Abstract
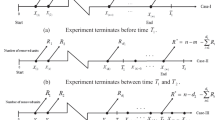
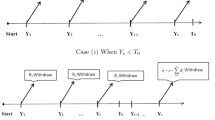
For reasons of time constraint and cost reduction, censoring is commonly employed in practice, especially in reliability engineering. Among various censoring schemes, progressive Type-I right censoring provides not only the practical advantage of known termination time but also greater flexibility to the experimenter in the design stage by allowing for the removal of test units at non-terminal time points. In this article, we consider a progressively Type-I censored life-test under the assumption that the lifetime of each test unit is exponentially distributed. For small to moderate sample sizes, a practical modification is proposed to the censoring scheme in order to guarantee a feasible life-test under progressive Type-I censoring. Under this setup, we obtain the maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) of the unknown mean parameter and derive the exact sampling distribution of the MLE under the condition that its existence is ensured. Using the exact distribution of the MLE as well as its asymptotic distribution and the parametric bootstrap method, we then discuss the construction of confidence intervals for the mean parameter and their performance is assessed through Monte Carlo simulations. Finally, an example is presented in order to illustrate all the methods of inference discussed here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anscombe FJ (1964) Normal likelihood functions. Ann Inst Stat Math 16: 1–19
Arnold BC, Balakrishnan N, Nagaraja HN (2008) A first course in order statistics, classic edition. SIAM, Philadelphia
Balakrishnan N (2007) Progressive censoring methodology: an appraisal (with discussions). Test 16: 211–296
Balakrishnan N, Aggarwala RA (2000) Progressive censoring: theory, methods, and applications. Birkhäuser, Boston
Balakrishnan N, Cohen AC (1991) Order statistics and inference: estimation methods. Academic Press, Boston
Balakrishnan N, Han D (2008) Optimal step-stress testing for progressively Type-I censored data from exponential distribution. J Stat Plan Inference 139: 1782–1798
Balakrishnan N, Iliopoulos G (2008) Stochastic monotonicity of the MLEs of parameters in exponential simple step-stress models under Type-I and Type-II censoring. Metrika (published online)
Casella G, Berger RL (2001) Statistical inference. Duxbury, Florence
Chatterjee SK, Sen PK (1973) Nonparametric testing under progressive censoring. Calcutta Stat Assoc Bull 22: 13–50
Cohen AC (1963) Progressively censored samples in life testing. Technometrics 5: 327–329
Cohen AC (1966) Life testing and early failure. Technometrics 8: 539–549
Cohen AC (1975) Multi-censored sampling in the three parameter Weibull distribution. Technometrics 17: 347–351
Cohen AC (1976) Progressively censored sampling in the three parameter log-normal distribution. Technometrics 18: 99–103
Cohen AC (1991) Truncated and censored samples: theory and applications. Marcel Dekker, New York
Cohen AC, Norgaard NJ (1977) Progressively censored sampling in the three parameter gamma distribution. Technometrics 19: 333–340
Cohen AC, Whitten BJ (1988) Parameter estimation in reliability and life span models. Marcel Dekker, New York
Efron B (1987) Better bootstrap confidence intervals. J Am Stat Assoc 82: 171–185
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman & Hall, New York
Gajjar AV, Khatri CG (1969) Progressively censored samples from log-normal and logistic distributions. Technometrics 11: 793–803
Gibbons DI, Vance LC (1983) Estimators for the 2-parameter Weibull distribution with progressively censored samples. IEEE Trans Reliab 32: 95–99
Gouno E, Sen A, Balakrishnan N (2004) Optimal step-stress test under progressive Type-I censoring. IEEE Trans Reliab 53: 388–393
Hall P (1988) Theoretical comparison of bootstrap confidence intervals. Ann Stat 16: 927–953
Han D, Balakrishnan N, Sen A, Gouno E (2006) Corrections on “Optimal step-stress test under progressive Type-I censoring”. IEEE Trans Reliab 55: 613–614
London D (1988) Survival models. Actex Publications, Connecticut
Majumdar H, Sen PK (1978) Nonparametric tests for multiple regression under progressive censoring. J Multivar Anal 8: 73–95
Nelson W (1982) Applied life data analysis. Wiley, New York
Nelson W (1990) Accelerated testing: statistical models, test plans, and data analyses. Wiley, New York
Ringer LJ, Sprinkle EE (1972) Estimation of the parameters of the Weibull distribution from multicensored samples. IEEE Trans Reliab 21: 6–51
Sampford MR (1952) The estimation of response-time distributions, Part II. Biometrics 9: 307–369
Shaked M, Shanthikumar JG (2007) Stochastic orders. Springer, New York
Sinha AN, Sen PK (1982) Tests based on empirical processes for progressive censoring schemes with staggered entry and random withdrawal. Sankhyā Ser B 44: 1–18
Sprott DA (1973) Normal likelihoods and their relation to large sample theory of estimation. Biometrika 60: 457–465
Wingo DR (1973) Solution of the three-parameter Weibull equations by constrained modified quasilinearization (progressively censored samples). IEEE Trans Reliab 22: 96–102
Wingo DR (1993) Maximum likelihood methods for fitting the Burr Type XII distribution to multiply (progressively) censored life test data. Metrika 40: 203–210
Wong JY (1993) Simultaneously estimating the three Weibull parameters from progressively censored samples. Microelectron Reliab 3: 2217–2224
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balakrishnan, N., Han, D. & Iliopoulos, G. Exact inference for progressively Type-I censored exponential failure data. Metrika 73, 335–358 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-009-0281-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00184-009-0281-0