Abstract
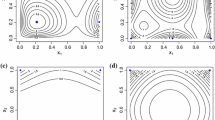
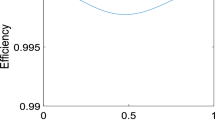
This paper considers constructions of optimal designs for heteroscedastic polynomial measurement error models. Corresponding approximate design theory is developed by using corrected score function approach, which leads to non-concave optimisation problems. For the weighted polynomial measurement error model of degree p with some commonly used heteroscedastic structures, the upper bounds for the number of support points of locally D-optimal designs can be determined explicitly. A numerical example is given to show how heteroscedastic structures affect the optimal designs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson A, Donev A, Tobias R (2007) Optimum experimental designs, with SAS. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Carroll R, Ruppert D, Stefanski L (2006) Measurement error in nonlinear models: a modern perspective, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Dette H, Trampisch M (2010) A general approach to \(D\)-optimal designs for weighted univariate polynomial regression models. J Korean Stat Soc 39:1–26
Dette H, Trampisch M (2012) Optimal designs for quantile regression models. J Am Stat Assoc 107:1140–1151
Donev AN (2004) Design of experiments in the presence of errors in factor levels. J Stat Plan Inference 126:569–585
Doví VG, Reverberi AP, Maga L (1993) Optimal design of sequential experiments for error-in-variables models. Comput Chem Eng 17:111–115
Fedorov VV (1972) Theory of optimal experiments. Academic Press, New York
Fuller WA (1987) Measurement error models. Wiley, New York
Gimenez P, Bolfarine H (1997) Corrected score functions in classical error-in-variables and incidental parameter models. Aust N Z J Stat 39:325–344
He L, Yue RX (2017) R-optimal designs for multi-factor models with heteroscedastic errors. Metrika 80:717–732
Karlin S, Studden WJ (1966) Tchebycheff systems: with applications in analysis and statistics. Wiley, New York
Keeler S, Reilly P (1992) The design of experiments when there are errors in all the variables. Can J Chem Eng 70:774–778
Kiefer J (1974) General equivalence theory for optimum designs (approximate theory). Ann Stat 2:849–879
Konstantinou M, Dette H (2015) Locally optimal designs for errors-in-variables models. Biometrika 102:951–958
Konstantinou M, Dette H (2017) Bayesian D-optimal designs for error-in-variables models. Appl Stoch Models Bus Ind 33:269–281
Nakamura T (1990) Corrected score function for errors-in-variables models: methodology and application to generalized linear models. Biometrika 77:127–137
Pólya G, Szegö G (1925) Aufgaben und Lehrsätze aus der Analysis, Band II. Springer, Berlin
Pukelsheim F (2006) Optimal design of experiments. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia
Pronzato L (2002) Information matrices with random regressors: application to experimental design. J Stat Plan Inference 108:189–200
Rodríguez C, Ortiz I (2005) D-optimum designs in multi-factor models with heteroscedastic errors. J Stat Plan Inference 128:623–631
Rodríguez C, Ortiz I, Martínez I (2016) A-optimal designs for heteroscedastic multifactor regression models. Commun Stat Theory Methods 45:757–771
Silvey SD (1980) Optimal design. Chapman and Hall, London
Stefanski LA (1989) Unbiased estimation of a nonlinear function of a normal mean with application to measurement error models. Commun Stat Theory Methods 18:4335–4358
Wong WK (1994) G-optimal designs for multi-factor experiments with heteroscedastic errors. J Stat Plan Inference 40:127–133
Wong WK (1995) On the equivalence of \(D\) and \(G\)-optimal designs in heteroscedastic models. Stat Probab Lett 25:317–321
Zavala AZ, Bolfarine H, Castro DM (2007) Consistent estimation and testing in heteroscedastic polynomial errors-in-variables models. Ann Inst Stat Math 59:515–530
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 11971318, 11871143.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, MJ., Yue, RX. Locally D-optimal designs for heteroscedastic polynomial measurement error models. Metrika 83, 643–656 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-019-00745-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-019-00745-2