Abstract
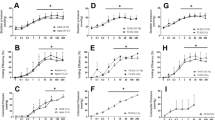
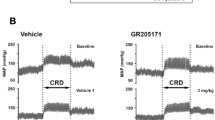
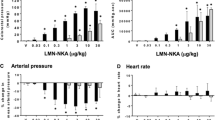
The purpose of this study was to determine feasibility of a novel therapeutic approach to drug-induced voiding after spinal cord injury (SCI) using a well-characterized, peptide, neurokinin 2 receptor (NK2 receptor) agonist, Lys5, MeLeu9, Nle10-NKA(4–10) (LMN-NKA). Cystometry and colorectal pressure measurements were performed in urethane-anesthetized, intact, and acutely spinalized female rats. Bladder pressure and voiding were monitored in response to intravenous LMN-NKA given with the bladder filled to 70% capacity. LMN-NKA (0.1–300 μg/kg) produced dose-dependent, rapid (<60 s), short-duration (<15 min) increases in bladder pressure. In intact rats, doses above 0.3–1 μg/kg induced urine release (voiding efficiency of ~70% at ≥1 μg/kg). In spinalized rats, urine release required higher doses (≥10 μg/kg) and was less efficient (30–50%). LMN-NKA (0.1–100 μg/kg) also produced dose-dependent increases in colorectal pressure. No tachyphylaxis was observed, and the responses were blocked by an NK2 receptor antagonist (GR159897, 1 mg/kg i.v.). No obvious cardiorespiratory effects were noted. These results suggest that rapid-onset, short-duration, drug-induced voiding is possible in acute spinal and intact rats with intravenous administration of an NK2 receptor agonist. Future challenges remain in regard to finding alternative routes of administration that produce clinically significant voiding, multiple times per day, in animal models of chronic SCI.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Advenier C et al (1992) Effects on the isolated human bronchus of SR 48968, a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurokinin A (NK2) receptors. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:1177–1181. doi:10.1164/ajrccm/146.5_Pt_1.1177
Ballester C, Sarria B, Garcia-Granero E, Morcillo EJ, Lledo S, Cortijo J (2007) Relaxation of the isolated human internal anal sphincter by sildenafil. The British journal of surgery 94:894–902. doi:10.1002/bjs.5724
Burcher E, Zeng XP, Strigas J, Shang F, Millard RJ, Moore KH (2000) Autoradiographic localization of tachykinin and calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors in adult urinary bladder. J Urol 163:331–337
Cardenas DD, Hoffman JM, Kirshblum S, McKinley W (2004) Etiology and incidence of rehospitalization after traumatic spinal cord injury: a multicenter analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 85:1757–1763
Carini F, Lecci A, Tramontana M, Giuliani S, Maggi CA (2001) Tachykinin NK(2) receptors and enhancement of cholinergic transmission in the inflamed rat colon: an in vivo motility study. Br J Pharmacol 133:1107–1113. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704164
Cohen J, Burggraaf J, Schoemaker RC, Sterk PJ, Cohen AF, Diamant Z (2005) Relationship between airway responsiveness to neurokinin A and methacholine in asthma. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 18:171–176. doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2004.11.008
Couture R, Laneuville O, Guimond C, Drapeau G, Regoli D (1989) Characterization of the peripheral action of neurokinins and neurokinin receptor selective agonists on the rat cardiovascular system. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:547–557
de Groat WC, Yoshimura N (2012) Plasticity in reflex pathways to the lower urinary tract following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 235:123–132. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.05.003
Evans TW, Dixon CM, Clarke B, Conradson TB, Barnes PJ (1988) Comparison of neurokinin A and substance P on cardiovascular and airway function in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 25:273–275
Fajardo NR, Pasiliao RV, Modeste-Duncan R, Creasey G, Bauman WA, Korsten MA (2003) Decreased colonic motility in persons with chronic spinal cord injury. Am J Gastroenterol 98:128–134. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07157.x
Floch A, Fardin V, Cavero I (1994) Characterization of NK1 and NK2 tachykinin receptors in guinea-pig and rat bronchopulmonary and vascular systems. Br J Pharmacol 111:759–768
Gandomkar H, Zeinoddini A, Heidari R, Amoli HA (2015) Partial lateral internal sphincterotomy versus combined botulinum toxin A injection and topical diltiazem in the treatment of chronic anal fissure: a randomized clinical trial. Dis Colon rectum 58:228–234. doi:10.1097/DCR.0000000000000307
Giuliani S et al (1993) Characterization of the tachykinin neurokinin-2 receptor in the human urinary bladder by means of selective receptor antagonists and peptidase inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:590–595
Gregory MC, Schumann GB, Schumann JL, Argyle JC (1984) The clinical significance of candidal casts. Am J Kidney Dis 4:179–184
Hoover DB, Chang Y, Hancock JC, Zhang L (2000) Actions of tachykinins within the heart and their relevance to cardiovascular disease. Jpn J Pharmacol 84:367–373
Hughes M (2014) Bowel management in spinal cord injury patients. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 27:113–115. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1383904
Jones OM, Brading AF, Mc CMNJ (2002) Phosphodiesterase inhibitors cause relaxation of the internal anal sphincter in vitro. Dis Colon rectum 45:530–536
Joos GF, Germonpre PR, Pauwels RA (2000) Role of tachykinins in asthma. Allergy 55:321–337
Kullmann FA, Kurihara R, Ye L, Wells GI, McKenna DG, Burgard EC, Thor KB (2013) Effects of the 5-HT4 receptor agonist, cisapride, on neuronally evoked responses in human bladder, urethra, and ileum. Autonomic neuroscience : basic & clinical 176:70–77. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2013.02.020
Kullmann FA, Wells GI, McKenna D, Thor KB (2014) Excitatory effects of bombesin receptors in urinary tract of normal and diabetic rats in vivo. Life Sci 100:35–44. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2014.01.071
Lecci A, Capriati A, Maggi CA (2004) Tachykinin NK2 receptor antagonists for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Br J Pharmacol 141:1249–1263. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705751
Lecci A, Capriati A, Altamura M, Maggi CA (2006) Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors in the gut, with special reference to NK2 receptors in human. Autonomic neuroscience : basic & clinical 126-127:232–249. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2006.02.014
Longmore J, Hill RG, Hargreaves RJ (1997) Neurokinin-receptor antagonists: pharmacological tools and therapeutic drugs. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 75:612–621
Lordal M, Theodorsson E, Hellstrom PM (1997) Tachykinins influence interdigestive rhythm and contractile strength of human small intestine. Dig Dis Sci 42:1940–1949
Lordal M, Navalesi G, Theodorsson E, Maggi CA, Hellstrom PM (2001) A novel tachykinin NK2 receptor antagonist prevents motility-stimulating effects of neurokinin A in small intestine. Br J Pharmacol 134:215–223. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704217
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Giuliani S, Regoli D, Meli A (1986) Activation of micturition reflex by substance P and substance K: indirect evidence for the existence of multiple tachykinin receptors in the rat urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:259–266
Maggi CA et al (1987) The contribution of capsaicin-sensitive innervation to activation of the spinal vesico-vesical reflex in rats: relationship between substance P levels in the urinary bladder and the sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Brain Res 415:1–13
Matuszek MA, Zeng XP, Strigas J, Burcher E (1998) An investigation of tachykinin NK2 receptor subtypes in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 352:103–109
Morrison J, Wen J, Kibble A (1999) Activation of pelvic afferent nerves from the rat bladder during filling. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 201:73–75
Mule F, D’Angelo S, Tabacchi G, Serio R (2000) Involvement of tachykinin NK2 receptors in the modulation of spontaneous motility in rat proximal colon. Neurogastroenterol Motil 12:459–466
Naline E, Devillier P, Drapeau G, Toty L, Bakdach H, Regoli D, Advenier C (1989) Characterization of neurokinin effects and receptor selectivity in human isolated bronchi. Am Rev Respir Dis 140:679–686. doi:10.1164/ajrccm/140.3.679
Palea S, Corsi M, Artibani W, Ostardo E, Pietra C (1996) Pharmacological characterization of tachykinin NK2 receptors on isolated human urinary bladder, prostatic urethra and prostate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:700–705
Panicker JN, Fowler CJ, Kessler TM (2015) Lower urinary tract dysfunction in the neurological patient: clinical assessment and management. Lancet Neurol 14:720–732. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00070-8
Quinn T, Collins C, Baird AW (2004) Mechanisms of neurokinin A- and substance P-induced contractions in rat detrusor smooth muscle in vitro. BJU Int 94:651–657. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05017.x
Schmidt PT, Lordal M, Gazelius B, Hellstrom PM (2003) Tachykinins potently stimulate human small bowel blood flow: a laser Doppler flowmetry study in humans. Gut 52:53–56
Sculptoreanu A, de Groat WC (2003) Protein kinase C is involved in neurokinin receptor modulation of N- and L-type Ca2+ channels in DRG neurons of the adult rat. J Neurophysiol 90:21–31. doi:10.1152/jn.00108.2003
Sculptoreanu A, Aura Kullmann F, de Groat WC (2008) Neurokinin 2 receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase C modulates capsaicin responses in DRG neurons from adult rats. Eur J Neurosci 27:3171–3181. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06267.x
Sculptoreanu A, Artim DE, de Groat WC (2009) Neurokinins inhibit low threshold inactivating K+ currents in capsaicin responsive DRG neurons. Exp Neurol 219:562–573. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.07.016
Sellers DJ, Chapple CR, W Hay DP, Chess-Williams R (2006) Depressed contractile responses to neurokinin A in idiopathic but not neurogenic overactive human detrusor muscle. Eur Urol 49:510–518. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2005.11.028
Singh R, Rohilla RK, Sangwan K, Siwach R, Magu NK, Sangwan SS (2011) Bladder management methods and urological complications in spinal cord injury patients. Indian journal of orthopaedics 45:141–147. doi:10.4103/0019-5413.77134
Tanahashi M, Karicheti V, Thor KB, Marson L (2012) Characterization of bulbospongiosus muscle reflexes activated by urethral distension in male rats. American journal of physiology Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology 303:R737–R747. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00004.2012
Tichenor SD, Buxton IL, Johnson P, O’Driscoll K, Keef KD (2002) Excitatory motor innervation in the canine rectoanal region: role of changing receptor populations. Br J Pharmacol 137:1321–1329. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704987
Tramontana M, Patacchini R, Lecci A, Giuliani S, Maggi CA (1998) Tachykinin NK2 receptors in the hamster urinary bladder: in vitro and in vivo characterization. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 358:293–300
Vaithianathan R, Panneerselvam S (2015) Randomised prospective controlled trial of topical 2% diltiazem versus lateral internal sphincterotomy for the treatment of chronic fissure in Ano. The Indian journal of surgery 77:1484–1487. doi:10.1007/s12262-014-1080-z
Walsh DA, F McWilliams D (2006) Tachykinins and the cardiovascular system. Curr Drug Targets 7:1031–1042
Warner FJ, Miller RC, Burcher E (2003) Human tachykinin NK2 receptor: a comparative study of the colon and urinary bladder. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:632–639
Yilmaz B et al (2014) Intermittent catheterization in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury: obstacles, worries, level of satisfaction. Spinal Cord. doi:10.1038/sc.2014.134
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Ed Burgard for the administrative work and helpful discussions of the data. We gratefully acknowledge Integrated Laboratory Systems for their collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the NICHD of the National Institutes of Health under award number R43HD080263.
Conflict of interest
Authors LM, KBT, MK are employed by Dignify Therapeutics. Authors FAK, LM, KBT, MK have equity ownership within Dignify Therapeutics.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Integrated Laboratory Systems animal care and use committee and followed the NIH Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kullmann, F.A., Katofiasc, M., Thor, K.B. et al. Pharmacodynamic evaluation of Lys5, MeLeu9, Nle10-NKA(4–10) prokinetic effects on bladder and colon activity in acute spinal cord transected and spinally intact rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 163–173 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1317-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1317-4