Abstract
Rationale
During the development of addiction, addictive drugs induce transient and long-lasting changes in the brain including expression of endogenous molecules and alteration of morphological structure. Of the altered endogenous molecules, some facilitate but others slow the development of drug addiction. Previously, we have reported that tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is a critical molecule among endogenous anti-addictive modulators using animal models of drug-conditioned place preference and drug discrimination.
Objectives
Does targeted deletion of the TNF-α gene in mice affect methamphetamine (METH) self-administration, motivation to self-administer METH, cue-induced reinstatement of METH-seeking behavior, and food reinforcement or seeking behavior?
Methods
Both METH self-administration and reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior and food self-delivery and food-seeking behavior were measured in TNF-α (−/−) and wild-type mice.
Results
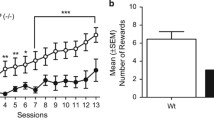
There were an upward shift of dose responses to METH self-administration under a fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement and higher breaking points under a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement in TNF-α knockout (TNF-α (−/−)) mice as compared with wild-type mice. There was no significant difference in cue-induced reinstatement of METH-seeking behavior, food-maintained operant behavior, motivation to natural food, and cue-induced food-seeking behavior between TNF-α (−/−) and wild-type mice.
Conclusion
TNF-α affects METH self-administration and motivation to self-administer METH but contributes to neither METH-associated cue-induced relapsing behavior nor food reward and food-seeking behavior. TNF-α may be explored for use as a diagnostic biomarker for the early stage of drug addiction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achur RN, Freeman WM, Vrana KE (2010) Circulating cytokines as biomarkers of alcohol abuse and alcoholism. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 5:83–91
Baldwin GC, Tashkin DP, Buckley DM, Park AN, Dubinett SM, Roth MD (1997) Marijuana and cocaine impair alveolar macrophage function and cytokine production. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:1606–1613
Carlezon WA Jr, Thomas MJ (2009) Biological substrates of reward and aversion: a nucleus accumbens activity hypothesis. Neuropharmacology 56:122–132
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004) Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305:1014–1017
Dyuizen I, Lamash NE (2009) Histo- and immunocytochemical detection of inducible NOS and TNF-alpha in the locus coeruleus of human opiate addicts. J Chem Neuroanat 37:65–70
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology 189:1–16
Feltenstein MW, See RE (2008) The neurocircuitry of addiction: an overview. Br J Pharmacol 154:261–274
Franchi S, Sacerdote P, Moretti S, Gerra G, Leccese V, Tallone MV, Panerai AE, Somaini L (2010) The effects of alcoholism pharmacotherapy on immune responses in alcohol-dependent patients. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 23:847–855
Friedman H, Eisenstein TK (2004) Neurological basis of drug dependence and its effects on the immune system. J Neuroimmunol 147:106–108
Gass JT, Olive MF (2008) Glutamatergic substrates of drug addiction and alcoholism. Biochem Pharmacol 75:218–265
Gonzalez-Quintela A, Campos J, Loidi L, Quinteiro C, Perez LF, Gude F (2008) Serum TNF-alpha levels in relation to alcohol consumption and common TNF gene polymorphisms. Alcohol 42:513–518
Grimm JW, See RE (2000) Dissociation of primary and secondary reward-relevant limbic nuclei in an animal model of relapse. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:473–479
Irwin MR, Olmos L, Wang M, Valladares EM, Motivala SJ, Fong T, Newton T, Butch A, Olmstead R, Cole SW (2007) Cocaine dependence and acute cocaine induce decreases of monocyte proinflammatory cytokine expression across the diurnal period: autonomic mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:507–515
Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Valladares EM, Breen EC, Ehlers CL (2009) Tumor necrosis factor antagonism normalizes rapid eye movement sleep in alcohol dependence. Biol Psychiatry 66:191–195
Knackstedt LA, Kalivas PW (2009) Glutamate and reinstatement. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:59–64
Koob GF (1992) Drugs of abuse: anatomy, pharmacology and function of reward pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:177–184
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2009) Neurocircuitry of addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:217–238
Kubera M, Filip M, Budziszewska B, Basta-Kaim A, Wydra K, Leskiewicz M, Regulska M, Jaworska-Feil L, Przegalinski E, Machowska A, Lason W (2008) Immunosuppression induced by a conditioned stimulus associated with cocaine self-administration. J Pharmacol Sci 107:361–369
Li SX, Shi J, Epstein DH, Wang X, Zhang XL, Bao YP, Zhang D, Zhang XY, Kosten TR, Lu L (2009) Circadian alteration in neurobiology during 30 days of abstinence in heroin users. Biol Psychiatry 65:905–912
Maier SF, Watkins LR (1998) Cytokines for psychologists: implications of bidirectional immune-to-brain communication for understanding behavior, mood, and cognition. Psychol Rev 105:83–107
Nakajima A, Yamada K, Nagai T, Uchiyama T, Miyamoto Y, Mamiya T, He J, Nitta A, Mizuno M, Tran MH, Seto A, Yoshimura M, Kitaichi K, Hasegawa T, Saito K, Yamada Y, Seishima M, Sekikawa K, Kim HC, Nabeshima T (2004) Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in methamphetamine-induced drug dependence and neurotoxicity. J Neurosci 24:2212–2225
Niwa M, Nitta A, Yamada Y, Nakajima A, Saito K, Seishima M, Noda Y, Nabeshima T (2007a) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and its inducer inhibit morphine-induced rewarding effects and sensitization. Biol Psychiatry 62:658–668
Niwa M, Nitta A, Yamada Y, Nakajima A, Saito K, Seishima M, Shen L, Noda Y, Furukawa S, Nabeshima T (2007b) An inducer for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects against methamphetamine-induced rewarding effects and sensitization. Biol Psychiatry 61:890–901
Niwa M, Yan Y, Nabeshima T (2008) Genes and molecules that can potentiate or attenuate psychostimulant dependence: relevance of data from animal models to human addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1141:76–95
O'Brien CP, Gardner EL (2005) Critical assessment of how to study addiction and its treatment: human and non-human animal models. Pharmacol Ther 108:18–58
Panlilio LV, Goldberg SR (2007) Self-administration of drugs in animals and humans as a model and an investigative tool. Addiction 102:1863–1870
Peng X, Zhou W, Cao D, Liu C, Li Z (1999) Changes and significance of natural killer cell, IL-2, IL-6 and TNF alpha of heroin addicts after detoxification. Hua Xi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 30:449–51
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:215–38
Roberts DC, Bennett SA (1993) Heroin self-administration in rats under a progressive ratio schedule of reinforcement. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 111:215–218
Sacerdote P, Franchi S, Gerra G, Leccese V, Panerai AE, Somaini L (2008) Buprenorphine and methadone maintenance treatment of heroin addicts preserves immune function. Brain Behav Immun 22:606–613
Self DW (1998) Neural substrates of drug craving and relapse in drug addiction. Ann Med 30:379–389
Taniguchi T, Tanaka M, Ikeda A, Momotani E, Sekikawa K (1997) Failure of germinal center formation and impairment of response to endotoxin in tumor necrosis factor α deficient mice. Lab Invest 77:647–658
Vanderschuren LJ, Everitt BJ (2004) Drug seeking becomes compulsive after prolonged cocaine self-administration. Science 305:1017–1019
Weber RJ, Gomez-Flores R, Smith JE, Martin TJ (2009) Neuronal adaptations, neuroendocrine and immune correlates of heroin self-administration. Brain Behav Immun 23:993–1002
Yamada K (2008) Endogenous modulators for drug dependence. Biol Pharm Bull 31:1635–1638
Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2004) Pro- and anti-addictive neurotrophic factors and cytokines in psychostimulant addiction: mini review. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:198–204
Yan Y, Nabeshima T (2009) Mouse model of relapse to the abuse of drugs: procedural considerations and characterizations. Behav Brain Res 196:1–10
Yan Y, Nitta A, Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2006) Relapse of methamphetamine-seeking behavior in C57BL/6 J mice demonstrated by a reinstatement procedure involving intravenous self-administration. Behav Brain Res 168:137–143
Yan Y, Yamada K, Nitta A, Nabeshima T (2007) Transient drug-primed but persistent cue-induced reinstatement of extinguished methamphetamine-seeking behavior in mice. Behav Brain Res 177:261–268
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Mizoguchi Hiroyuki, Tsuneyuki Yamamoto, and Masayuki Nadai for their technical assistance in the establishment of a mouse model of self-administration in our laboratory. We also appreciate Mr. Yaroslaw Pryslawsky’s assistance in the three-way statistical analyses of data. This study was supported by grants-in-aid for Scientific Research (A) (22248033), Scientific Research (B)(20390073)(21390045), and Exploratory Research(19659017)(22659213); by the joint research project under the Japan–Korea basic scientific corporation program from the Japan Society for the promotion of science; by the ‘Academic Frontier’ Project for private universities (2007–2011); by the Regional Joint Research Program supported by grants to private universities to cover current expenses from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT); by the Research on Regulatory Science of Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices; by the Research on Risk of Chemical Substances, Health and Labour Science research grants from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW); and by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) (Translational Research Promotion Project).
Disclosure/conflicts of interest
The authors of this manuscript report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Nitta, A., Koseki, T. et al. Dissociable role of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene deletion in methamphetamine self-administration and cue-induced relapsing behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 221, 427–436 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2589-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2589-5