Abstract
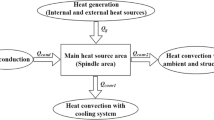
The temperature-sensitive point selection of computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools is crucial to thermal error modeling and compensation. Using the comprehensive analysis method which is a combination of fuzzy clustering, gray correlation, stepwise regression, and determination coefficient optimizes temperature measuring points. First of all, using fuzzy clustering and F statistic classifies temperature variables. Secondly, according to the gray correlation degree between the temperature variables and thermal error, the key temperature variable of each class is selected. Then, the significance of regression equation and parameters of thermal error model are tested, based on the stepwise regression analysis and the non-significant variables are excluded. Finally, the selected temperature variables are arranged to simple permutation and combination, and compares determination coefficients to determine the optimal temperature-sensitive points. The above method is verified on the Leaderway V-450 of CNC machining center. The thermal error prediction model is established. The accuracy and robustness of the model are analyzed. The results show that the temperature measuring point number is reduced from 10 to 2, the fitting accuracy of thermal error prediction model is high, and the model can achieve a good prediction effect and strong robustness under different conditions of spindle speeds and ambient temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bryan J (1990) International status of thermal error research. Ann CIRP 39(2):645–656
Aronson RB (1996) War against thermal expansion. Manuf Eng 116(6):45–50
Yang S, Yuan J, Ni J (1996) Accuracy enhancement of a horizontal machining center by real-time error compensation. J Manuf Syst 15(2):113–124
Miao EM, Gong YY, Cheng TJ, Chen HD (2013) Application of support vector regression to thermal error modeling of machine tools. Opt Precis Eng 21(4):980–986
Miao EM, Niu PC, Fei YT, Yan Y (2011) Selecting temperature-sensitive points and modeling thermal errors of machine tools. J Chin Soc Mech Eng 32(6):559–565
Miao EM, Gong YY, Niu PCH, Ji CHZH, Chen HD (2013) Robustness of thermal error compensation modeling models of CNC machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(9):2593–2603
Lo CH, Yuan JX, Ni J (1999) Optimal temperature variable selection by grouping approach for thermal error modeling and compensation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 39:1386–1396
Yu J, Zhao SHG, Yu ZHM (2000) Research on recognition of thermal distortion key points and compensation method in NC machine tool. Mach Des Manuf 6:73–74
Luo LH, Guo JG, Su JL (2006) Study on actuality of the method of temperature measurement point optimization and compensating model for the thermal error on machine tools. Mach Tool Hydraul 9:52–53
Ma SHW, Xu ZHH (2007) A study on thermal error compensation for the spindle of XH718 machining center. Mech Sci Technol 26(4):511–514
Fan ZHL, Li ZHH, Yang JG (2010) NC machine tool temperature measuring point optimization and thermal error modeling based on partial correlation analysis. Chin J Mech Eng 21(17):2025–2027
Yang H, Ni J (2005) Dynamic neural network modeling for nonlinear, nonstationary machine tool thermally induced error. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45(4):455–465
Yang JG, Deng WG, Ren YQ, Li YS, Dou XL (2004) Grouping optimization modeling by selection of temperature variables for the thermal error compensation on machine tools. Chin J Mech Eng 15(6):478–481
Kim SK, Cho DW (1997) Real-time estimation of temperature distribution in a ball-screw system. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37(4):451–464
Yang S, Yuan J, Ni J (1996) The improvement of thermal error modeling and compensation on machine tools by CMAC neural network. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 36(4):527–534
Chen C, Zhang CY, Chen H (2011) Selection and modeling of temperature variables for the thermal error compensation in servo system. The Tenth International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments ICEMI2011, Cheng Du, China, 16–18 Aug 2011
Han J, Wang LP, Wang HT, Cheng NB (2012) A new thermal error modeling method for CNC machine tools. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62:205–212
Yang JG, Ren YQ, Liu GL, Zhao HT, Dou XL, Chen WZ, He SW (2005) Testing, variable selecting and modeling of thermal errors on an INDEX-G200 turning center. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:814–818
Zhang T, Ye WH, Liang RJ, Lou PH, Yang XL (2013) Temperature variable optimization for precision machine tool thermal error compensation on optimal threshold. Chin J Mech Eng 26(1):158–165
Yang JG, Yuan JX, Ni J (1999) Thermal error mode analysis and robust modeling for error compensation on a CNC turning center. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 39:1367–1381
Le ZK (1996) Fuzzy relation compositions and pattern recognition. Inf Sci 89:107–130
Dunn JC (1974) A graph theoretic analysis of pattern classification via Tamura’s fuzzy relation. IEEE Trans SMC 4(3):310–313
Fei YT (2004) Error theory and data processing. Machinery Industry Press, Bei Jing
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
En-ming, M., Ya-yun, G., Lian-chun, D. et al. Temperature-sensitive point selection of thermal error model of CNC machining center. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 74, 681–691 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6009-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6009-y