Abstract
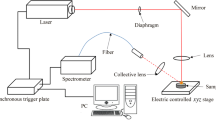
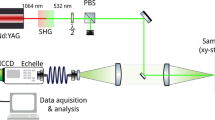
LIBS can be used as an online method of characterizing galvanized coatings on sheet steel moving through a production line. The traversing sheet steel is irradiated with a series of single laser bursts, each at a different position on the sheet steel. An ablation depth in the same range as the coating thickness (about 10 μm) is achieved by using a Nd:YAG laser at 1064 nm in collinear double-pulse mode. The coating thickness is determined from the ratio of the intensities of an iron line and a zinc line measured at a burst energy high enough to penetrate the coating with a single burst. Experiments at different burst energies were carried out to optimize the thickness resolution, and a method of systematically selecting iron and zinc lines was deduced, which is based on multivariate data analysis (MVDA) of the intensity ratios calculated for a set of 6 zinc lines and 21 iron lines. A temperature correction was applied, because the parameters of the plasma change with burst energy, and the influence of this on the thickness resolution is discussed. The ambient atmosphere present (air, Ar, N2) as well as self-absorption of spectral lines both have an influence on the thickness resolution. At optimum conditions, a thickness measurement accuracy of better than 150 nm was obtained for a set of electrolytic galvanized sheet steels with coating thicknesses in the range 4.1–11.2 μm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISO (2000) Metallic coatings—measurement of coating thickness—X-ray spectrometric methods—ISO-Norm 3497:2000(E). International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland
Balzer H, Hoehne M, Sturm V, Noll R (2005) Spectrochim Acta B 60:1172–1178
Payling R, Jones D, Bengtson A (eds) (1997) Glow discharge optical emission spectrometry. Wiley, New York
Anderson DR, McLeod CW, English T, Smith AT (2000) Appl Spectrosc 49:691–701
St-Onge L, Sabsabi M (2000) Spectrochim Acta B 55:299–308
Margetic V, Bolshov M, Stockhaus A, Niemax K, Hergenröder R (2001) J Anal Atom Spectrom 16:616–621
Mateo MP, Vadillo JM, Laserna JJ (2001) J Anal Atom Spectrom 16:1317–1321
Vadillo JM, Garcia CC, Palanco S, Laserna JJ (1998) J Anal Atom Spectrom 13:793–797
Garcia CC, Corral M, Vadillo JM, Laserna JJ (2000) Appl Spectrosc 54:1027–1031
Mateo MP, Cabalín LM, Laserna JJ (2003) Appl Optics 42:6057–6062
Papazoglou DG, Papadakis V, Anglos D (2004) J Anal Atom Spectrom 19:483–488
Mowery MD, Sing R, Kirsch J, Razaghi A, Bechard S, Reed R (2002) J Pharm Biomed Anal 28:935–943
Pouli P, Melessanaki K, Giakoumaki A, Argyropoulos V, Anglos D (2005) Spectrochim Acta B 60:1163–1171
Martin MZ, Labbe N, Rials TG, Wullschleger SD (2005) Spectrochim Acta B 60:1179–1185
Kraushaar M, Noll R, Schmitz H-U (2003) Appl Spectrosc 57:1282–1287
Fink H, Panne U, Niessner R (2002) Anal Chem 74:4334–4342
Palanco S, Laserna JJ (2000) J Anal Atom Spectrom 15:1321–1327
Huang J-S, Lin K-C (2005) J Anal Atom Spectrom 20:53–59
Lazic V, Fantoni R, Colao F, Santagata A, Morone A, Spizzichino V (2004) J Anal Atom Spectrom 19:429–436
Lui SL, Cheung NH (2003) Spectrochim Acta B 58:1613–1623
Detalle V, Sabsabi M, St-Onge L, Hamel A, Heon R (2003) Appl Optics 42:5971–5977
Peter L, Sturm V, Noll R (2003) Appl Optics 42:6199–6204
Aragón C, Bengoechea J, Aguilera JA (2001) Spectrochim Acta B 56:619–628
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. S. Janssen, ThyssenKrupp Stahl AG (TKS), Germany for providing the different sheet steel samples and for sample analysis. Financial support by the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the Fraunhofer Society is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balzer, H., Hölters, S., Sturm, V. et al. Systematic line selection for online coating thickness measurements of galvanised sheet steel using LIBS. Anal Bioanal Chem 385, 234–239 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0348-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0348-y