Abstract
Cisplatin is a widely used citostatic drug employed in the treatment of many solid tumors. Its principal side-effect is nephrotoxicity. The organic anion transporter 5 (Oat5) is exclusively expressed in the kidneys. The aim of this study was to evaluate the time course of Oat5 urinary excretion and changes in conventional biomarkers, such as creatinine and urea plasma levels (Urp and Crp), and protein and glucose urinary levels (Pu and Gluu), between others, and compared them to the onset and progression of histological changes after cisplatin treatment. Male Wistar rats were treated with cisplatin with 5 mg/kg b.w., i.p., and experiments were carried out after 2, 4, 7 and 14 days of treatment. Two days after cisplatin administration, only Oat5 urinary excretion was found markedly modified. On day 4, Urp, Crp, PU and GluU were increased. By the seventh day, a severe impairment in tubular architecture was observed, and from this point and thereon, Oat5 urinary excretion and PU showed a tendency to return to their basal values. Meanwhile, Urp, Crp and GluU tended to return to their basal values by the day 14 of treatment, when kidney morphology showed an important recovery. So Oat5 urinary abundance was elevated 2 days after cisplatin treatment, when no modifications of traditional markers of renal injury were still observed. Therefore, the results showed in this work, in addition to previous data obtained by our group, propose that Oat5 urinary excretion might potentially serve as a noninvasive early biomarker of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman AL, Al Salam S, AlMahruqui AS, Al husseni IS, Mansour MA, Ali BH (2010) N-acetylcysteine improves renal hemodynamics in rats with cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. J Appl Toxicol 30:15–21
Ali BH, Al-Moundhri M, Eldin MT, Nemmar A, Al-Siyabi S, Annamalai K (2008) Amelioration of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats by tetramethylpyrazine, a major constituent of the Chinese herb Ligusticum wallichii. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 233:891–896
Anzai N, Jutabha P, Enomoto A, Yokoyama H, Nonoguchi H, Hirata T, Shiraya K, He X, Cha SH, Takeda M, Miyazaki H, Sakatada T, Tomita K, Igarashi T, Kanai Y, Endou H (2005) Functional characterization of rat organic anion transporter 5 (Slc22a19) at the apical membrane of renal proximal tubules. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:534–544
Anzai N, Kanai Y, Endou H (2006) Organic anion transporter family: current knowledge. J Pharmacol Sci 100:411–426
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C (2012) Acute kidney injury. Lancet 380:756–766
Bonventre JV, Vaidya VS, Schmouder R, Feig P, Dieterle F (2010) Next-generation biomarkers for detecting kidney toxicity. Nat Biotechnol 28:436–440
Brandoni A, Anzai N, Kanai Y, Endou H, Torres AM (2006) Renal elimination of paminohippurate (PAH) in response to three days of biliary obstruction in the rat. The role of OAT1 and OAT3. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:673–682
Bulacio RP, Torres AM (2013) Organic anion transporter 5 (Oat5) renal expression and urinary excretion in rats treated with cisplatin: a potential biomarker of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 87:1953–1962
Bulacio R, Hazelhoff MH, Torres AM (2012) Renal expression and function of oat1 and oat3 in rats with vascular calcification. Pharmacology 90:66–77
Burckhardt G (2012) Drug transport by organic anion transporters (OATs). Pharmacol Ther 136:106–130
Di Giusto G, Torres AM (2010) Organic anion transporter 5 renal expression and urinary excretion in rats exposed to mercuric chloride: a potential biomarker of mercury-induced nephropathy. Arch Toxicol 84:741–749
Di Giusto G, Anzai N, Endou H, Torres AM (2009) Oat5 and NaDC1 protein abundance in kidney and urine after renal ischemic reperfusion injury. J Histochem Cytochem 57:17–27
Ecelbarger CA, Sands JM, Doran JJ, Cacini W, Kishore BK (2001) Expression of salt and urea transporters in rat kidney during cisplatin-induced polyuria. Kidney Int 60:2274–2282
Fang DY, King HW, Li JY, Gleadle JM (2013) Exosomes and the kidney: blaming the messenger. Nephrology (Carlton) 18:1–10
Ferguson MA, Vaidya VS, Bonventre JV (2008) Biomarkers of nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Toxicology 245:182–193
Gonzales PA, Zhou H, Pisitkun T, Wang NS, Star RA, Knepper MA, Yuen PS (2010) Isolation and purification of exosomes in urine. Methods Mol Biol 641:89–99
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 62:237–244
Han WK, Waikar SS, Johnson A, Betensky RA, Dent CL, Devarajan P, Bonventre JV (2008) Urinary biomarkers in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 73:863–869
Hazelhoff MH, Bulacio RP, Torres AM (2013) Organic anion transporter 5 renal expression and urinary excretion in rats with vascular calcification. Biomed Res Int 2013:283429
Higashijima Y, Sonoda H, Takahashi S, Kondo H, Shigemura K, Ikeda M (2013) Excretion of urinary exosomal AQP2 in rats is regulated by vasopressin and urinary pH. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F1412–F1421
Hosohata K, Ando H, Fujimura A (2012) Urinary vanin-1 as a novel biomarker for early detection of drug-induced acute kidney injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 341:656–662
Kim SW, Lee JU, Nah MY, Kang DG, Ahn KY, Lee HS, Choi KC (2001) Cisplatin decreases the abundance of aquaporin water channels in rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:875–882
Kwak JO, Kim HW, Oh KJ, Ko CB, Park H, Cha SHJ (2005) Characterization of mouse organic anion transporter 5 as a renal steroid sulfate transporter. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 97:369–375
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McDuffie JE, Ma JY, Sablad M, Sonee M, Varacallo L, Louden C, Guy A, Vegas J, Liu X, La D, Snook S (2013) Time course of renal proximal tubule injury, reversal, and related biomarker changes in rats following Cisplatin administration. Int J Toxicol 32:251–260
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2:2490–2518
Mishra J, Ma Q, Prada A, Mitsnefes M, Zahedi K, Yang J, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2003) Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel early urinary biomarker for ischemic renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2534–2543
Pabla N, Dong Z (2008) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int 73:994–1007
Pabla N, Dong G, Jiang M, Huang S, Kumar MV, Messing RO, Dong Z (2011) Inhibition of PKCδ reduces cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity without blocking chemotherapeutic efficacy in mouse models of cancer. J Clin Invest 121:2709–2722
Peres LA, Cunha Júnior AD, Schäfer AJ, Silva AL, Gaspar AD, Scarpari DF, Alves JB, Girelli Neto R, Oliveira TF (2013) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. J Bras Nefrol 35:229–236
Pinches M, Betts C, Bickerton S, Burdett L, Thomas H, Derbyshire N, Jones HB, Moores M (2012) Evaluation of novel renal biomarkers with a cisplatin model of kidney injury: gender and dosage differences. Toxicol Pathol 40:522–533
Pisitkun T, Shen RF, Knepper MA (2004) Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13368–13373
Rifai N, Gillette MA, Carr SA (2006) Protein biomarker discovery and validation: the long and uncertain path to clinical utility. Nat Biotechnol 24:971–983
Sabolić I (2006) Common mechanisms in nephropathy induced by toxic metals. Nephron Physiol 104:p107–p114
Sekine T, Cha SH, Hosoyamada M, Kanai Y, Watanabe N, Furuta Y, Fukuda K, Igarashi T, Endou H (1998) Cloning, functional characterization, and localization of a rat renal Na+-dicarboxylate transporter. Am J Physiol 275:298–305
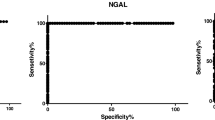
Sinha V, Vence LM, Salahudeen AK (2013) Urinary tubular protein-based biomarkers in the rodent model of cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a comparative analysis of serum creatinine, renal histology, and urinary KIM-1, NGAL, and NAG in the initiation, maintenance, and recovery phases of acute kidney injury. J Investig Med 61:564–568
Slocum JL, Heung M, Pennathur S (2012) Marking renal injury: can we move beyond serum creatinine? Transl Res 159:277–289
Uehara T, Yamate J, Torii M, Maruyama T (2011) Comparative nephrotoxicity of cisplatin and nedaplatin: mechanisms and histopathological characteristics. J Toxicol Pathol 24:87–94
Villar SR, Brandoni A, Torres AM (2008) Time course of organic anion excretion in rats with bilateral ureteral obstruction: role of organic anion transporters (Oat1 and Oat3). Nephron Physiol 110:p45–p56
Wensing KU, Ciarimboli G (2013) Saving ears and kidneys from cisplatin. Anticancer Res 33:4183–4188
Westhuyzen J, Endre ZH, Reece G, Reith DM, Saltissi D, Morgan TJ (2003) Measurement of tubular enzymuria facilitates early detection of acute renal impairment in the intensive care unit. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:543–551
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124
Yokoo S, Yonezawa A, Masuda S, Fukatsu A, Katsura T, Inui K (2007) Differential contribution of organic cation transporters, OCT2 and MATE1, in platinum agent-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol 74:477–487
Youngblood GL, Sweet DH (2004) Identification and functional assessment of the novel murine organic anion transporter Oat5 (Slc22a19) expressed in kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F236–F244
Zalups RK (2000) Molecular interactions with mercury in the kidney. Pharmacol Rev 52:113–143
Zhou H, Pisitkun T, Aponte A, Yuen PS, Hoffert JD, Yasuda H, Hu X, Chawla L, Shen RF, Knepper MA, Star RA (2006) Exosomal Fetuin-A identified by proteomics: a novel urinary biomarker for detecting acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 70:1847–1857
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following grants: Fondo para la Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (FONCYT), Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), Universidad Nacional de Rosario (UNR). The authors thank to Prof. H. Endou and to Prof. N. Anzai (Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan) for kindly providing Oat5-specific antibodies and Mrs Alejandra Martínez (Area Morfología, Facultad de Ciencias Bioquímicas y Farmacéuticas, U.N.R.) for her collaboration in the present work. The authors also thank Wiener Lab Argentina for analytical kits.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bulacio, R.P., Torres, A.M. Time course of organic anion transporter 5 (Oat5) urinary excretion in rats treated with cisplatin: a novel urinary biomarker for early detection of drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 89, 1359–1369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1345-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1345-0