Abstract
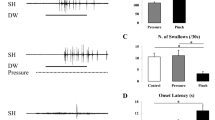
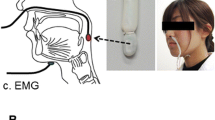
The aims of the present study were to determine whether the interval between swallows and the electromyographic (EMG) burst patterns of the suprahyoid muscles is affected by peripheral inputs during swallowing. Eighteen normal adults were asked to perform repetitive voluntary swallowing as quickly as possible, and three variables of swallowing were measured and evaluated, i.e., the swallowing intervals and the time interval between the onset and peak (rising time) and between the peak and offset (falling time) of the suprahyoid EMG burst. During recording, pharyngeal fluid infusion was applied with distilled water or 0.3 M NaCl solution at a very slow infusion rate (0.2 mL/min). The former and latter were used to activate and inhibit the excitation of water-sensitive receptors in the pharynx, respectively. The swallowing interval was significantly shorter during infusion of water than during infusion of NaCl solution. The rising time was also significantly shorter during infusion of water than during infusion of NaCl solution. There was a linear positive correlation between these values and facilitatory effects: the longer either the swallowing interval or rising time with infusion of 0.3 M NaCl solution, the stronger the facilitation of swallowing by the activation of water receptors. Facilitatory effects on the swallowing interval and rising time showed a linear correlation. It is suggested that weak liquid stimulation changed sensory inputs into the swallowing center and synchronously modulated the swallowing interval and time interval between the onset and peak of the EMG burst.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfonsi E, Bergamaschi R, Cosentino G, Ponzio M, Montomoli C, Restivo DA, Brighina F, Ravaglia S, Prunetti P, Bertino G, Benazzo M, Fontana D, Moglia A (2013) Electrophysiological patterns of oropharyngeal swallowing in multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurophysiol 2457:00214–00217
Al-Toubi AK, Abu-Hijleh A, Huckabee ML, Macrae P, Doeltgen SH (2011) Effects of repeated volitional swallowing on the excitability of submental corticobulbar motor pathways. Dysphagia 26:311–317
Boggs DF, Bartlett D Jr (1982) Chemical specificity of a laryngeal apneic reflex in puppies. J Appl Physiol 53:455–462
Chee C, Arshad S, Singh S, Mistry S, Hamdy S (2005) The influence of chemical gustatory stimuli and oral anaesthesia on healthy human pharyngeal swallowing. Chem Senses 30:393–400
Crary MA, Baldwin BO (1997) Surface electromyographic characteristics of swallowing in dysphagia secondary to brainstem stroke. Dysphagia 12:180–187
Crary MA, Carnaby Mann GD, Groher ME (2006) Biomechanical correlates of surface electromyography signals obtained during swallowing by healthy adults. J Speech Lang Hear Res 49:186–193
Dodds WJ, Stewart ET, Logemann JA (1990) Physiology and radiology of the normal oral and pharyngeal phases of swallowing. AJR Am J Roentgenol 154:953–963
Donner MW (1985) Radiologic evaluation of swallowing. Am Rev Respir Dis 131:S20–S23
Ertekin C (2011) Voluntary versus spontaneous swallowing in man. Dysphagia 26:183–192
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I (2003) Neurophysiology of swallowing. Clin Neurophysiol 114:2226–2244
Ertekin C, Pehlivan M, Aydogdu I, Ertas M, Uludag B, Celebi G, Colakoglu Z, Sagduyu A, Yuceyar N (1995) An electrophysiological investigation of deglutition in man. Muscle Nerve 18:1177–1186
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yuceyar N, Tarlaci S, Kiylioglu N, Pehlivan M, Celebi G (1998) Electrodiagnostic methods for neurogenic dysphagia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 109:331–340
Ertekin C, Aydogdu I, Yuceyar N, Kiylioglu N, Tarlaci S, Uludag B (2000) Pathophysiological mechanisms of oropharyngeal dysphagia in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 123:125–140
Ertekin C, Kiylioglu N, Tarlaci S, Turman AB, Secil Y, Aydogdu I (2001) Voluntary and reflex influences on the initiation of swallowing reflex in man. Dysphagia 16:40–47
Fraser C, Rothwell J, Power M, Hobson A, Thompson D, Hamdy S (2003) Differential changes in human pharyngoesophageal motor excitability induced by swallowing, pharyngeal stimulation, and anesthesia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 285:G137–G144
Gay T, Rendell JK, Spiro J (1994) Oral and laryngeal muscle coordination during swallowing. Laryngoscope 104:341–349
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Aziz Q, Singh KD, Thompson DG (1998) Long-term reorganization of human motor cortex driven by short-term sensory stimulation. Nat Neurosci 1:64–68
Hamdy S, Mikulis DJ, Crawley A, Xue S, Lau H, Henry S, Diamant NE (1999a) Cortical activation during human volitional swallowing: an event-related fMRI study. Am J Physiol 277:G219–G225
Hamdy S, Rothwell JC, Brooks DJ, Bailey D, Aziz Q, Thompson DG, Mikulis DJ, Crawley A, Xue S, Lau H, Henry S, Diamant NE (1999b) Identification of the cerebral loci processing human swallowing with H2(15)O PET activation cortical activation during human volitional swallowing: an event-related fMRI study. J Neurophysiol 81:1917–1926
Huckabee ML, Butler SG, Barclay M, Jit S (2005) Submental surface electromyographic measurement and pharyngeal pressures during normal and effortful swallowing. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:2144–2149
Jean A (2001) Brain stem control of swallowing: neuronal network and cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 81:929–969
Kitada Y, Yahagi R, Okuda-Akabane K (2010) Effect of stimulation of the laryngopharynx with water and salt solutions on voluntary swallowing in humans: characteristics of water receptors in the laryngopharyngeal mucosa. Chem Senses 35:743–749
Mansson I, Sandberg N (1975a) Oro-pharyngeal sensitivity and elicitation of swallowing in man. Acta Otolaryngol 79:140–145
Mansson I, Sandberg N (1975b) Salivary stimulus and swallowing reflex in man. Acta Otolaryngol 79:445–450
Martin RE, Goodyear BG, Gati JS, Menon RS (2001) Cerebral cortical representation of automatic and volitional swallowing in humans. J Neurophysiol 85:938–950
Miller AJ (1972) Characteristics of the swallowing reflex induced by peripheral nerve and brain stem stimulation. Exp Neurol 34:210–222
Miller AJ (1982) Deglutition. Physiol Rev 62:129–184
Mosier K, Patel R, Liu WC, Kalnin A, Maldjian J, Baredes S (1999) Cortical representation of swallowing in normal adults: functional implications. Laryngoscope 109:1417–1423
Perlman AL, Palmer PM, McCulloch TM, Vandaele DJ (1999) Electromyographic activity from human laryngeal, pharyngeal, and submental muscles during swallowing. J Appl Physiol 86:1663–1669
Pouderoux P, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ (1996) Pharyngeal swallowing elicited by fluid infusion: role of volition and vallecular containment. Am J Physiol 270:G347–G354
Shingai T (1977) Ionic mechanism of water receptors in the laryngeal mucosa of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 27:27–42
Shingai T, Shimada K (1976) Reflex swallowing elicited by water and chemical substances applied in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx of the rabbit. Jpn J Physiol 26:455–469
Shingai T, Miyaoka Y, Ikarashi R, Shimada K (1989) Swallowing reflex elicited by water and taste solutions in humans. Am J Physiol 256:R822–R826
Storey AT (1968a) A functional analysis of sensory units innervating epiglottis and larynx. Exp Neurol 20:366–383
Storey AT (1968b) Laryngeal initiation of swallowing. Exp Neurol 20:359–365
Sumi T (1972) Role of the pontine reticular formation in the neural organization of deglutition. Jpn J Physiol 22:295–314
Takahashi S, Ono T, Ishiwata Y, Kuroda T (2002) Breathing modes, body positions, and suprahyoid muscle activity. J Orthod 29:307–313 (discussion 279)
Taniguchi H, Tsukada T, Ootaki S, Yamada Y, Inoue M (2008) Correspondence between food consistency and suprahyoid muscle activity, tongue pressure, and bolus transit times during the oropharyngeal phase of swallowing. J Appl Physiol 105:791–799
Tsukada T, Taniguchi H, Ootaki S, Yamada Y, Inoue M (2009) Effects of food texture and head posture on oropharyngeal swallowing. J Appl Physiol 106:1848–1857
Tsukano H, Taniguchi H, Hori K, Tsujimura T, Nakamura Y, Inoue M (2012) Individual-dependent effects of pharyngeal electrical stimulation on swallowing in healthy humans. Physiol Behav 106:218–223
Vaiman M, Eviatar E, Segal S (2004a) Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 1. Quantitative data: timing measures. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:548–555
Vaiman M, Eviatar E, Segal S (2004b) Surface electromyographic studies of swallowing in normal subjects: a review of 440 adults. Report 3. Qualitative data. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:977–985
Watanabe Y, Abe S, Ishikawa T, Yamada Y, Yamane GY (2004) Cortical regulation during the early stage of initiation of voluntary swallowing in humans. Dysphagia 19:100–108
Yahagi R, Okuda-Akabane K, Fukami H, Matsumoto N, Kitada Y (2008) Facilitation of voluntary swallowing by chemical stimulation of the posterior tongue and pharyngeal region in humans. Neurosci Lett 448:139–142
Zald DH, Pardo JV (1999) The functional neuroanatomy of voluntary swallowing. Ann Neurol 46:281–286
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (#24390431 to M.I.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, Y., Hatakeyama, A., Kitada, Y. et al. Effects of pharyngeal water stimulation on swallowing behaviors in healthy humans. Exp Brain Res 230, 197–205 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3641-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-013-3641-y