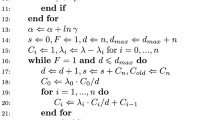Abstract
In this paper, a structural analysis of hybrid censoring models is presented. This new modularization approach to hybrid censoring models enables a convenient derivation of distributional results. For instance, it allows to derive the exact distribution of the MLEs under an exponential assumption for very complex hybrid scenarios. In order to illustrate the benefit of this idea, we apply it to four new unified progressive hybrid censoring schemes. They are extensions of already proposed unified Type-I/II/III/IV hybrid censoring schemes to progressively Type-II censored data. The resulting analysis shows that the modularization approach provides a powerful, efficient, and elegant tool to study even more complex hybrid censoring models.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan N, Cramer E (2014) The art of progressive censoring: applications to reliability and quality, statistics for industry and technology. Springer, New York
Balakrishnan N, Kundu D (2013) Hybrid censoring: models, inferential results and applications. Comput Stat Data Anal 57(1):166–209
Balakrishnan N, Rasouli A, Farsipour NS (2008) Exact likelihood inference based on an unified hybrid censored sample from the exponential distribution. J Stat Comput Simul 78(5):475–488
Burkschat M, Cramer E, Górny J (2016) Type-I censored sequential \(k\)-out-of-\(n\) systems. Appl Math Model 40:8156–8174
Chandrasekar B, Childs A, Balakrishnan N (2004) Exact likelihood inference for the exponential distribution under generalized Type-I and Type-II hybrid censoring. Naval Res Logist (NRL) 51(7):994–1004
Childs A, Chandrasekar B, Balakrishnan N (2008) Exact likelihood inference for an exponential parameter under progressive hybrid censoring schemes. In: Vonta F, Nikulin M, Limnios N, Huber-Carol C (eds) Statistical models and methods for biomedical and technical systems, statistics for industry and technology. Birkhäuser, Boston, pp 323–334
Childs A, Chandrasekar B, Balakrishnan N, Kundu D (2003) Exact likelihood inference based on Type-I and Type-II hybrid censored samples from the exponential distribution. Ann Inst Stat Math 55(2):319–330
Cramer E, Balakrishnan N (2013) On some exact distributional results based on Type-I progressively hybrid censored data from exponential distributions. Stat Methodol 10(1):128–150
Cramer E, Burkschat M, Górny J (2016) On the exact distribution of the MLEs based on Type-II progressively hybrid censored data from exponential distributions. J Stat Comput Simul 86(10):2036–2052
Curry HB, Schoenberg IJ (1947) On spline distributions and their limits: the Polya distribution functions. Bull Am Math Soc 53:1114
de Boor C (2001) A practical guide to splines, revised edn. Springer, Berlin, New York
Epstein B (1954) Truncated life tests in the exponential case. Ann Math Stat 25(3):555–564
Górny J (2017) A new approach to hybrid censoring. PhD Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany. https://doi.org/10.18154/RWTH-2017-05192
Górny J, Cramer E (2016) Exact likelihood inference for exponential distributions under generalized progressive hybrid censoring schemes. Stat Methodol 29:70–94
Górny J, Cramer E (2017a) From B-spline representations to gamma representations in hybrid censoring. Stat Pap. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-016-0866-4
Górny J, Cramer E (2017b) Type-I hybrid censoring of uniformly distributed lifetimes. Commun Stat Theory Methods (accepted)
Huang W-T, Yang K-C (2010) A new hybrid censoring scheme and some of its properties. Tamsui Oxf J Math Sci 26(4):355–367
Panahi H, Sayyareh A (2015) Estimation and prediction for a unified hybrid-censored Burr Type XII distribution. J Stat Comput Simul 86(1):55–73
Park S, Balakrishnan N (2012) A very flexible hybrid censoring scheme and its Fisher information. J Stat Comput Simul 82(1):41–50
Rad AH, Izanlo M (2011) An EM algorithm for estimating the parameters of the generalized exponential distribution under unified hybrid censored data. J Stat Res Iran 8(2):149–162
Schumaker LL (2007) Spline functions: basic theory, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Górny, J., Cramer, E. Modularization of hybrid censoring schemes and its application to unified progressive hybrid censoring. Metrika 81, 173–210 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-017-0639-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-017-0639-7