Abstract
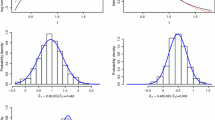
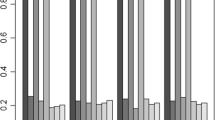
We consider a varying-coefficient partially linear proportional odds model with current status data. This model enables one to examine the extent to which some covariates interact nonlinearly with an exposure variable, while other covariates present linear effects. B-spline approach and sieve maximum likelihood estimation method are used to get an integrated estimate for the linear coefficients, the varying-coefficient functions and the baseline function. The proposed parameter estimators are proved to be semiparametrically efficient and asymptotically normal, and the estimators for the nonparametric functions achieve the optimal rate of convergence. Simulation studies and a real data analysis are used for assessment and illustration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett S (1983) Analysis of survival data by the proportional odds model. Stat Med 2:273–277
Bickel PJ, Klaassen CA, Ritov Y, Wellner JA (1993) Efficient and adaptive estimation for semiparametric models. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Cheng G, Wang X (2011) Semiparametric additive transformation model under current status data. Electron J Stat 5:1735–1764
De Gruttola V, Lagakos SW (1989) Analysis of doubly-censored survival data, with application to aids. Biometrics 1:1–11
Diamond ID, McDonald JW (1992) Analysis of current status data. Demogr Appl Event Hist Anal 58:231–252
Diamond ID, McDonald JW, Shah IH (1986) Proportional hazards models for current status data: application to the study of differentials in age at weaning in pakistan. Demography 23:607–620
Dinse GE, Lagakos S (1983) Regression analysis of tumour prevalence data. Appl Stat 32:236–248
Finkelstein DM (1986) A proportional hazards model for interval-censored failure time data. Biometrics 42:845–854
Finkelstein DM, Wolfe RA (1985) A semiparametric model for regression analysis of interval-censored failure time data. Biometrics 41:933–945
Geman S, Hwang C-R (1982) Nonparametric maximum likelihood estimation by the method of sieves. Ann Stat 10:401–414
Gray RJ (1992) Flexible methods for analyzing survival data using splines, with applications to breast cancer prognosis. J Am Stat Assoc 87:942–951
Grenander U (1981) Abstract inference. Wiley, New York
Heung M, Wolfgram DF, Kommareddi M, Hu Y, Song PX-K, Ojo AO (2012) Fluid overload at initiation of renal replacement therapy is associated with lack of renal recovery in patients with acute kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transpl 27:956–961
Hoel DG, Walburg H (1972) Statistical analysis of survival experiments. J Natl Cancer Inst 49:361–372
Hu T, Cui H-J, Tong X-W (2009) Efficient estimation for semiparametric varying-coefficient partially linear regression models with current status data. Acta Math Appl Sin English Ser 25(2):195–204
Huang J (1995) Maximum likelihood estimation for proportional odds regression model with current status data. Lect Notes Monogr Ser 27:129–145
Huang J (1996) Efficient estimation for the proportional hazards model with interval censoring. Ann Stat 24:540–568
Huang J (1999) Efficient estimation of the partly linear additive cox model. Ann Stat 27:1536–1563
Jewell NP, Malani HM, Vittinghoff E (1994) Nonparametric estimation for a form of doubly censored data, with application to two problems in aids. J Am Stat Assoc 89:7–18
Kongerud J, Samuelsen SO (1991) A longitudinal study of respiratory symptoms in aluminum potroom workers 1–3. Am Rev Respirat Dis 144:10–6
Ma S, Kosorok MR (2005) Penalized log-likelihood estimation for partly linear transformation models with current status data. Ann Stat 33:2256–2290
Martinussen T, Scheike TH (2002) Efficient estimation in additive hazards regression with current status data. Biometrika 89:649–658
McCullagh P (1980) Regression models for ordinal data. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 42:109–142
Pettitt A (1982) Inference for the linear model using a likelihood based on ranks. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodological) 44:234–243
Rossini A, Tsiatis A (1996) A semiparametric proportional odds regression model for the analysis of current status data. J Am Stat Assoc 91:713–721
Self SG, Grossman EA (1986) Linear rank tests for interval-censored data with application to pcb levels in adipose tissue of transformer repair workers. Biometrics 42:521–530
Shiboski SC, Jewell NP (1992) Statistical analysis of the time dependence of hiv infectivity based on partner study data. J Am Stat Assoc 87:360–372
Stone CJ (1985) Additive regression and other nonparametric models. Ann Stat 13:689–705
Wang Q, Tong X, Sun L (2012) Exploring the varying covariate effects in proportional odds models with censored data. J Multivar Anal 109:168–189
Xue H, Lam KF, Li G (2004) Sieve maximum likelihood estimator for semiparametric regression models with current status data. J Am Stat Assoc 99:346–356
Zhang Y, Hua L, Huang J (2010) A spline-based semiparametric maximum likelihood estimation method for the cox model with interval-censored data. Scand J Stat 37:338–354
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge with gratitude the support for this research by the Discovery Grants from National Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, S., Wu, J. & Lu, X. Efficient estimation of the varying-coefficient partially linear proportional odds model with current status data. Metrika 82, 173–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-018-0698-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-018-0698-4