AP, and serum BGP is not indicated as biochemical marker in these types of studies. Urinary hydroxyproline seems to be the most reliable biochemical marker of bone resorption. More studies should be performed with urinary Pyr and CrossLaps determinations. Serum ICTP is not adequate for the follow-up of tiludronate treatment in Paget’s disease of bone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delmas PD (1993) Biochemical markers of bone turnover. J Bone Miner Res 8 (suppl 2):S549-S555
Riis BJ (1993) Biochemical markers of bone turnover II: diagnosis, prophylaxis and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med 95 (suppl 5A):17S-21S
Eastell R, Robins SP, Col well T, Assiri AMA, Riggs BL, Russell RGG (1993) Evaluation of bone turnover in type I osteoporosis using biochemical markers specific for both bone formation and bone resorption. Osteoporosis Int 3:255–260
Risteli L, Risteli J (1993) Biochemical markers of bone metabolism. Ann Med 25:385–393
Garnero P, Delmas PD (1993) Assessment of the serum levels of bone alkaline phosphatase with a new immunoradiometric assay in patients with metabolic bone disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 77:1046–1053
Gomez B, Haugen S, Ardakani S, Cerelli MJ, Leung SS, Ju HS, Lundgard R, Daniloff GY, Kung VT (1994) Measurement of bone-specific alkaline phosphatase activity in serum using a monoclonal antibody (abstract). J Bone Miner Res 9 (suppl I):S348
Garnero P, Grimaux M, Seguin P, Delmas PD (1994) Characterization of immunoreactive forms of human osteocalcin generated in vivo and in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 9:255–264
Masters PW, Jones RG, Purves DA, Cooper EH, Cooney JM (1994) Commercial assays for serum osteocalcin give clinically discordant results. Clin Chem 40:358–363
Díaz Diego EM, Guerrero R, De la Piedra C (1994) Six osteocalcin assays compared. Clin Chem 40:2071–2077
Black D, Duncan A, Robins SP (1988) Quantitative analysis of the pyridinium crosslinks of collagen in urine using ionpaired reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 169:197–203
Seyedin SM, Kung VT, Daniloff YN, Hesley RP, Gomez B, Nielsen LA, Rosen HN, Zuk RF (1993) Immunoassay for urinary pyridinoline: the new marker of bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res 8:635–641
Risteli J, Elomaa I, Niemi S, Novamo A, Risteli L (1993) Radioimmunoassay for the pyridinoline cross-linked carboxyterminal telopeptide of type I collagen: a new serum marker of bone collagen degradation. Clin Chem 39:635–640
Hanson DA, Weis MAE, Bollen AM, Maslan SL, Singer FR, Eyre DR (1992) A specific immunoassay for monitoring human bone resorption: quantitation of type I collagen crosslinked N-telopeptides in urine. J Bone Miner Res 7:1251–1258
Bonde M, Qvist P, Fledelius C, Riis BJ, Christiansen C (1994) Immunoassay for quantifying type I collagen degradation products in urine evaluated. Clin Chem 40:2022–2025
Hill CS, Wolfert RL (1989) The preparation of monoclonal antibodies which react preferentially with human bone alkaline phosphatase and not liver alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chim Acta 186:315–320
Price CP, Mitchell CA, Nooman K (1993) Experience with an immunoradiometric assay for skeletal alkaline phosphatase (abstract). Calcif Tissue Int 52 (suppl 1):S94
Kress BC, Payne G, Woodroom D, Cerrito M, Darte C (1993) Tamdem R Ostase, an immunoradiometric assay for measuring the skeletal isoenzyme of alkaline phosphatase in serum (abstract). Calcif Tissue Int 52 (suppl 1):S95
Melkko J, Niemo S, Risteli L, Risteli J (1990) Radioimmunoassay of the carboxyterminal propeptide of human type I procollagen. Clin Chem 36:1328–1332
Kivirikko KI, Laitinen O, Prokop DJ (1967) Modifications of a specific assay for hydroxyproline in urine. Anal Biochem 19:249–255
Meunier PJ, Coindre JM, Edouard CM, Arlot MD (1980) Bone histomorphometry in Paget’s disease. Quantitative and dynamic analysis of pagetic and non-pagetic bone tissues. Arthritis Rheum 23:1095–1103
Singer FR 1991 Clinical efficacy of salmon calcitonin in Paget’s disease of bone. Calcif Tissue Int 49 (suppl 2):S7-S8
Wimalawansa SJ, Gunasekera RD (1993) Pamidronate is effective for Paget’s disease of bone refractory to conventional therapy. Calcif Tissue Int 53:237–241
Reginster JY, Lecart MP, Deroisy R, Ethgen D, Zegels B, Franchimont P (1993) Paget’s disease of bone treated with a five-day course of oral tiludronate. Ann Rheum Dis 52:54–57
O’Doherty DP, Gertz BJ, Tindale W, Sciberras DG, Survill TT, Kanis JA (1992) Effects of five daily 1 h infusions of alendronate in Paget’s disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res 7:81–87
Reginster JY, Colson F, Morlock G, Combe B, Ethgen D, Geusens P (1992) Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of oral tiludronate in Paget’s disease of bone. A double-blind, multiple dosage, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 35: 967–974
Reginster JY, Treves R, Renier JC, Amor B, Sany J, Ethgen D, Picot C, Frauchimont P (1994) Efficacy and tolerability of a new formulation of oral tiludronate (tablet) in the treatment of Paget’s disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res 9:615–619
Delmas PD, Malaval L (1986) Serum bone Gla-protein is not a sensitive marker of bone turnover in Paget’s disease of bone. Calcif Tissue Int 38:60–61
Torres R, De la Piedra C, Rapado A (1991) Binding of serum osteocalcin to hydroxyapatite in Paget’s disease of bone. Bone Miner 14:55–65
Davie MW, Worsfold M, Sharp CA (1991) Differential response of serum alkaline phosphatase and serum osteocalcin in Paget’s osteosarcoma. Ann Clin Biochem 28:194–195
Ryan PJ, Sherry M, Gibson T, Fogelman I (1992) Treatment of Paget’s disease by weekly infusions of 3-amino hydroxypropylidene-1, 1-bisphosphonate (APD). Br J Rheumatol 31: 97–101
Charles P, Mosekilde L, Risteli L, Risteli J, Eriksen EF (1994) Assessment of bone remodeling using biochemical indicators of type I collagen synthesis and degradation: relation to calcium kinetics. Bone Miner 24:81–94
Robins SP, Black D, Paterson CR, Reid DM, Duncan A, Scibel MJ (1991) Evaluation of urinary hydroxypyridinium crosslinks measurements as resorption markers in metabolic bone disease. Eur J Clin Invest 21:310–315
Delmas PD, Gineyts E, Bertholin A, Garnero P, Marchand F (1993) Immunoassay of pyridinoline crosslink excretion in normal adults and in Paget’s disease. J Bone Miner Res 8: 643–648
Hamdy NA, Papapoulos SE, Colwell A, Eastell R, Russell RG (1993) Urinary collagen crosslink excretion: a better index of bone resorption than hydroxyproline in Paget’s disease of bone? Bone Miner 22:1–8
Scibel MJ, Robins SP, Bilezikian JP (1992) Urinary pyridinium crosslinks of collagen. Specific markers of bone resorption in metabolic bone disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 3:263–270
Bettica P, Moro L, Robins SP, Taylor AK, Talbot J, Singer FR, Baylink DJ (1992) Bone resorption markers galactosyl hydroxylysine, pyridinium crosslinks and hydroxyproline compared. Clin Chem 38:2313–2318
Alvarez L, Guañabens N, Peris P, Monegal A, Bedini JL, Deulofen R, Martinez de Osaba MJ, Munoz Gomez J, Rivera-Fillat F, Ballesta AM (1995) Discriminative value of biochemical markers of bone turnover in assessing the activity of Paget’s disease. J Bone Miner Res 10:458–465
Hankey DP, Hughes AE, Mollan RA, Nicholas RM (1993) Extracellular protein secretion of cultured normal and Pagetic osteoblasts. Electrophoresis 14:644–649
Garnero P, Gineyts E, Riou JP, Delmas PD (1994) Assessment of bone resorption with a new marker of collagen degradation in patients with metabolic bone disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 79:780–785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de la Piedra, C., Rapado, A., Diego, E.M.D. et al. Variable efficacy of bone remodeling biochemical markers in the management of patients with Paget’s disease of bone treated with tiludronate. Calcif Tissue Int 59, 95–99 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900093
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002239900093