Abstract
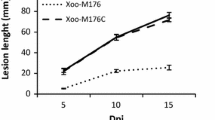
Acidovorax oryzae (Ao) cause bacterial brown stripe in rice that result in great economic loss. However, the pathogenic mechanism of this rice bacterial pathogen still remains unclear. Interestingly, transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of in vivo infection indicate that the pathogenicity of Ao strain RS-1 may be associated with the type six secretion system (T6SS), which was identified by in silico comparative genomic analysis in our previous studies. This makes it necessary to further examine the role of each core component of T6SS in the pathogenicity of Ao strain RS-1 to rice plants. Results from this study highlight the mutual interaction between IcmF and DotU, which was determined by bacterial two-hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays. Furthermore, a difference was observed in bacterial pathogenicity, biofilm formation, secreted proteins identified by LC–MS/MS analysis and the expression of T6SS other genes examined by quantitative real-time PCR between the wild-type and both single-gene knockout mutants, which were respectively constructed based on the insertional mutagenesis of Ao strain RS-1 in this study. Overall, our results clearly revealed the importance of T6SS icmF and dotU in pathogenicity of Ao strain RS-1 to rice plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basler M, Pilhofer M, Henderson G, Jensen G, Mekalanos J (2012) Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure. Nature 483:182–186
Bingle LE, Bailey CM, Pallen MJ (2008) Type VI secretion: a beginner’s guide. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:3–8
Chen Y, Chai Y, Guo JH, Losick R (2012) Evidence for cyclic di-GMP-mediated signaling in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 194:5080–5090
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ (2006) Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124:803–814
Chow J, Mazmanian SK (2010) A pathobiont of the microbiota balances host colonization and intestinal inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 7:265–276
Chung JW, Ng-Thow-Hing C, Budman LI, Gibbs BF, Nash JHE, Jacques M, Coulton JW (2007) Outer membrane proteome of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae: LC-MS/MS analyses validate in silico predictions. Proteomics 7:1854–1865. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200600979
Cui ZQ, Jin GQ, Li B, Kakar KU, Ojaghian MR, Wang YL, Xie GL, Sun GC (2015) Gene expression of type VI secretion system associated with environmental survival in Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae by principle component analysis. Int J Mol Sci 16:22008–22026
Davies DG, Parsek MR, Pearson JP, Iglewski BH, Costerton J, Greenberg E (1998) The involvement of cell-to-cell signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science 280:295–298
Dow JM, Crossman L, Findlay K, He YQ, Feng JX, Tang JL (2003) Biofilm dispersal in Xanthomonas campestris is controlled by cell–cell signaling and is required for full virulence to plants. Proc Nati Acad Sci 100:10995–11000
Fernández-Acero FJ, Jorge I, Calvo E, Vallejo I, Carbú M, Camafeita E, López JA, Cantoral JM, Jorrín J (2006) Two-dimensional electrophoresis protein profile of the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Proteomics 6:S88-S96
Filloux A (2011) Protein secretion systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an essay on diversity, evolution, and function. Front Microbiol 2:155
Filloux A, Hachani A, Bleves S (2008) The bacterial type VI secretion machine: yet another player for protein transport across membranes. Microbiology 154:1570–1583
Fronzes R, Christie PJ, Waksman G (2009) The structural biology of type IV secretion systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:703–714
Hong PC, Tsolis RM, Ficht TA (2000) Identification of genes required for chronic persistence of Brucella abortus in mice. Infect Immun 68:4102–4107
Huang JQ, Zhi Ming W, Hai Long A, Zhu YX (2001) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of rice with the spider insecticidal gene conferring resistance to leaffolder and striped stem borer. Cell Res 11:149–155
Ibrahim M, Shi Y, Qiu H, Li B, Jabeen A, Li L, Liu H, Kube M, Xie G, Wang Y (2012) Differential expression of in vivo and in vitro protein profile of outer membrane of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae. PloS One 7:e49657
Jani AJ, Cotter PA (2010) Type VI secretion: not just for pathogenesis anymore. Cell Host Microbe 8:2–6
Joung JK, Ramm EI, Pabo CO (2000) A bacterial two-hybrid selection system for studying protein–DNA and protein–protein interactions. Proc Nati Acad Sci 97:7382–7387
Kaakoush NO, Sirianni A, Raftery MJ, Mitchell HM (2013) The secretome of Helicobacter trogontum. Helicobacter 18:316–320
Karimova G, Pidoux J, Ullmann A, Ladant D (1998) A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway. Proc Nati Acad of Sci 95:5752–5756
Karimova G, Dautin N, Ladant D (2005) Interaction network among Escherichia coli membrane proteins involved in cell division as revealed by bacterial two-hybrid analysis. J bacteriol 187:2233–2243
Leiman PG, Basler M, Ramagopal UA, Bonanno JB, Sauder JM, Pukatzki S, Burley SK, Almo SC, Mekalanos JJ (2009) Type VI secretion apparatus and phage tail-associated protein complexes share a common evolutionary origin. Proc Nati Acad Sci 106:4154–4159
Leung KY, Siame BA, Snowball H, Mok YK (2011) Type VI secretion regulation: crosstalk and intracellular communication. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:9–15
Li B, Liu BP, Yu RR, Tao ZY, Wang YL, Xie GL, Li HY, Sun GC (2011a) Bacterial brown stripe of rice in soil-less culture system caused by Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae in China. J Gen Plant Pathol 77:64–67
Li YR, Che YZ, Zou HS, Cui YP, Guo W, Zou LF, Biddle EM, Yang CH, Chen GY (2011b) Hpa2 required by HrpF to translocate Xanthomonas oryzae transcriptional activator-like effectors into rice for pathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3809–3818
Li B, Ibrahim M, Ge MY, Cui ZQ, Sun GC, Xu F, Kube M (2014) Transcriptome analysis of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae cultivated in vivo and co-culture with Burkholderia seminalis. Sci Rep 4:5698
Li B, Wang L, Ibrahim M, Ge MY, Wang YL, Mannan S, Asif M, Sun GC (2015) Membrane protein profiling of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae under various growth conditions. Arch Microbial 197:673–682
Li B, Ge MY, Zhang Y, Wang L, Ibrahim M, Wang YL, Sun GC, Chen GY (2016) New insights into virulence mechanisms of rice pathogen Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae strain RS-1 following exposure to ß-lactam antibiotics. Sci Rep 6:22241
Linhartová I, Bumba L, Mašín J, Basler M, Osička R, Kamanová J, Procházková K, Adkins I, Hejnová-Holubová J, Sadílková L (2010) RTX proteins: a highly diverse family secreted by a common mechanism. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:1076–1112
Liu H, Gu D, Sheng L, Wang Q, Zhang Y (2012a) Investigation of the roles of T6SS genes in motility, biofilm formation, and extracellular protease Asp production in Vibrio alginolyticus with modified Gateway-compatible plasmids. Lett Appl Microbiol 55:73–81
Liu H, Tian WX, Ibrahim M, Li B, Zhang GQ, Zhu B, Xie GL (2012b) Characterization of pilP, a gene required for twitching motility, pathogenicity, and biofilm formation of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae RS-1. Eur J Plant Pathol 134:551–560
Liu H, Yang CL, Ge MY, Ibrahim M, Li B, Zhao WJ, Chen GY, Zhu B, Xie GL (2014) Regulatory role of tetR gene in a novel gene cluster of Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae RS-1 under oxidative stress. Front Microbiol 5:547
Ma LS, Lin JS, Lai EM (2009) An IcmF family protein, ImpLM, is an integral inner membrane protein interacting with ImpKL, and its walker a motif is required for type VI secretion system-mediated Hcp secretion in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 191:4316–4329
Ma L-S, Narberhaus F, Lai E-M (2012) IcmF family protein TssM exhibits ATPase activity and energizes type VI secretion. J Biol Chem 287(19):15610–15621
Mavromatis K, Ivanova N, Anderson I, Lykidis A, Hooper SD, Sun H, Kunin V, Lapidus A, Hugenholtz P, Patel B (2009) Genome analysis of the anaerobic thermohalophilic bacterium Halothermothrix orenii. PLoS One 4:e4192
Merrell DS, Falkow S (2004) Frontal and stealth attack strategies in microbial pathogenesis. Nature 430:250–256
Miyata ST, Kitaoka M, Brooks TM, McAuley SB, Pukatzki S (2011) Vibrio cholerae requires the type VI secretion system virulence factor VasX to kill Dictyostelium discoideum. Infect Immun 79:2941–2949
Morgan D, Baumgartner J, Hazelbauer G (1993) Proteins antigenically related to methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Escherichia coli detected in a wide range of bacterial species. J Bacteriol 175:133–140
Nowlin D, Nettleton D, Ordal G, Hazelbauer G (1985) Chemotactic transducer proteins of Escherichia coli exhibit homology with methyl-accepting proteins from distantly related bacteria. J Bacteriol 163:262–266
Peeters E, Nelis HJ, Coenye T (2008) Comparison of multiple methods for quantification of microbial biofilms grown in microtiter plates. J Microbiol Methods 72:157–165
Penfold RJ, Pemberton JM (1992) An improved suicide vector for construction of chromosomal insertion mutations in bacteria. Gene 118:145–146
Pfeiffer D, Jendrossek D (2011) Interaction between poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) granule-associated proteins as revealed by two-hybrid analysis and identification of a new phasin in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Microbiology 157:2795–2807
Pukatzki S, Ma AT, Sturtevant D, Krastins B, Sarracino D, Nelson WC, Heidelberg JF, Mekalanos JJ (2006) Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 103:1528–1533
Salinero KK, Keller K, Feil WS, Feil H, Trong S, Di Bartolo G, Lapidus A (2009) Metabolic analysis of the soil microbe Dechloromonas aromatica str. RCB: indications of a surprisingly complex life-style and cryptic anaerobic pathways for aromatic degradation. BMC Genom 10:351
Segal G, Feldman M, Zusman T (2005) The Icm/Dot type-IV secretion systems of Legionella pneumophila and Coxiella burnetii. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:65–81
Sexton JA, Miller JL, Yoneda A, Kehl-Fie TE, Vogel JP (2004) Legionella pneumophila DotU and IcmF are required for stability of the Dot/Icm complex. Infect Immun 72:5983–5992
Shrivastava S, Mande SS (2008) Identification and functional characterization of gene components of Type VI secretion system in bacterial genomes. PloS One 3:e2955
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Nat Biotechnol 1:784–791
Smith MD, Guild WR (1980) Improved method for conjugative transfer by filter mating of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol 144:457–459
Wang YL, Zhou Q, Li B, Liu BP, Wu GX, Ibrahim M, Xie GL, Li HY, Sun GC (2012) Differentiation in MALDI-TOF MS and FTIR spectra between two closely related species Acidovorax oryzae and Acidovorax citrulli. BMC Microbiol 12:182
Wootton L (2013) Bacterial physiology: ready, aim, fire! Nat Rev Microbiol 11:224–225
Xie GL, Zhang GQ, Liu H, Lou MM, Tian WX, Li B, Zhou XP, Zhu B, Jin GL (2011) Genome sequence of the rice-pathogenic bacterium Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae RS-1. J Bacteriol 193:5013–5014
Yamaoka T, Yano M, Kondo M, Sasaki H, Hino S, Katashima R, Moritani M, Itakura M (2001) Feedback inhibition of amidophosphoribosyltransferase regulates the rate of cell growth via purine nucleotide, DNA, and protein syntheses. J Biol Chem 276:21285–21291
Yan W, Cai Y, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Xu W, Yin Y, He Y, Wang H, Zhang X (2013) Screening and identification of ClpE interaction proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae by a bacterial two-hybrid system and co-immunoprecipitation. J Microbiol 51:453–460
Yang CL, Li B, Ge MY, Zhou KL, Wang YL, Luo J, Ibrahim M, Xie GL, Sun GC (2014) Inhibitory effect and mode of action of chitosan solution against rice bacterial brown stripe pathogen Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae RS-1. Carbohyd Res 391:48–54
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Li B, Yang YZ, Ibrahima M, Fang YS, Qiu W, Masum MMI, Oliva R (2017) Characterization and functional analysis of clpB gene from Acidovorax avenae subsp. avenae RS-1. Plant Pathol 66:1369–1379
Zheng J, Leung KY (2007) Dissection of a type VI secretion system in Edwardsiella tarda. Mol Microbiol 66:1192–1206
Zoued A, Durand E, Bebeacua C, Brunet YR, Douzi B, Cambillau C, Cascales E, Journet L (2013) TssK is a trimeric cytoplasmic protein interacting with components of both phage-like and membrane anchoring complexes of the type VI secretion system. J Biol Chem 288:27031–27041
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31571971, 31371904), Zhejiang Provincial Project (2017C02002), Shanghai Agricultural Basic Research Project (2014:7-3-1), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Agricultural Ministry of China (nyhyzx 201303015), Dabeinong Funds for Discipline Development and Talent Training in Zhejiang University, Key Subject Construction Program of Zhejiang for Modern Agricultural Biotechnology and Crop Disease Control (2010DS700124- KF1710).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Jorge Membrillo-Hernández.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Wang, X., Chen, J. et al. IcmF and DotU are required for the virulence of Acidovorax oryzae strain RS-1. Arch Microbiol 200, 897–910 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1497-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1497-z